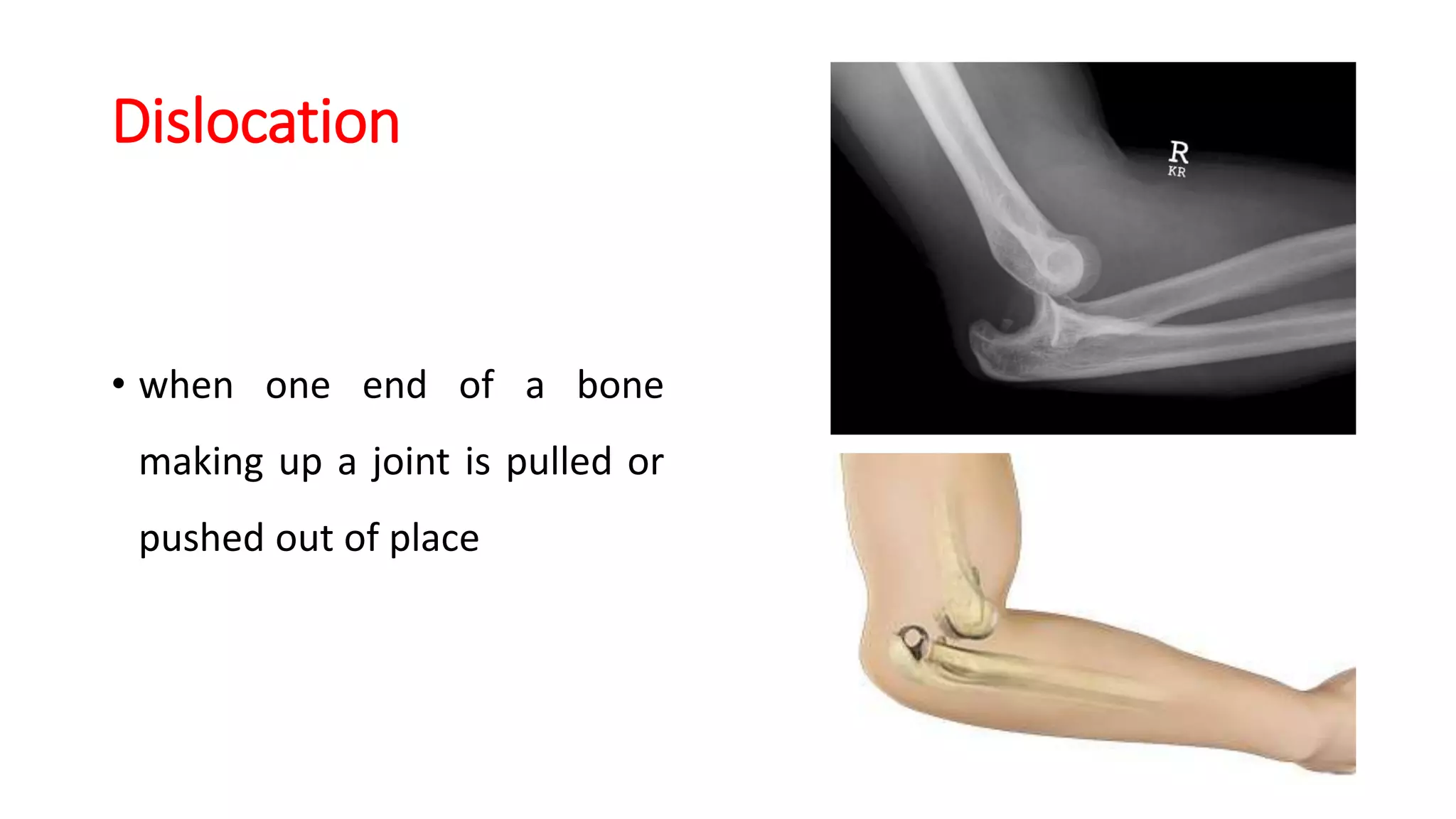
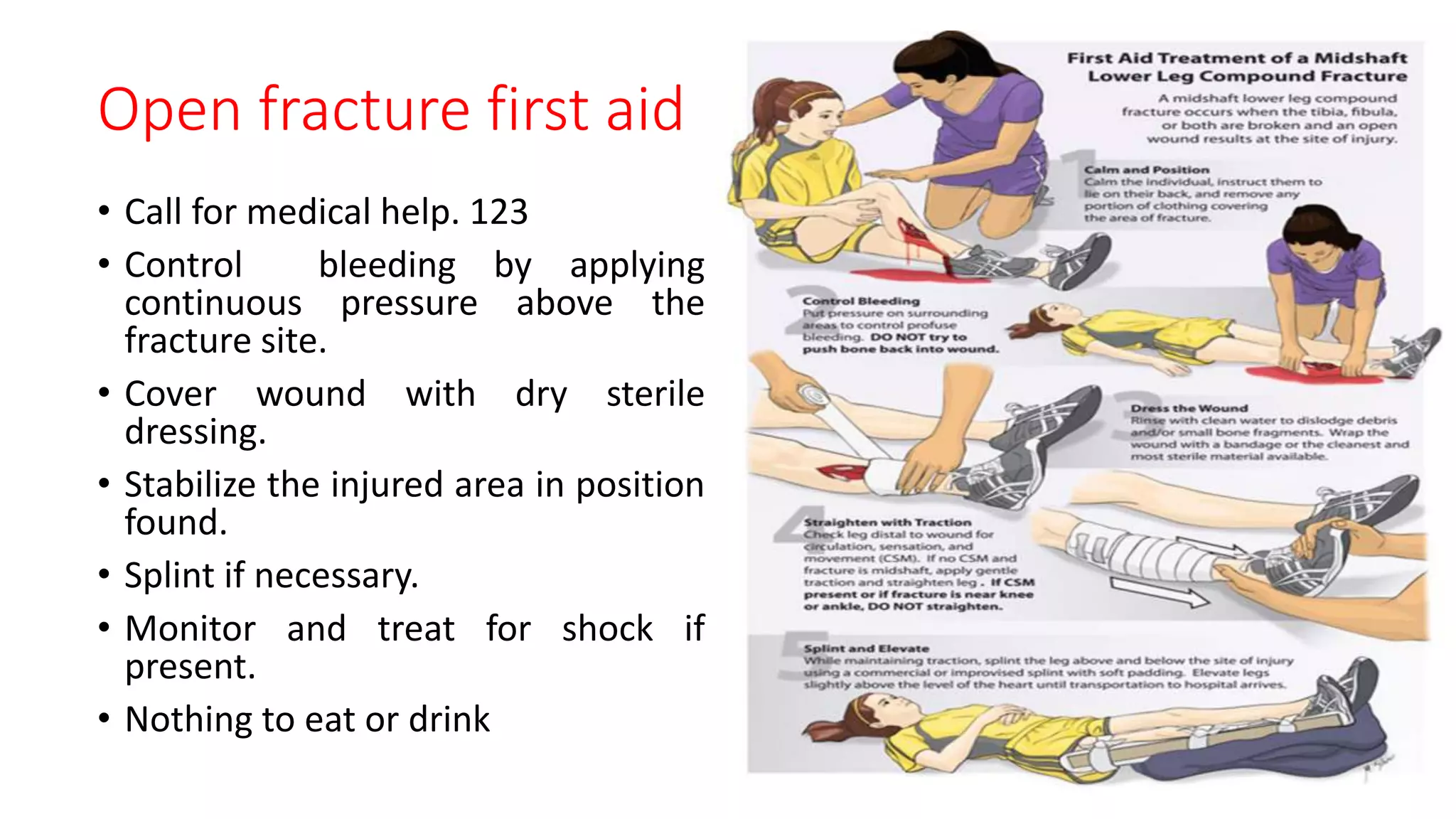
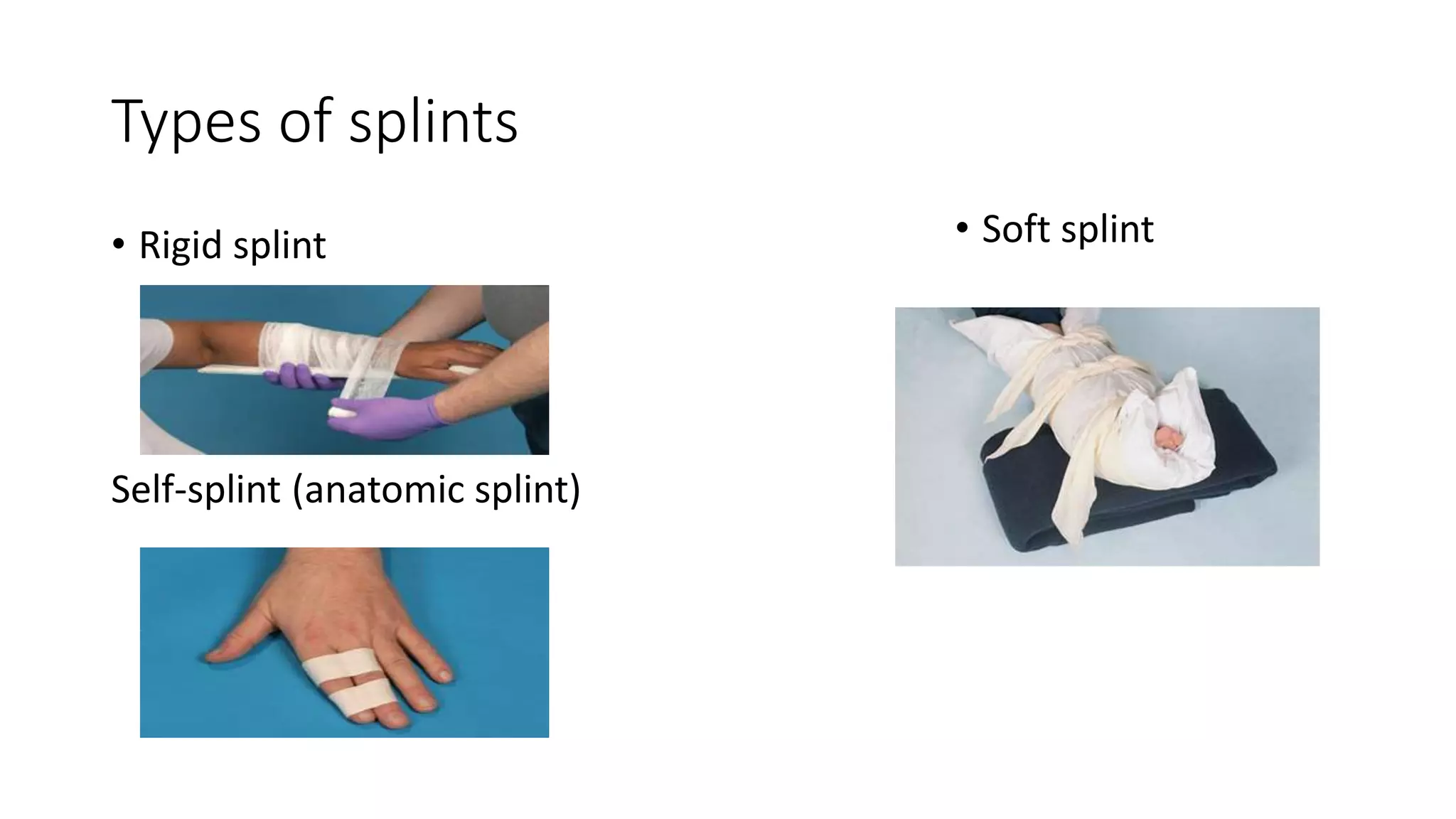
