This document summarizes several studies on the parallel economy and black money in India from the 1950s to 1980s. Key findings include:
- Estimates of black money as a percentage of GNP increased from under 10% in the 1970s to over 50% by the late 1980s, indicating black money was growing faster than the overall economy.
- Different studies using variations of the Kaldor method produced generally consistent estimates of increasing black money over time, though actual amounts varied between studies.
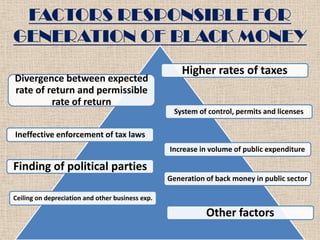
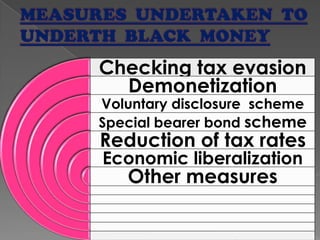
- Higher tax rates, controls on business activities, and ineffective tax enforcement were cited as primary drivers of black money generation.
- Growth of black money was seen as distorting the economy and tax base with