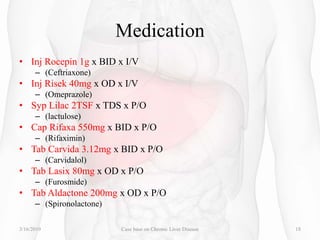
The document presents a case study of a 53-year-old male patient diagnosed with chronic liver disease, specifically from hepatitis C, highlighting symptoms, medical history, and physical assessment findings. It discusses cirrhosis, its causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and nursing management strategies. Key complications and necessary interventions for effective patient care are also outlined.