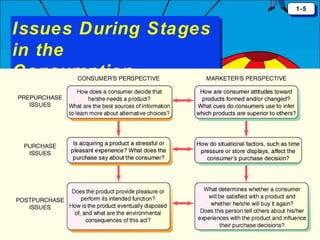
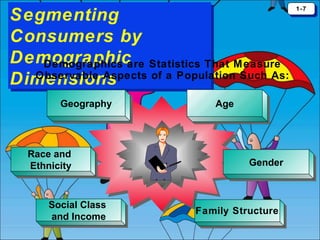
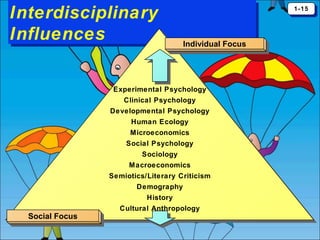
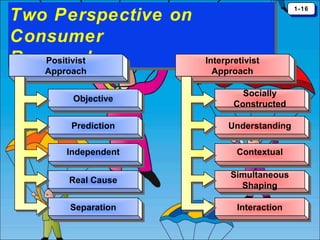
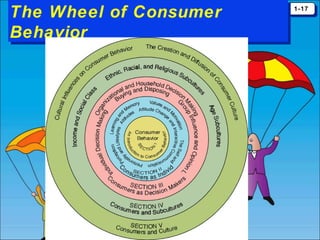
The document discusses consumer behavior as the process through which individuals or groups select, use, or dispose of products to satisfy their needs. It emphasizes the importance of understanding consumer needs for effective marketing strategies, including market segmentation and relationship marketing. Additionally, it touches on the impact of consumption on identity, emotional connections, and marketing ethics, including the potential downsides of consumer behavior such as compulsive and addictive consumption.