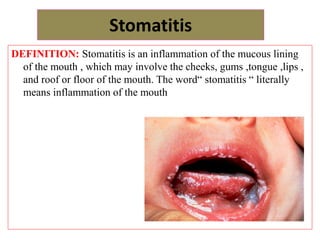
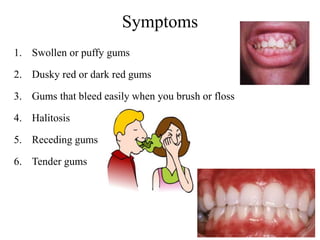
This document discusses several disorders of the oral cavity including stomatitis, gingivitis, and glossitis. Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mouth lining that can be caused by chemotherapy, radiation, trauma, or other factors. Symptoms include pain, sores, fever and irritability. Treatment involves medications to reduce inflammation and pain. Gingivitis is a non-destructive gum disease caused by plaque, diseases like diabetes, drugs, or smoking. Symptoms include swollen or bleeding gums. Prevention relies on good oral hygiene habits. Glossitis refers to tongue inflammation that can cause swelling, color changes, and texture changes. It has several types and causes including infections, mechanical irritation, nutritional deficiencies