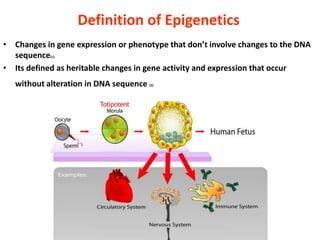
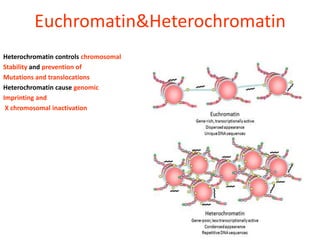
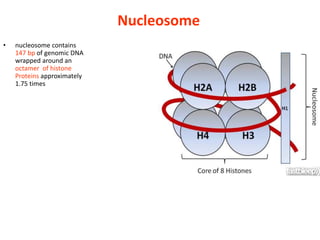
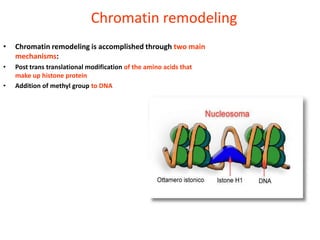
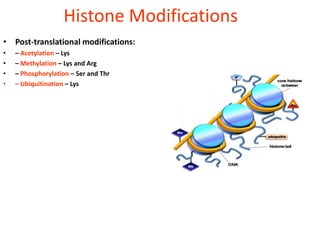
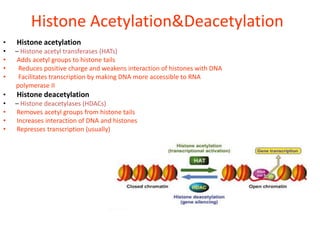
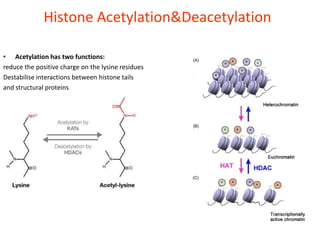
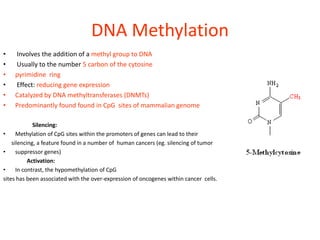
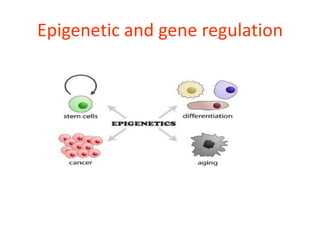
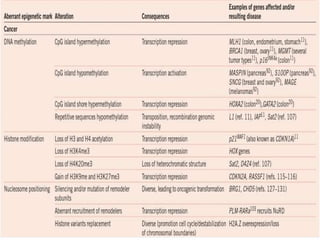
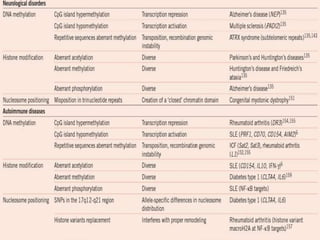
Epigenetics involves heritable changes in gene expression that do not involve changes to DNA sequence. The main epigenetic mechanisms are chromatin remodeling, DNA methylation, and histone modification. Environmental factors like smoking, diet, and toxins can influence the epigenome. Errors in epigenetic programming have been linked to diseases. The epigenome responds dynamically to the environment and directs gene expression patterns during development and differentiation.












![References
• 1.http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epigenetics
• 2.Bird A.Nature ,447 ,396-98[2007]
• 3. Turner B (2007). "Defining an epigenetic code". Nat Cell Biol 9 (1): 2–6.
• 4.Gupta, Swati; Se Y. Kim, Sonja Artis, David L. Molfese, Armin Schumacher, J. David Sweatt, Richard E. Paylor, and Farah D. Lubin (10 March 2010). "Histone Methylation Regulates Memory Formation". The
Journal of Neuroscience 30 (10): 3589–3599](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/epigenetics-130328044428-phpapp01/85/Epigenetics-27-320.jpg)
