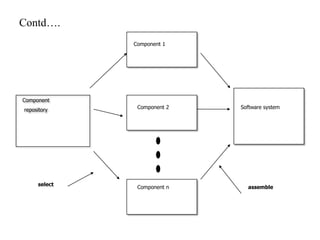
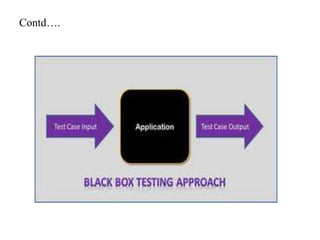
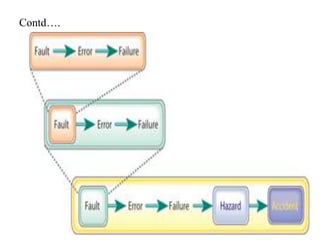
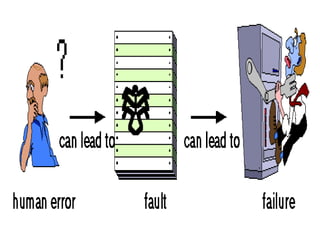
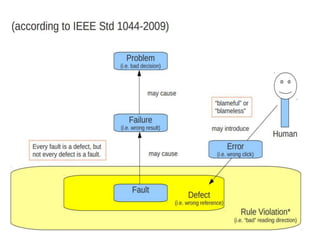
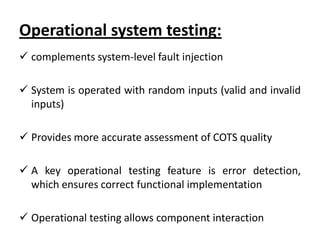
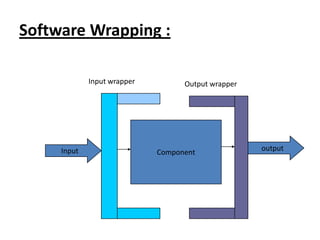
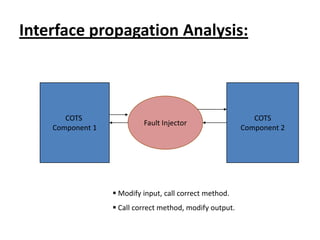
This document discusses testing off-the-shelf (COTS) components. It defines COTS components as independently developed and reusable parts that are selected from a repository and assembled to build software systems. While COTS components reduce development costs and time, they present challenges to testing due to being treated as black boxes without access to requirements or development processes. The document outlines types of COTS component testing, including black-box testing of inputs/outputs, fault injection to evaluate error handling, operational testing in integrated systems, and interface propagation analysis to observe impacts of faults between components.