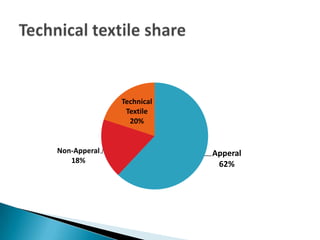
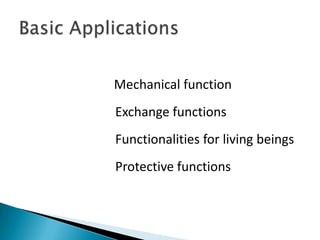
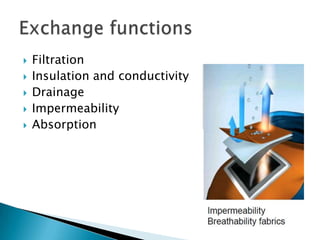
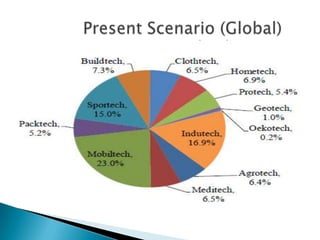
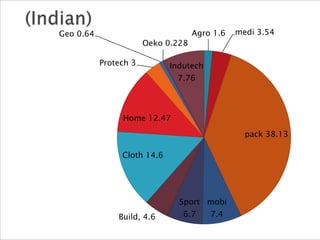
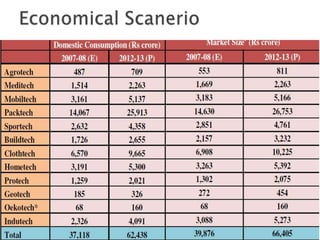
The document discusses technical textiles, providing definitions and terms used over time. It notes that technical textiles are a research-oriented industry and have increased globally from 25% to 37% from 1998-2010. The largest segments contribute 55-57% to the global market. The market size in India is estimated at Rs. 63,202 crore with an 11% annual growth rate expected to reach 20% growth. Total employment from technical textiles in India is 8.8 lakh persons with exports of $12.6 billion. There are four centers of excellence focused on different applications of technical textiles.