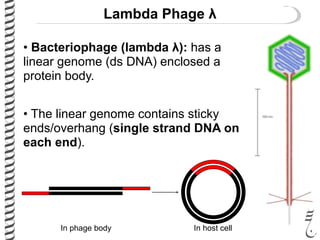
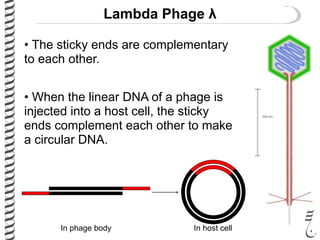
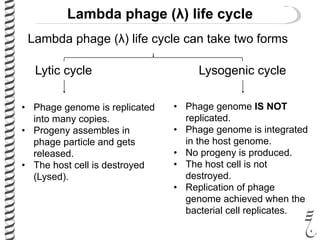
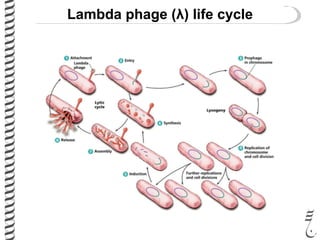
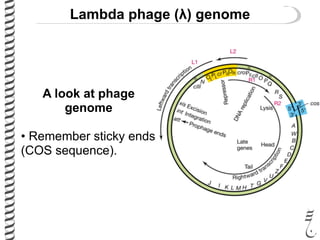
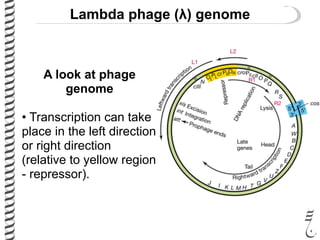
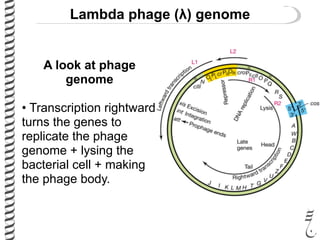
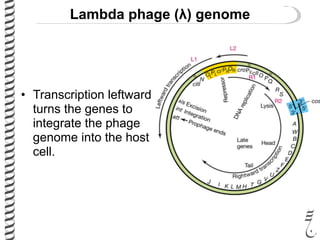
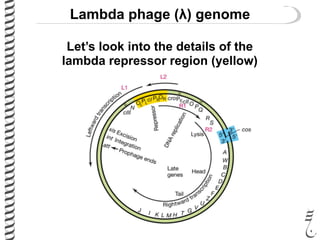
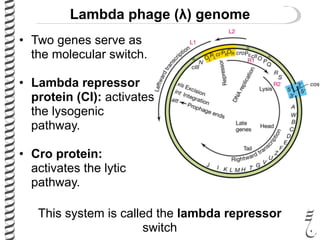
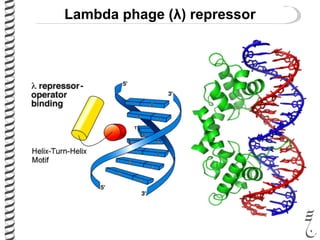
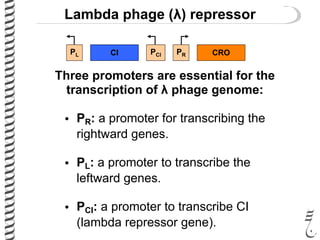
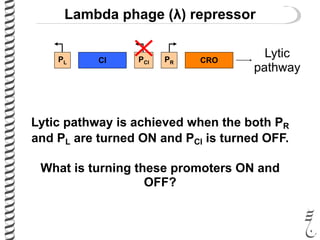
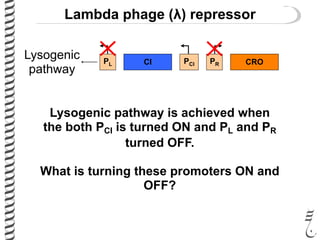
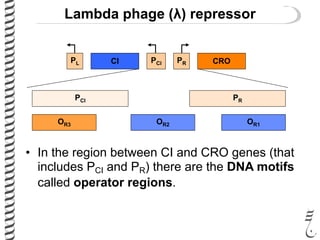
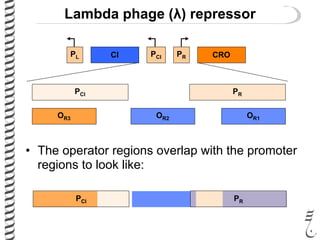
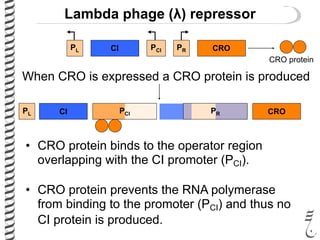
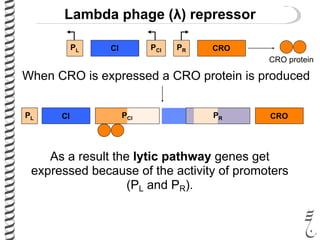
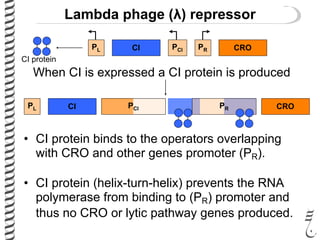
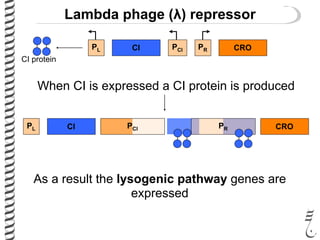
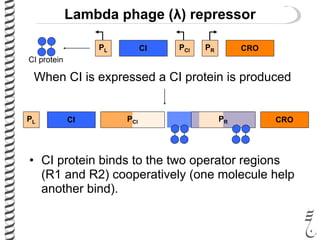
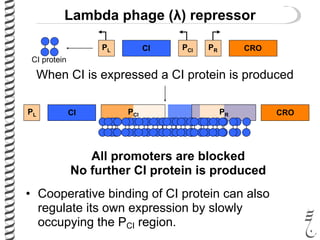
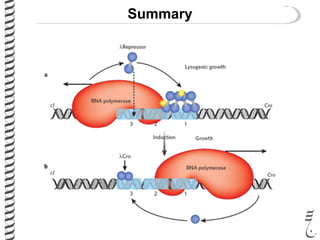
The document discusses the lambda (λ) phage repressor system that regulates the virus's life cycle pathways. The λ phage can either undergo lytic or lysogenic cycles. In the lytic cycle, the phage replicates itself many times and bursts the host cell. In the lysogenic cycle, the phage genome integrates into the host genome without replicating. The choice between these cycles is controlled by a molecular switch involving the CI and CRO repressor proteins. CI activates the lysogenic pathway by binding operator sites and blocking transcription of lytic genes. CRO activates the lytic pathway by blocking CI transcription. Environmental conditions like host stress can trigger a switch from lysogenic to lytic cycling.