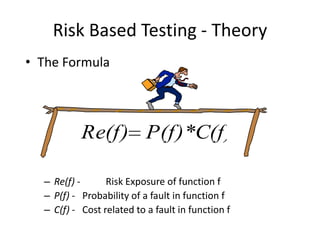
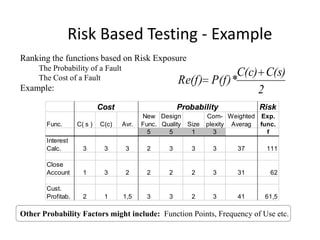
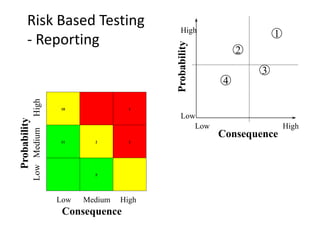
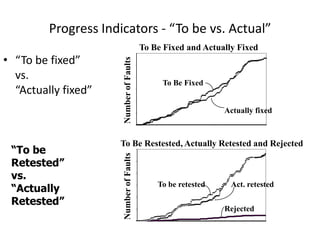
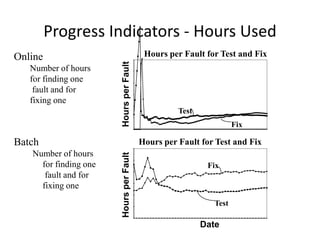
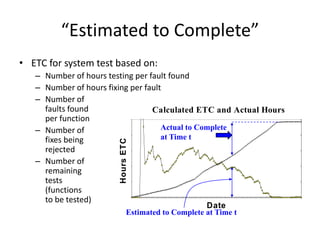
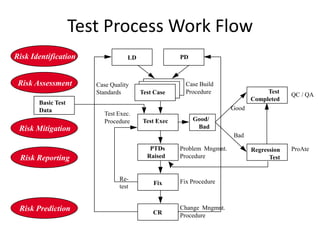
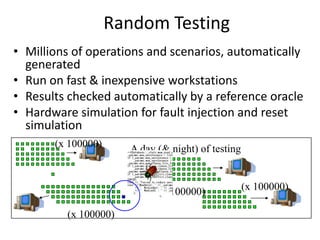
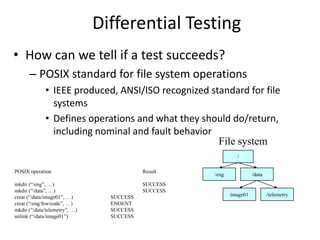
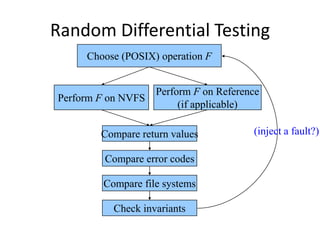
The document discusses risk based testing and random testing approaches. It outlines the challenges of time and resource constraints when testing software. Risk based testing uses risk analysis and metrics to focus testing on high risk areas in order to save time and money while maintaining quality. Metrics are developed to manage and organize large test projects. Random testing involves automatically generating random inputs and scenarios to stress test software in ways not covered by nominal testing. It can be used with differential and fault injection testing against a reference implementation to automatically check test results.