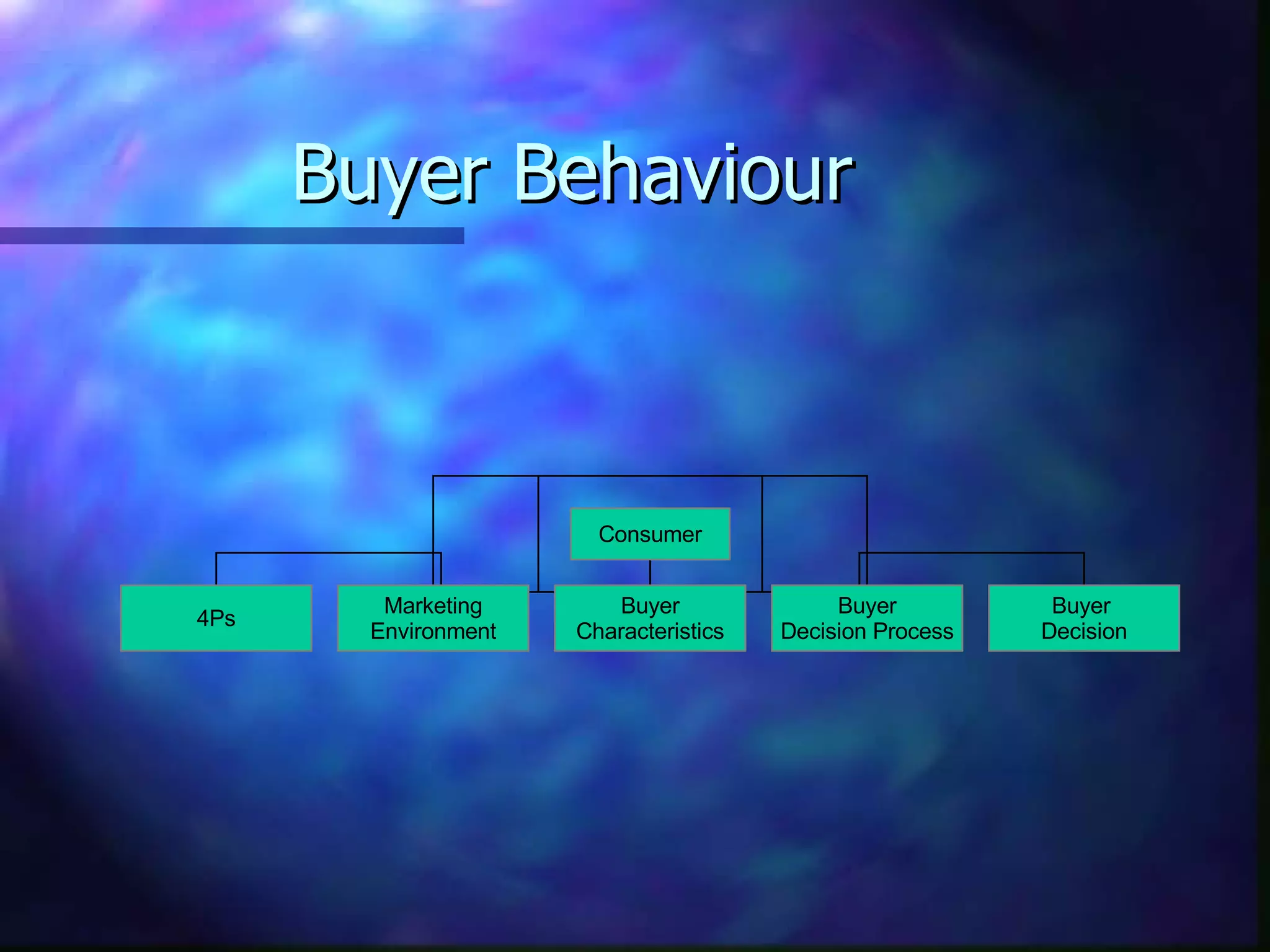
The document discusses key concepts in consumer behavior including why it is important to study, factors that influence purchasing decisions, and challenges in marketing to different cultures. It notes that failure rates of new products are high, that consumer motivation and behavior must be analyzed, and that standardizing marketing across cultures is difficult due to differences in tastes and habits. Examples of lost in translation marketing messages that had unintended meanings in other cultures are also provided.