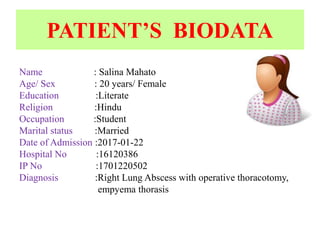
1. Salina Mahato, a 20-year old female, presented with a 15-day history of cough and sputum production and 3 days of fever. She was diagnosed with a right lung abscess and underwent operative thoracotomy.
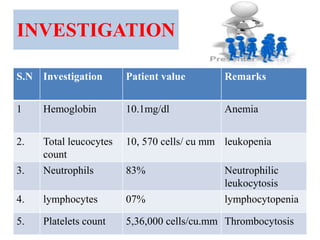
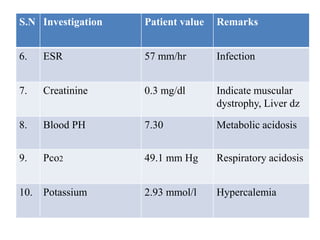
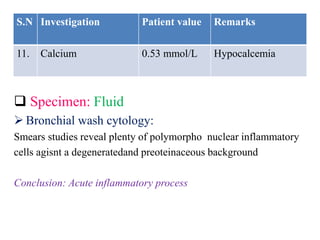
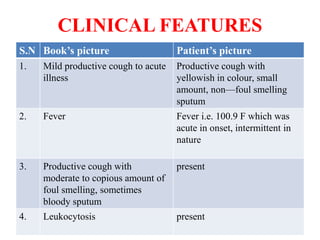
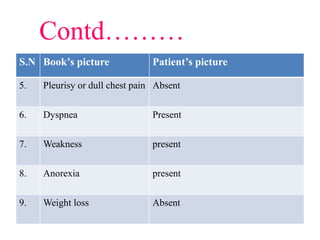
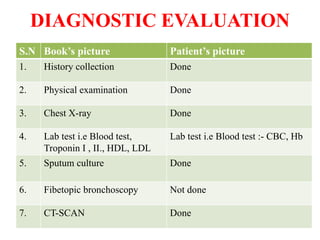
2. On examination, she had dullness and decreased breath sounds on the right lung with coarse inspiratory crackles. Laboratory tests showed anemia and leukocytosis. A chest X-ray and CT scan confirmed the presence of a lung abscess.
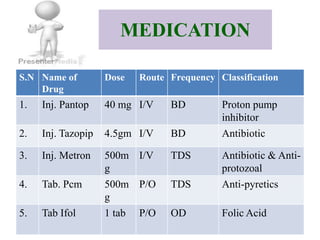
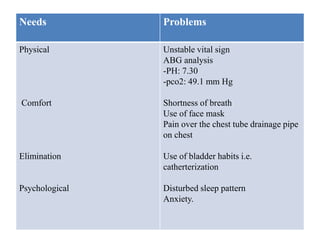
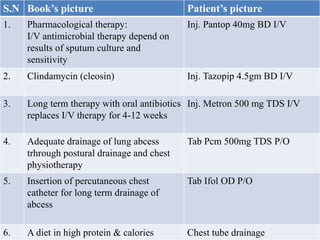
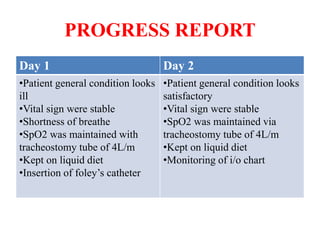
3. She was treated with IV antibiotics, chest physiotherapy, oxygen supplementation, and chest tube drainage. Her condition improved over the next 2 days though she remained short of breath and kept NPO with IV fluids