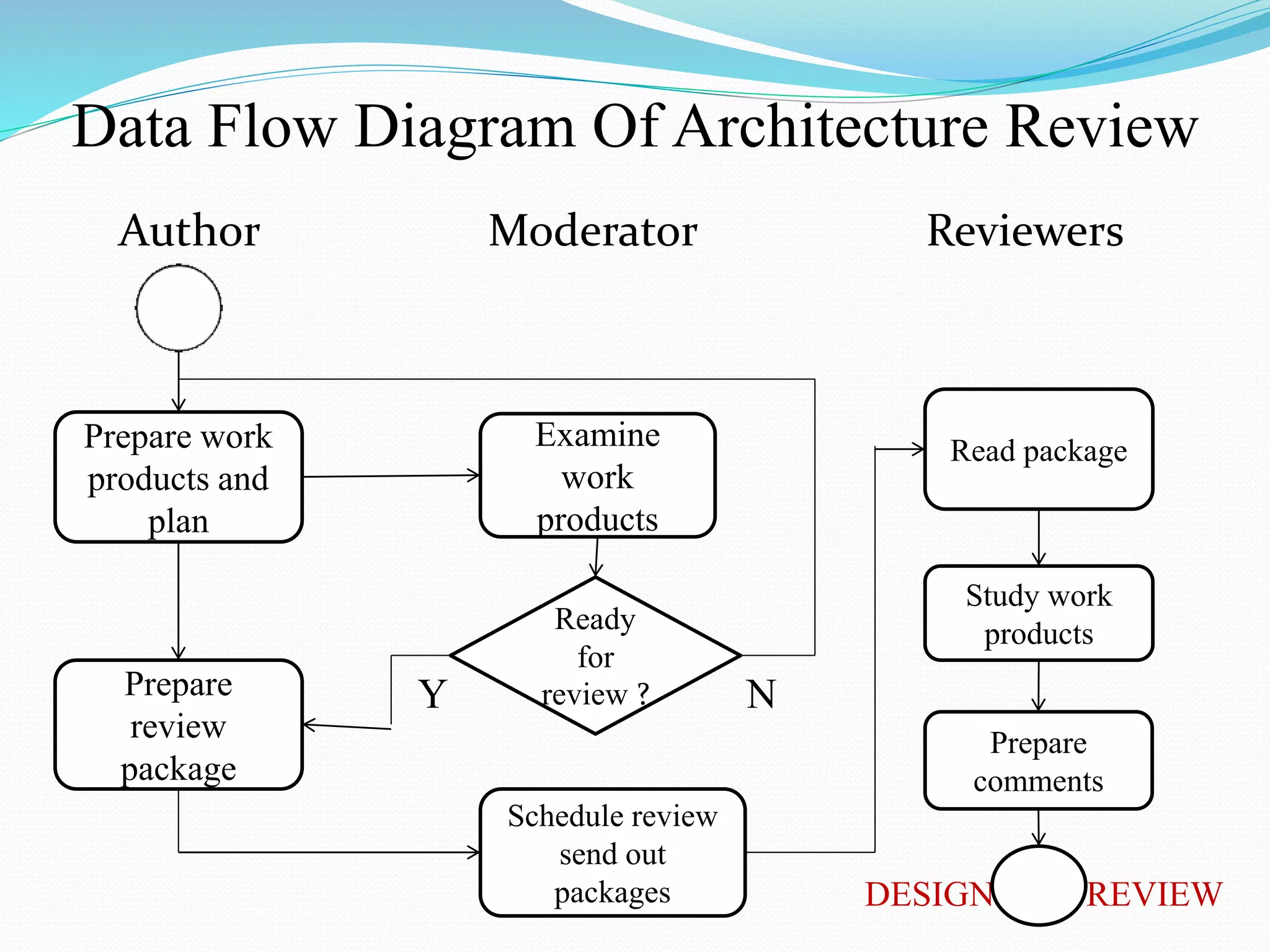
The document discusses architecture reviews, which assess an architecture's ability to fulfill quality requirements and identify risks. It describes the goals of ensuring documentation, coherence, standards compliance, and achieving project goals. Types of reviews include project process, purchase process, and iterative reviews. The basic review flow involves submitting documents, review, resolving issues, and approval or rejection. Roles in the process include the moderator, recorder, reviewers, and author/design team. Benefits are identifying risks, assessing quality attributes, promoting practices, and capturing design rationale.