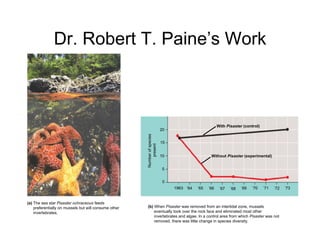
This document discusses different examples of keystone and foundation species. It provides Robert Paine's research on the sea star Pisaster ochraceus, which controls populations of mussels and maintains high biodiversity in intertidal zones. It also discusses James Brown's research on kangaroo rats in desert ecosystems and how their removal changed the plant community composition and increased grasslands. Foundation species like kelp are also discussed as dominant primary producers that many other species rely on for food and shelter.