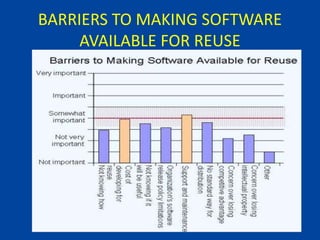
The document discusses software reuse, which refers to using existing software components to build or update new software, improving quality and reducing costs. It highlights various benefits, types of reuse, and approaches that support it, such as architectural and design patterns. Additionally, it addresses barriers to reuse, the importance of proper planning, and concludes that successful software reuse relies on understanding and integrating these concepts within the development process.