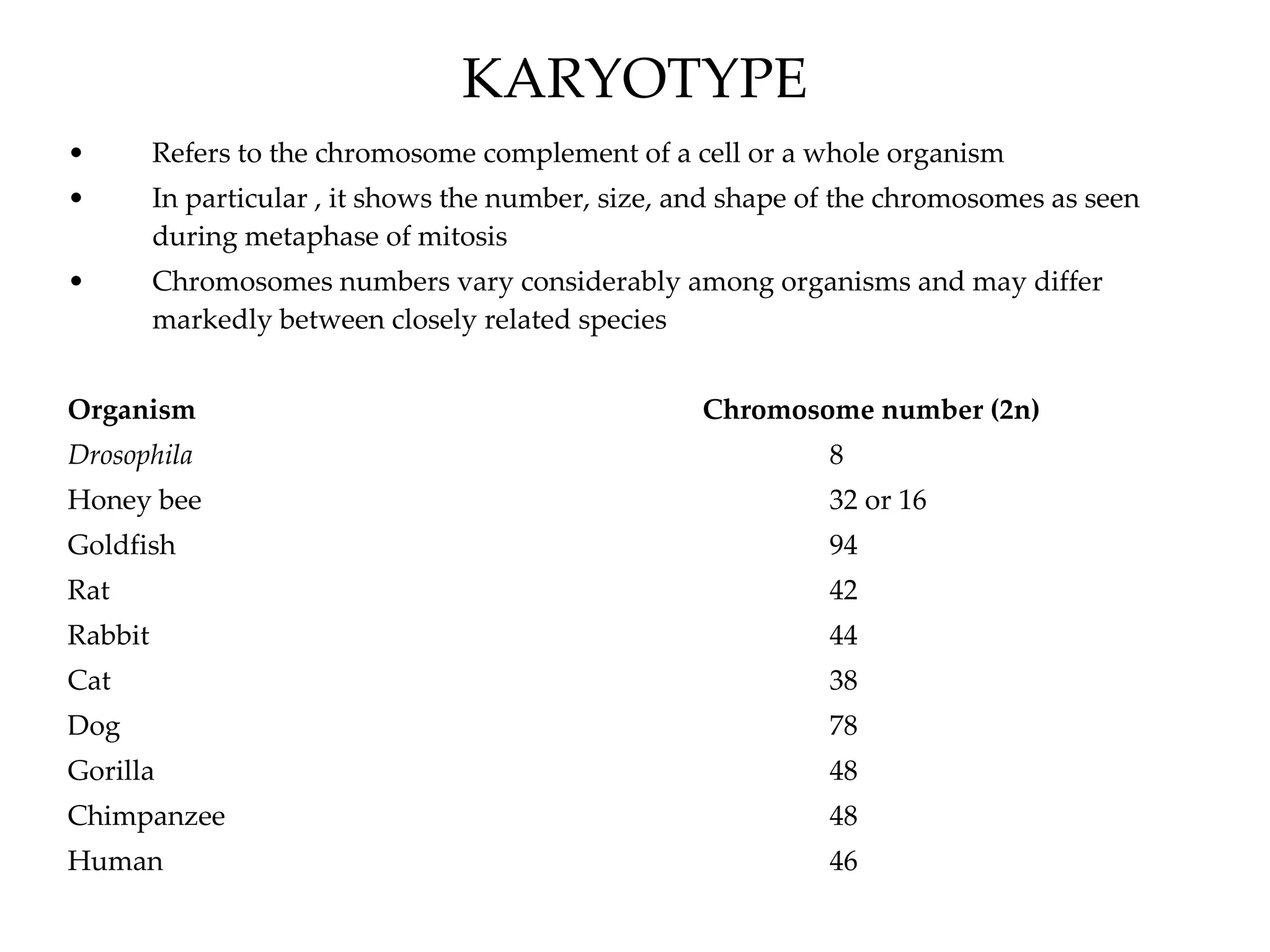
The document discusses karyotypes and chromosomes. It defines a karyotype as the chromosome complement of an organism and shows the number, size, and shape of chromosomes. It provides examples of chromosome numbers in various species. It also summarizes techniques like karyotyping, amniocentesis, and chorionic villus sampling that are used to analyze chromosomes. Sex linkage and examples of sex-linked conditions like color blindness and hemophilia are also covered.