This document provides an overview of technical textiles used in civil engineering applications, known as "buildtech". It discusses various fibers, technologies, and examples used in buildtech applications. Some key points include:
- Technical textiles are increasingly used in construction for properties like strength, lightweight, and durability. Common fibers include polyester, glass, and nylon.
- Applications include reinforcement, insulation, roofing, scaffolding, and architectural membranes. New applications in textile architecture are also discussed.
- The market for technical textiles in construction is growing due to advantages over traditional materials like lower weight and easier manufacturing. The future of buildtech is expected to include new materials and applications.


![and to be light-weight. In addition to these properties, textile materials also with fair
price. However, to meet the achievements, textiles used in civil engineering
applications also have to have the properties such as; air conditioning, noise
prevention, tear-resistant, water and vapor impermeable, anti-slip ensures safe
installation, non-allergenic, bacteria resistant and rot-proof.
The average weight of the textile material used in a standard building; is abut
1/30 of the weight of brick, steel or concrete. Thus, it needs less reinforcement so the
cost is reduced. Also, manufacturing of textile materials is more easy and taking less
time than traditional construction materials.
Fibers used in buildtech
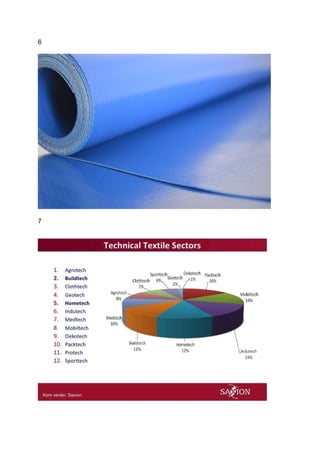
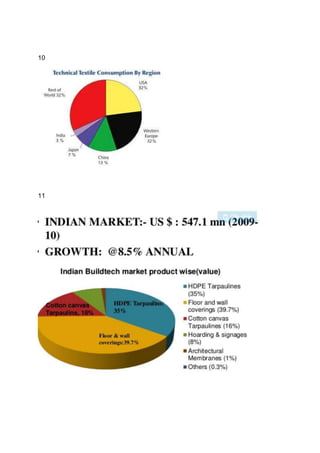
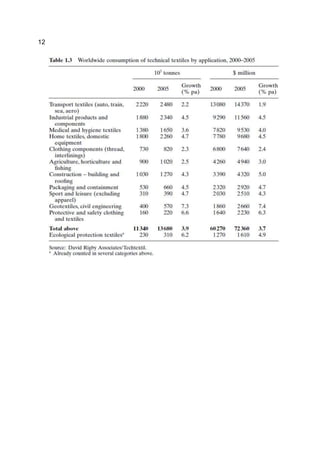
Technical textiles generally made from synthetic fibres. 22% of the fibre
consumption in the world is for manufacturing of technical textiles[Table1]. The most
common ones are; high-tenacity polyester, glass fiber and nylon. Because of the
tensile properties, strength and cost polyester is used more than the others. Also
nylon fiber used for membranes sometimes but this fiber is more expensive than
polyester(more durable at the same time).
Glass is an incombustible textile fibre and has high tenacity too. It has been
used for fire-retardant applications and also is commonly used in insulation of
buildings. Because of its properties and low cost, glass fibre is widely used in the
manufacture of reinforcement for composites. Glass fibers fairly resistant for tensions
and they also and reflect the some of sun's rays and this provides to the keep
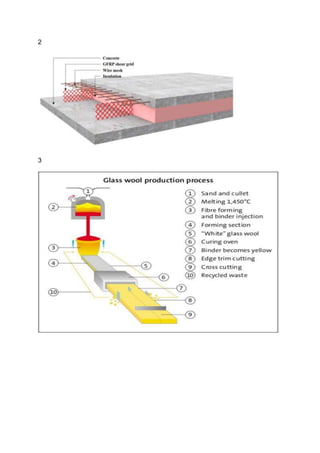
structures cold. Glass fibre applications can be between 2 layers of concrete(as an
insulation material)[Figure 2]. Also fabrics from glass fiber generally manufactured as
nonwovens. [Figure 3]
Polyethylene and polypropylene have a density less than that of water, which
allows them to float as ropes, nets and other similar applications. The availability, low
cost and good resistance to acid and alkaline environments of polypropylene has
greatly influenced its growth and substantial use in geotextile applications.
Hemp fibres with a higher durability than traditional cellulose fibres are more
suited for this kind of application, and therefore a lot of research was performed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/technicaltextilesesinyegin-160813225527/85/Technical-textiles-for-buildtech-3-320.jpg)

