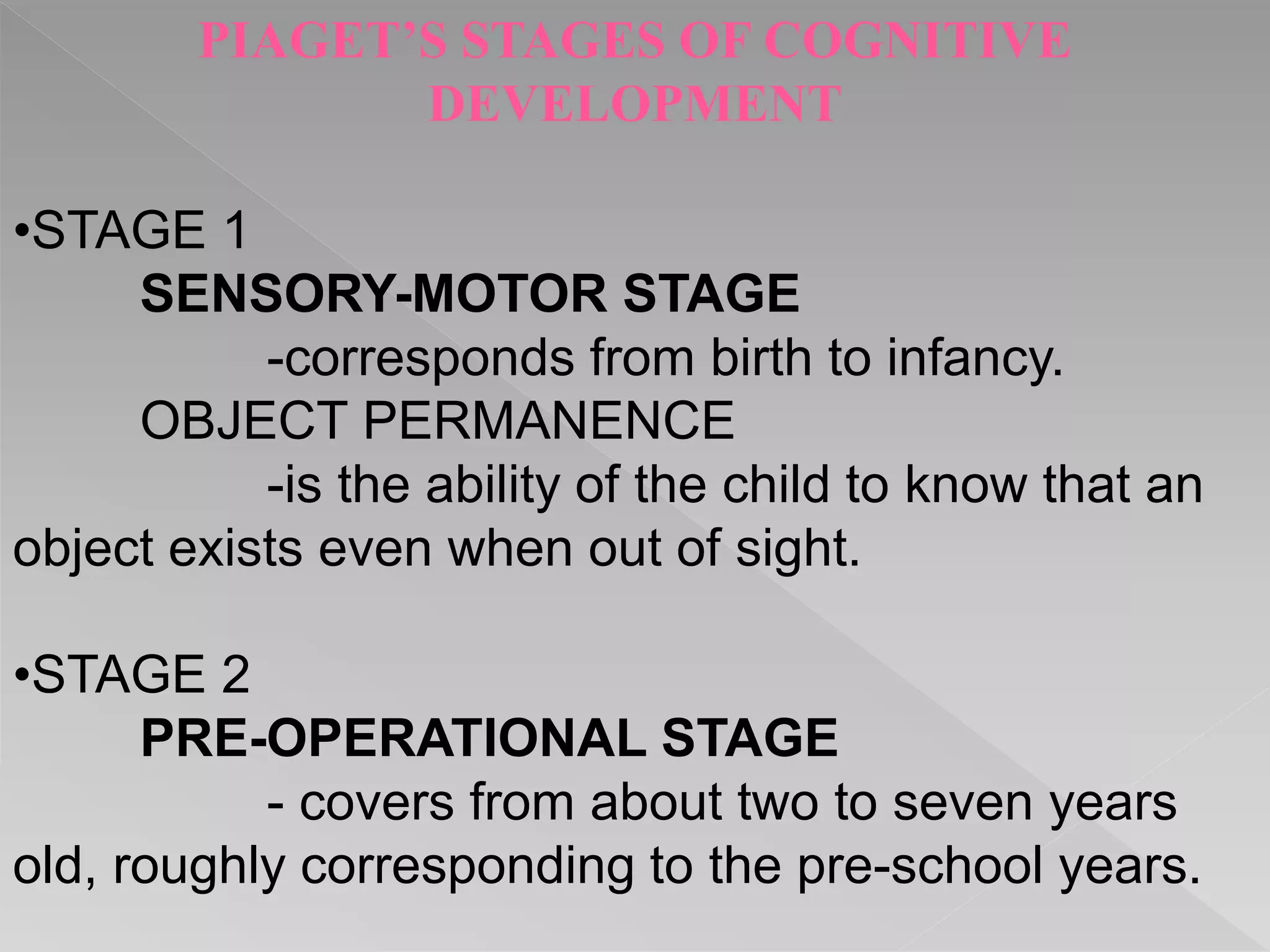
This document outlines Piaget's four stages of cognitive development:
1) Sensory-motor stage (birth to 2 years) - development of object permanence.
2) Pre-operational stage (2 to 7 years) - development of symbolic thought and egocentrism.
3) Concrete operational stage (7 to 11 years) - ability to think logically about concrete objects through processes like conservation and seriation.
4) Formal operational stage (11 to 15 years) - ability to think hypothetically and use formal operations like analogical and deductive reasoning.