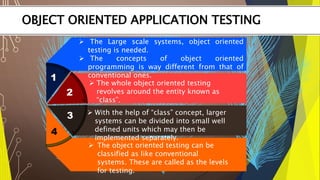
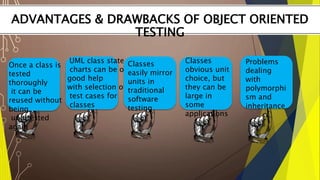
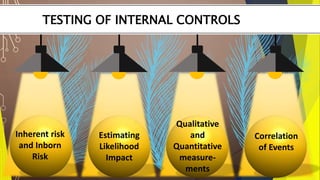
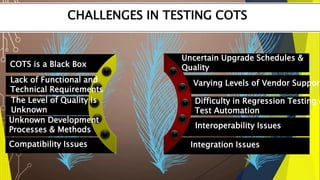
The document discusses testing for various types of software applications and systems. It covers testing for object oriented applications, internal controls, commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) software, and client-server systems. Specific topics mentioned include object oriented testing techniques, testing of transaction processing and security controls, challenges in testing COTS software, and approaches for client-server testing.