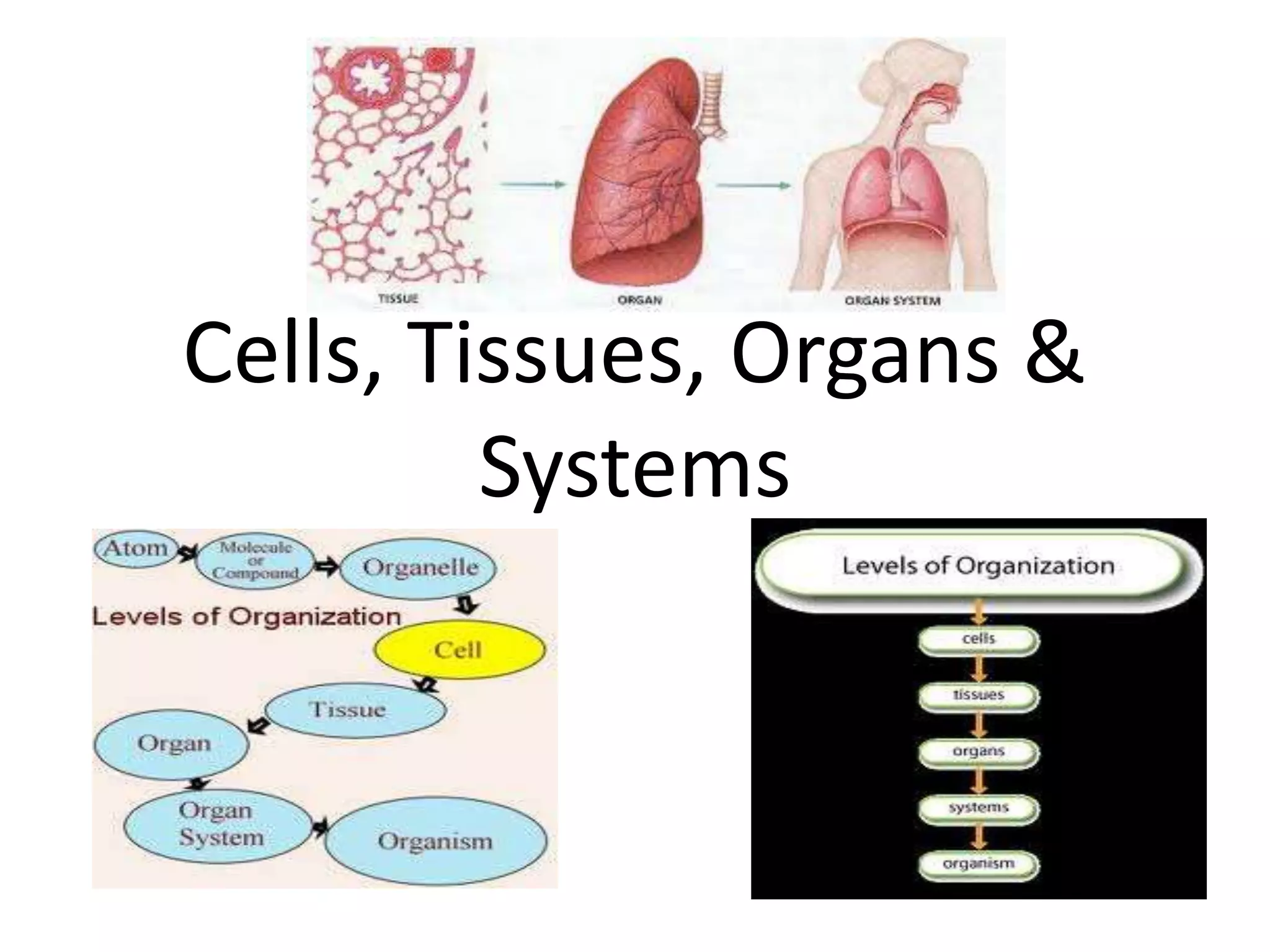
Cells differentiate through gene expression to become specialized cell types like muscle cells, red blood cells, and guard cells. Cells of the same type group together to form tissues like epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. Organs consist of multiple tissue types working together to perform a specific function, like the stomach uses epithelial, blood, and muscle tissues to store, digest food, and allow peristalsis. Systems are groups of interacting organs that work as a unit, such as the digestive system of which the stomach is a part.