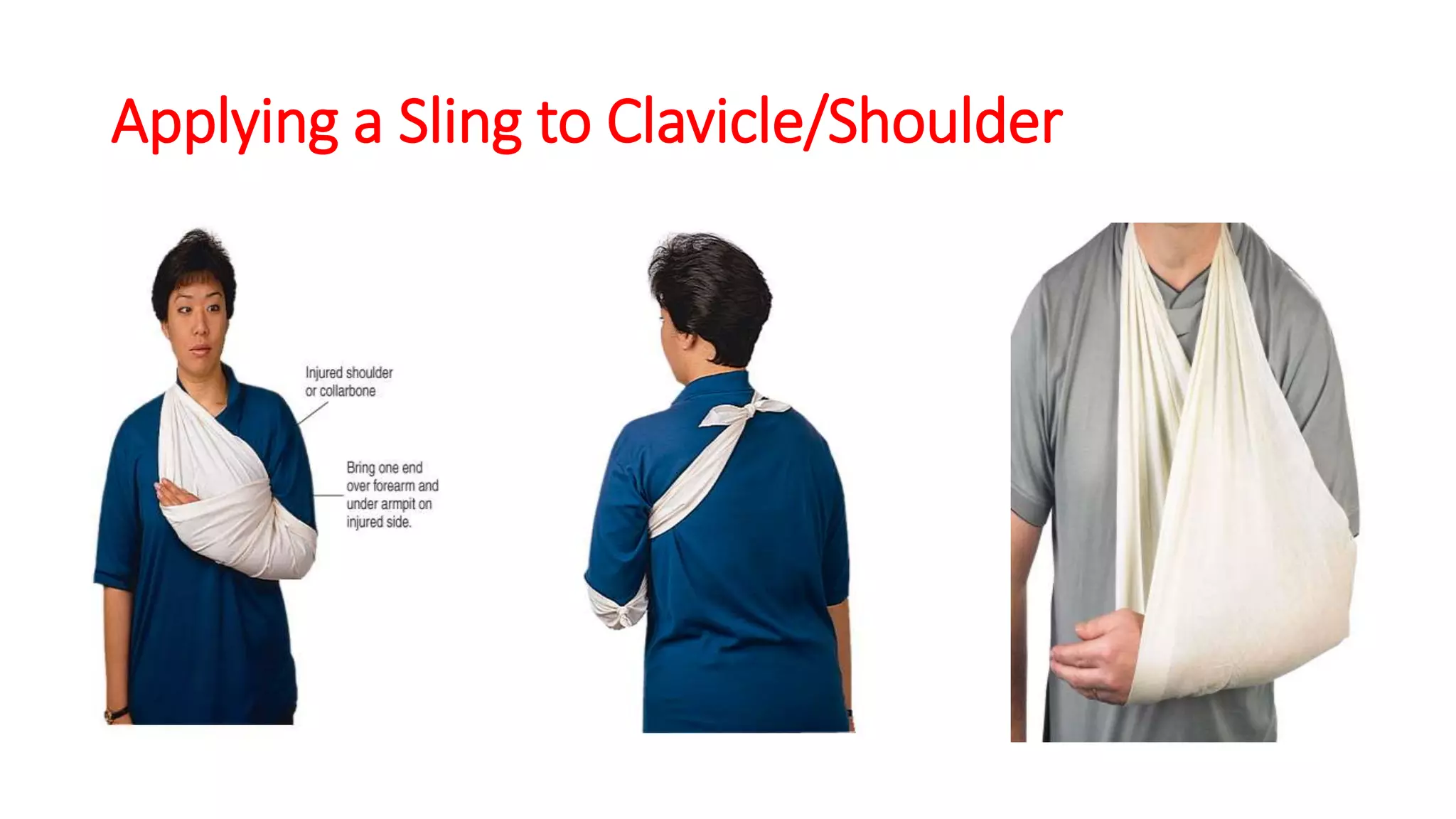
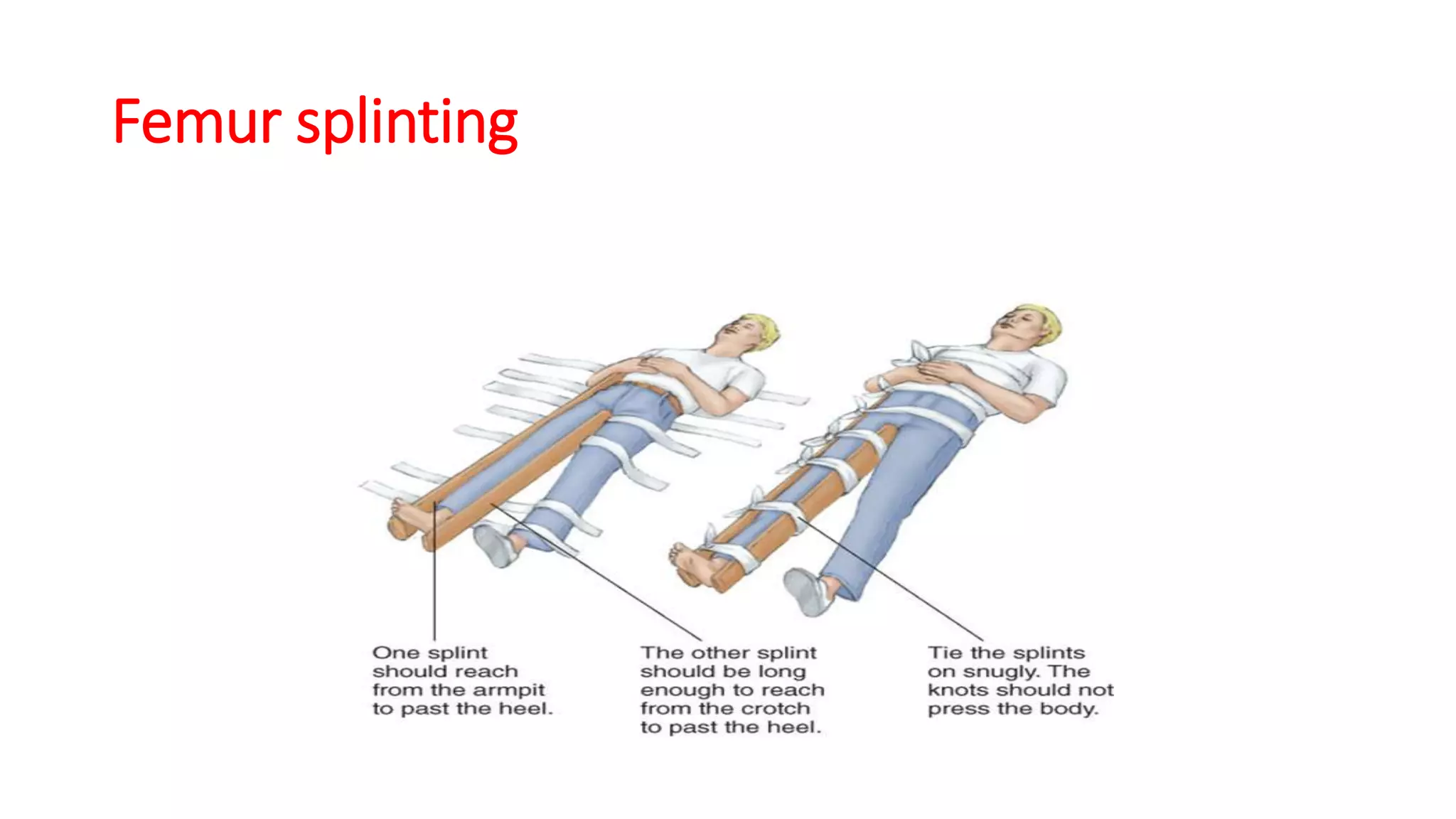
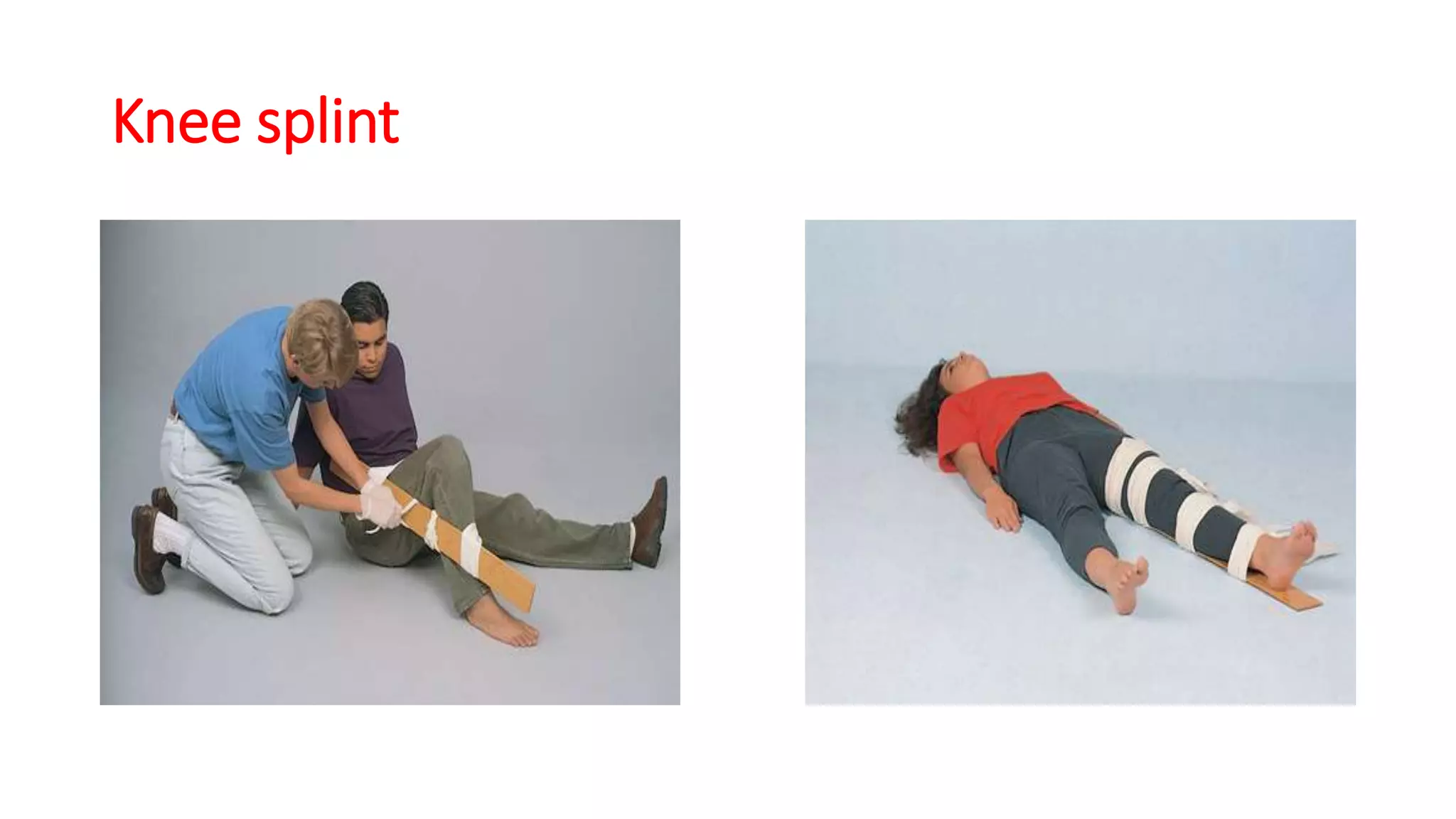
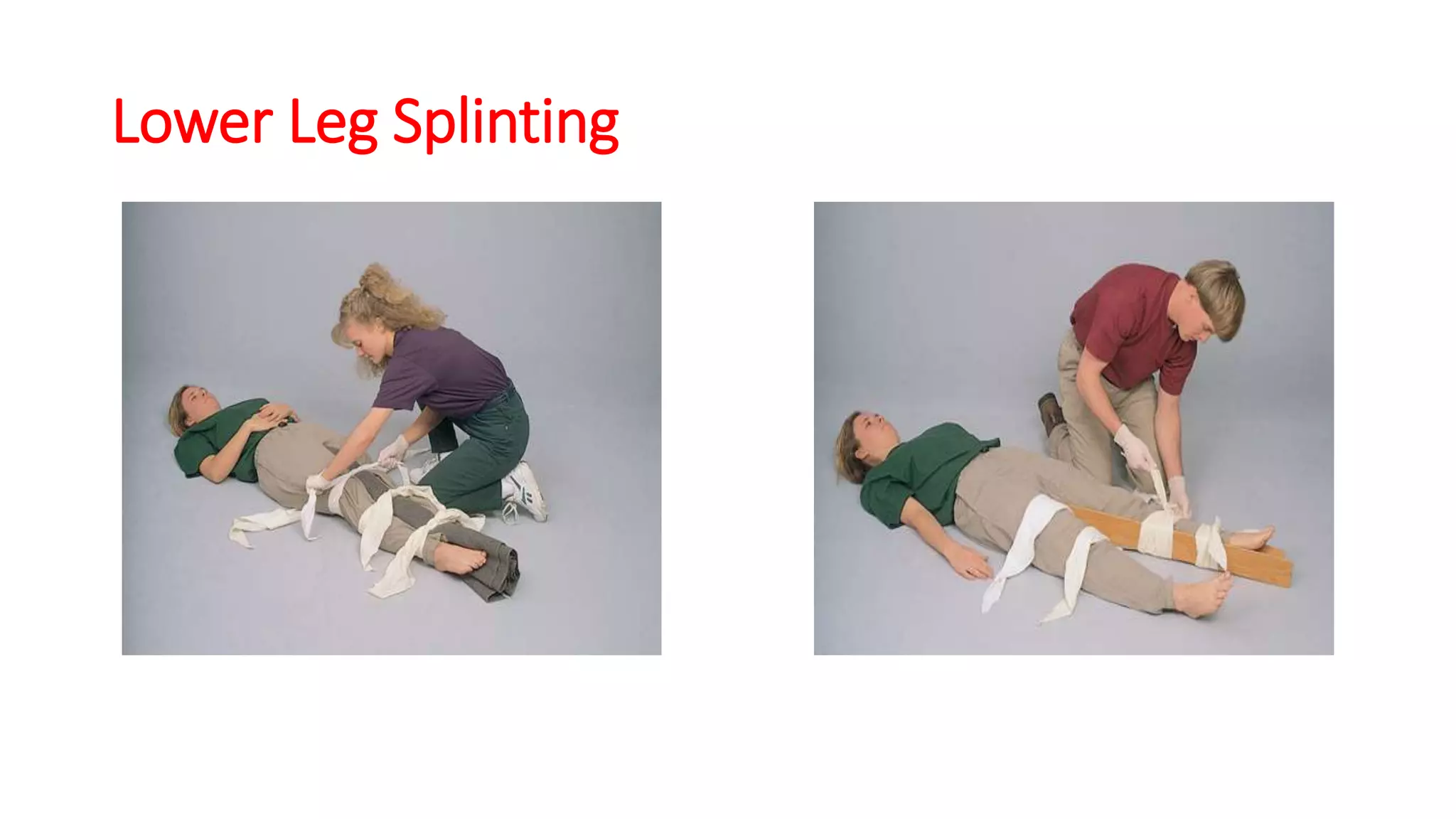
This document provides information on first aid for fractures and soft tissue injuries. It discusses the aims of first aid, including preserving life, protecting from further harm, providing pain relief, preventing worsening of injuries, and promoting recovery. It describes the signs and symptoms of fractures, dislocations, sprains, and strains and appropriate first aid actions for each, which generally involve immobilization (splinting), controlling bleeding if needed, and calling for medical help. The RICE treatment of rest, ice, compression and elevation is recommended for soft tissue injuries. Throughout, it emphasizes not moving fractures or attempting to set bones.