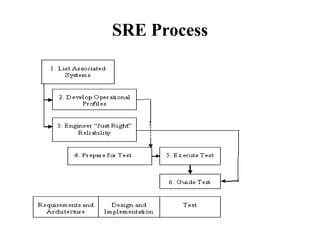
The document outlines the software reliability engineering (SRE) process. It defines software reliability as the ability of a system to perform without failure under specified conditions for a given time period. The SRE process involves 6 steps: 1) listing systems to test, 2) developing operational profiles, 3) defining acceptable reliability levels, 4) preparing tests, 5) executing tests, and 6) guiding the testing and release process. The goal is to measure, predict, and manage reliability through statistical modeling from the customer's perspective of minimizing failures.