Structure of chromosome chandu 1
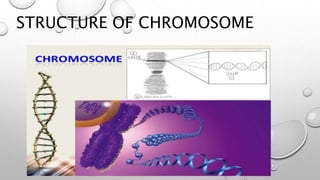
- 2. CHROMOSOME : CHROMO MEANS ----- COLOUR , SOMA MEANS --- - BODY. CHROMOSOMES WERE FIRST DESCRIBED BY STRAUSBERG IN 1875. THE TERM FIRST USED BY WALDEYER IN 1888. CHROMOSOMES ARE ROD SHAPED ,FILAMENTOUS BODIES PRESENT IN THE NUCLEUS , WHICH BECOME VISIBLE DURING CELL DIVISION. THEY ARE CARRIERS OF THE GENE OR UNIT OF HERIDETERY. CHROMOSOMES ARE VISIBLE IN ACTIVE NUCLEUS BECAUSE OF ITS WATER CONTENT ,IT IS VISIBLE DURING THE TIME OF CELL DIVISION.
- 3. TYPES OF CHROMOSOME: • Chromosomes are of two types : • Autosomes: That control characters other than sex characters or carry genes for somatic characters. • Sex chromosomes (gonosomes) : chromosomes involved in sex humans and most other mammals have two sex chromosomes x & y, also called heterosome. Females have two x chromosomes in diploid cells; males have an x and a y chromosome. In birds the female (zw) is hetero-gametic and male (zz) is determination is homogametic.
- 4. • Chromatid : • Each metaphase chromosome appears to be longitudinally divided into two identical parts each of which is called chromatid. • Both the chromatids of a chromosome appear to be joined together at a point known as centromere. • The two chromatids of chromosome separate from each other through replication of a single chromatid during synthesis (S) phase of interphase, they are referred to as sister chromatids. • In contrast, the chromatids of homologous chromosomes are er during mitotic anaphase (and during anaphase II of meiosis) and move towards opposite poles. • Since the two chromatids making up a chromosome are produced through replication of a single chromatid during synthesis (S) phase of interphase ,they are referred to as a SISTER CHROMATID. • In contrast, the chromatids of homologous chromosomes are known as NON SISTER CHROMATIDS.
- 5. Centromere (primary constriction) : centromere is the landmark for identification of chromosome. Each chromosome has a constriction point called the centromere (synonym: kinetochore), which divides the chromosome into two sections or arms. The short arm of the chromosome is labeled the "p" arm. The long arm of the chromosome is labeled the "q" arm. Telomere : The two ends of a chromosome are known as telomeres, they play critical roles in chromosome replication and maintenance of chromosomal length. The telomeres are highly stable and telomeres of different chromosomes do not fuse. The telomeric region of chromosome is made up of repeatative sequence of T and G bases. Secondary constriction : In some chromosome addition to centromere / primary constriction, one or more constrictions in the chromosome are present termed secondary constrictions. Satellite : The chromosomal region between the secondary constriction and nearest telomere is called as satellite and chromosomes that possess this region called as satellite .
- 7. NUMBER OF CHROMOSOMES: Normally all the individuals of a species have the same number of chromosomes . Presence of whole set of chromosomes is called EUPLOIDY. When a change in chromosome number doesn’t involve in the entire set of chromosome ,but only a few of chromosomes – ANEUPLOIDY. Gametes normally contain only a set of chromosomes – this is called – HAPLOID. Somatic cells usually contain 2 sets of chromosomes : 2n -- Diploid 3n -- Triploid 4n – Tetraploid.
- 8. SIZE OF CHROMOSOME : In contrast to other cell organelles ,the size of chromosomes shows a remarkable variation depending upon the stages of cell division. INTERPHASE : chromosomes are longest and thinnest. PROPHASE :There is a progressive decrease in their length accompanied with an increase in thickness. ANAPHASE : chromosomes are smallest. METAPHASE : chromosomes are most easily observed and studied during metaphase when they r very thick ,quite short and well spread in the cell.
- 10. CHROMATIN : • chromatin is the combination of DNA and proteins that make up the contents of the nucleus of a cell. • the primary functions of chromatin are: to package DNA into a smaller volume to fit in the cell, to strengthen the DNA to allow mitosis and meiosis and prevent DNA damage, and to control gene expression and DNAreplication. • the primary protein components of chromatin are histones that compact the DNA. chromatin is only found in eukaryotic cells. prokaryotic cells have a very different organization of their DNA which is referred to as a genophore
- 11. • THE TWO BASIC TYPES OF CHROMATIN ARE 1. EUCHROMATIN 2. HETEROCHROMATIN • 1.EUCHROMATIN : The chromatin fibres in this region are loosely coiled . • Euchromatin undergoes the normal process of condensation and de condensation in the cell cycle. • Euchromatin constitutes the majority of the chromosomal material and is where most transcription takes place. 2. HETEROCHROMATIN:The chromatin fibres in this region are more tightly folded • Heterochromatin remains in a highly condensed state throughout the cell cycle, even during interphase. • All chromosomes have heterochromatin at the centromeres and telomeres. • In addition to remaining condensed throughout the cell cycle, heterochromatin is characterized by a general lack of transcription.
- 15. GENOME COMPLEXITY: • This introduction to genetics takes you through the basic components of genetics such as DNA, genes, chromosomes and genetic inheritance. • Genitics is build around the molecule DNA. DNA molecules hold all the genetic information for an organism. It provides cells with the information they need to perform tasks that allow an organism to survive,grow and reproduction. • Heredity is what makes children look like their parents. During reproduction, DNA is replicated and passed from a parent to their offspring. This inheritance of genetic material by offspring influences appearance and behavior of the offspring. The environment that an organism lives in can also influence how genes are expressed. • Some of the genes are dominant- they produce the trait in every generation. Other genes are recessive- produce trait that skips several generations. • • Genes do not act alone; rather they are influenced by the genetic background of an individual and by external and internal environment. • • Each human nucleated somatic cell has about 30,000 genes in the nucleus. Cells also have some non-nuclear genes located within the mitochondria within the cytoplasm.
- 16. • Alternate forms of a gene are termed as alleles (particular character). • • For each gene, an individual receives an allele from each parent, and thus has two alleles for each gene on the autosomes and also on the X chromosome in females only. • Males have only one X chromosome and therefore have only one allele for all genes on the X chromosome. They are hemizygous for all X linked genes. At any autosomal locus, or gene site, an individual can have two identical alleles (homozygous) for that locus or can have different alleles (heterozygous) at a particular locus e.G. For eye color. • Genotype refers to the constitution of genetic material of an individual; for practical purpose it is commonly used to address a specific pair E.G. The gene of sickle cell anaemia and gene of cystic fibrosis .