![types are discovering. Such as, fiberglass used 3 axial fabric or using friction hybrid
yarn knitted spacer fabrics.
Warp knitted fabrics are used as buildtech especially when strength is
important. Using of fibers such as glass fibers, Kevlar fibers, strength is further
increased. Also with using 3 axial knitting machines and with glass fiber, some fabrics
are produced and they provide heat insulation. [Figure 4]
Also in building sector, with aesthetic and strength concerns, there are starting
to produce spacer fabrics for heat and sound insulations. To reinforce to concrete,
also there are some sandwich structures which spacer fabrics and concrete are
combined together. [Figure 5]
Examples for buildtechs
Textile architecture
Most people have at one time or another spent the night in a tent and have
benefited from the protection provided by its fabric, while at the same time enjoying
the sensation of being separated from nature by nothing more than a thin shell.
Textile forms of habitation have a long history going back to palaeolithic times and
represent an archetypal form of building which has endured to the present day.
Textiles are light, easy to convert or dismantle, and they provide protection against
wind, ultra-violet rays and rain.
“More fabrics are being used in buildings to provide solar protection. By adding
textiles in architecture of a building not only can the UV rays be kept at bay but also a
shade can be provided. Energy efficiency has also increased the use of textiles.
From production and fabrication to the installation of membrane systems a lot of
energy can be saved than using conventional concrete structures. Textile also
provide a way of letting natural light being harnessed in a building by using
translucent materials, thereby saving electricity and being environment friendly.”
Today, the textiles used in stadiums, sport complexes and fairs etc. generally
are membranes they they are resistant to light and water and at the same time they
are breathable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/technicaltextilesesinyegin-160813225527/85/Technical-textiles-for-buildtech-5-320.jpg)
![Modern architecture has rediscovered the principle of the tent as an
architectural form and taken its development further – not just for temporary
structures but also for permanent buildings. Advanced and durable fabrics enable
large areas to be spanned, which has turned their use into a highly specialised sector
within the construction industry.
When the textile elements are no longer required they can be folded up and
stored compactly in a cupboard. In addition the fabrics are machine washable.
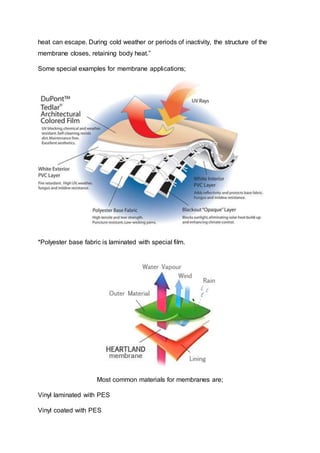
In general, membranes used in building and construction field, are formed at
both sides of the composite coated textile surface.[Figure 6] Two basic units forming
the membrane; It is ground fabric and coatings. Ground fabric usually used in
synthetic fibers and ground fabric acts as a carrier layer which provides structure and
strength necessary to lift the entire load on the structure.
The firm of Planex calculated the dimensions of each sail by modelling based
on highly accurate measurements, and all the seams were welded using high-
frequency welding equipment.
The Soltis material is produced using precontraint technology. During manufacturing
both the warp and the weft yarn is pre-stressed and then coated. This guarantees a
high level of surface stability and is a precondition for ensuring adequate wind
resistance, which can only be guaranteed if the sails neither expand nor contract in
response to changes in temperature. Soltis is UV-resistant and is available not just](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/technicaltextilesesinyegin-160813225527/85/Technical-textiles-for-buildtech-6-320.jpg)







![Also reinforcements for columns can be done by textiles. In these columns, woven
fabrics preferred constructed from the extremely high strength Kevlar or fibers such
as high density polyethylene.
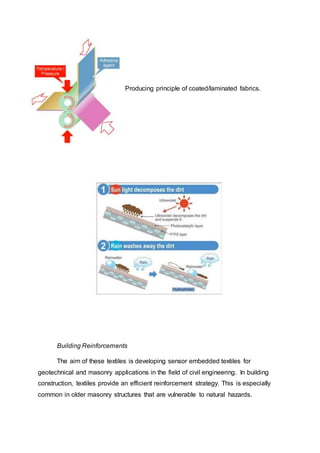
Quality control and testing of builtechs
To achieve some standarts these tests are required for buildtechs;
resistance to weathering, burning and smoke behaviour, indoor air quality, burial
tests – biodegradation, permeability, colour fastness, physical and mechanical
properties, insulation, acoustics, formaldehyde content etc.
Also these are the certifications for the textiles that used in constructions;
CE -marking of textile, resilient and laminate floor coverings and wall coverings
Oeko-Tex© Standard 100: absence of harmful substances
GuT: eco-friendly carpet production
IGI Quality mark for wallcoverings
Market statistics and future expectations
Buildtech products offer characteristics such as lightness, strength and resilience as
well as resistance to many factors such as defamation, creep, degradation by
chemicals and pollutants in the air, rain or other construction material as well as the
effects of sunlight & acid is much useful in construction of permanent and temporary
buildings as well as structures.
Buildtechs have 11% share of all technical textiles. [Table 7]
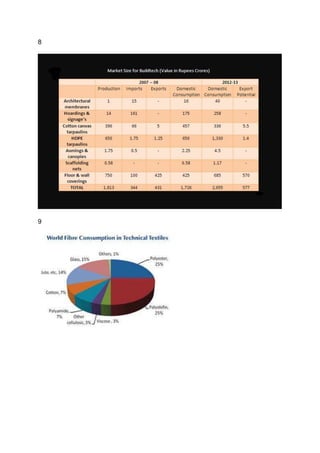
HDPE tarpaulins, wall and floor coverings and cotton canvas tarpaulins are the most
consumption groups.[Table 8]
Global markets of technical textiles and nonwovens continue to grow. World
market for technical textiles at 21 million tonnes (US $ 120 billion) during 2007-08 is
expected to increase to 26 million tonnes (US $139 billion) by 2015.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/technicaltextilesesinyegin-160813225527/85/Technical-textiles-for-buildtech-17-320.jpg)