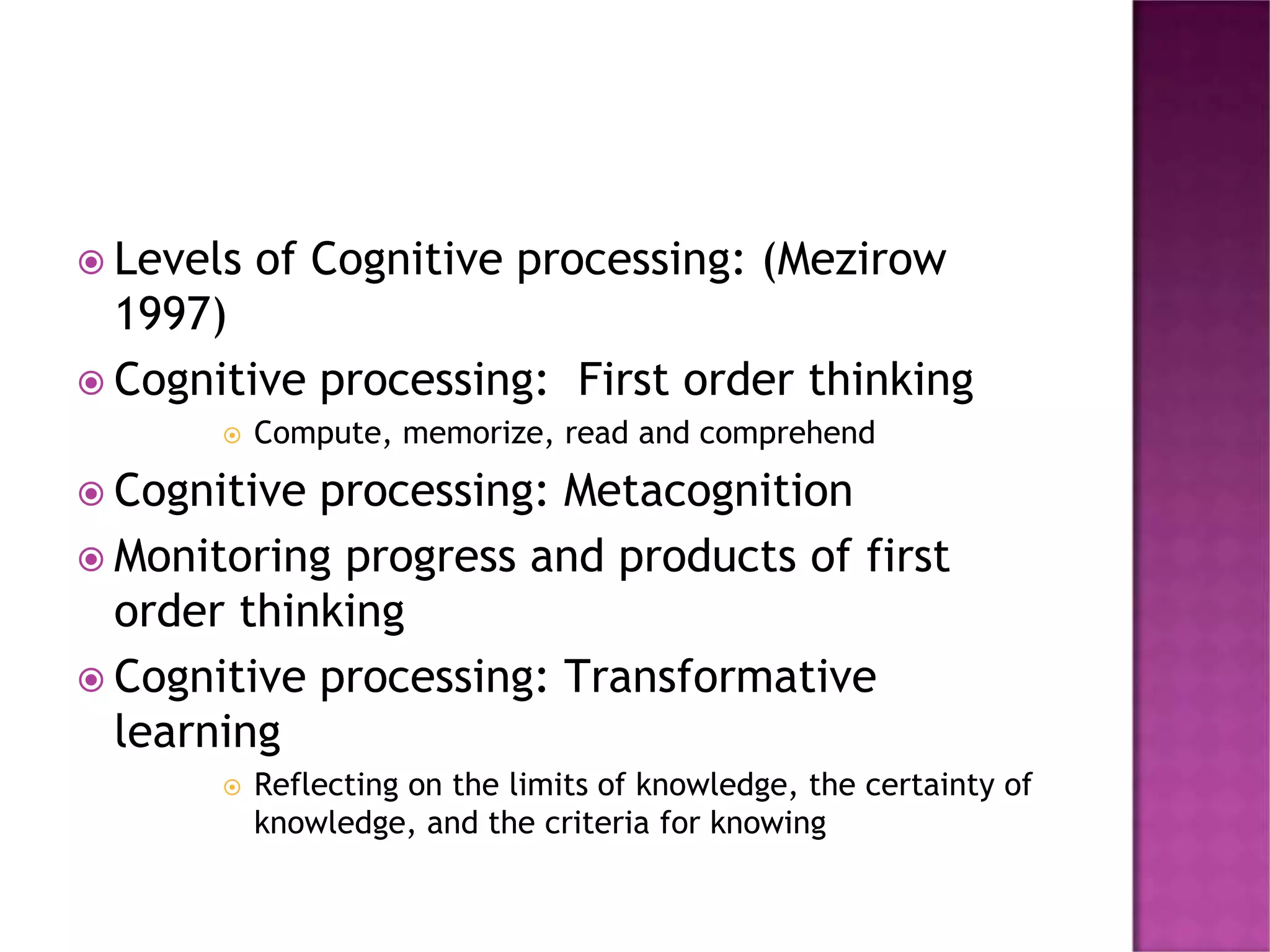
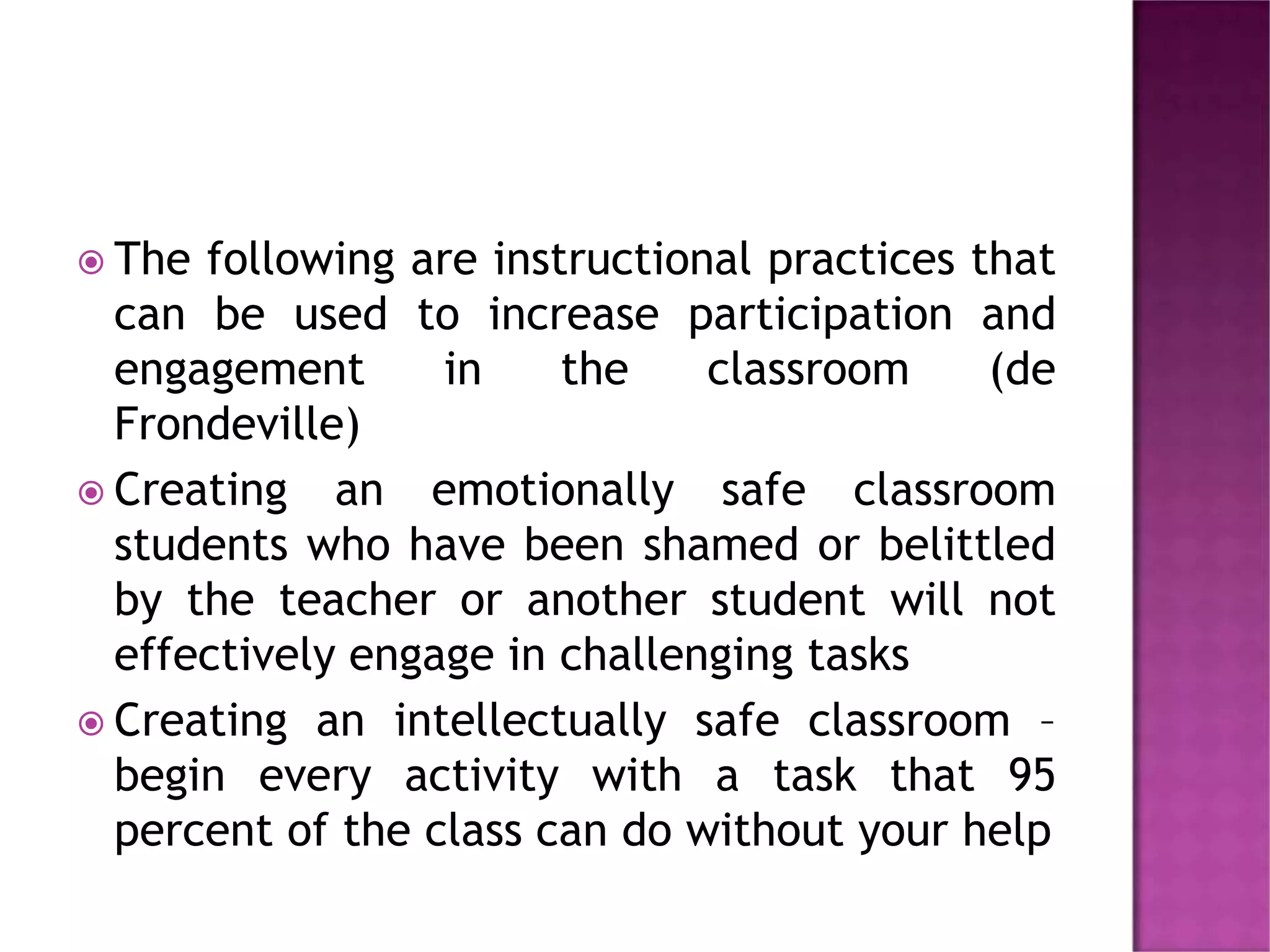
Transformational learning theory involves a deep shift in how learners see themselves and the world. It can occur through a disorienting dilemma or accumulation of changes over time. There are two types of learning - instrumental which focuses on problem solving, and communicative which involves understanding others' perspectives. The goal is to change frames of reference by elaborating, learning new frames, transforming points of view, or habits of mind. Educators can foster transformative learning by promoting reflection, a safe learning environment, and learner-centered practices.