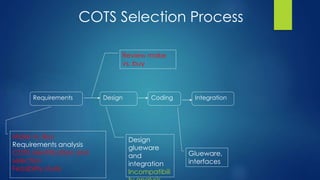
The document discusses selecting a COTS (Commercial Off-The-Shelf) vendor for software development. It describes COTS as commercially available software sold without source code. Selecting a COTS vendor requires defining requirements, identifying selection criteria, applying filters to candidate vendors based on published information, then further evaluating top candidates. Key challenges include integrating products from different vendors, limited access to COTS internals, and rapidly changing COTS landscapes. The document stresses the importance of understanding requirements, carefully analyzing capabilities and limitations of each COTS option, and assessing product quality.