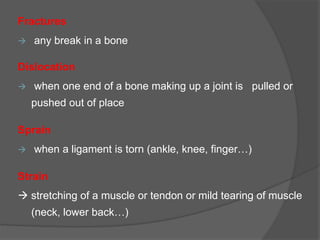
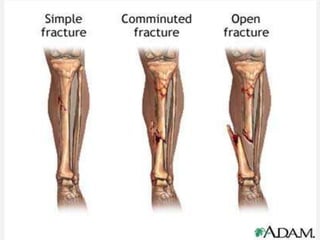
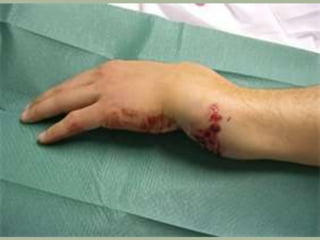
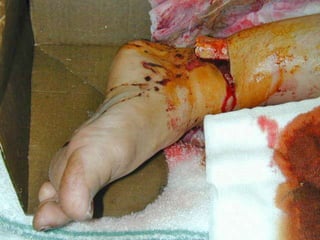
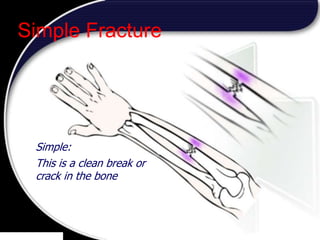
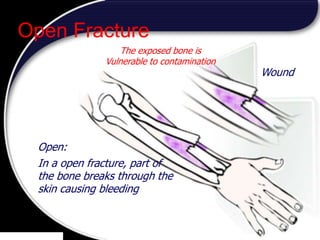
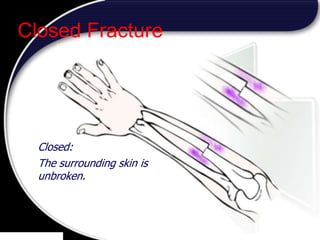
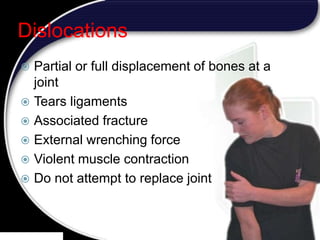
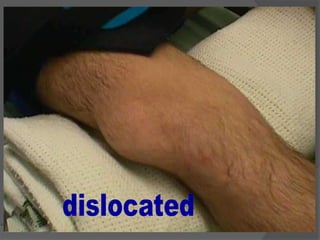
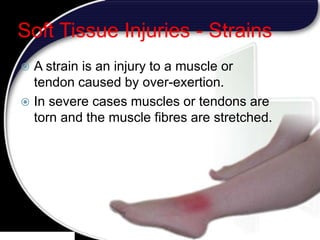
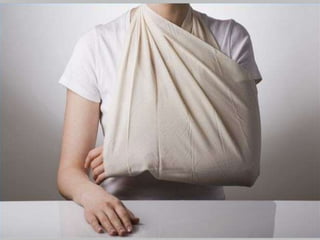
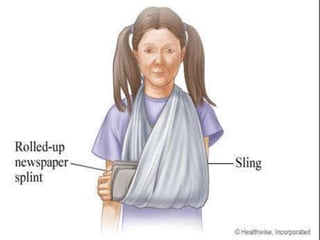
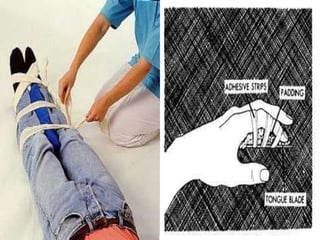
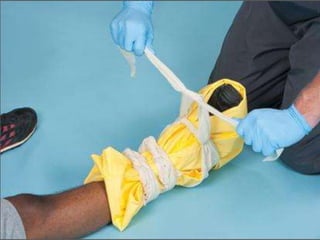
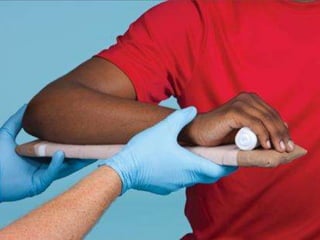
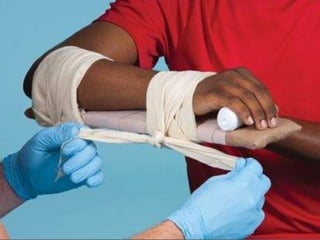
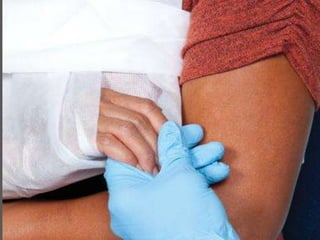
This document discusses signs of serious muscle, bone, or joint injuries and provides information about fractures, dislocations, sprains, and strains. It notes that significant deformity, bruising, swelling, inability to use the affected area normally, bone fragments sticking out of wounds, feeling bone grating after injury, hearing a pop or snap at time of injury, or the area being cold or numb could indicate a serious injury. It provides details on closed and open fractures, as well as treatment guidelines for soft tissue injuries using RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation).