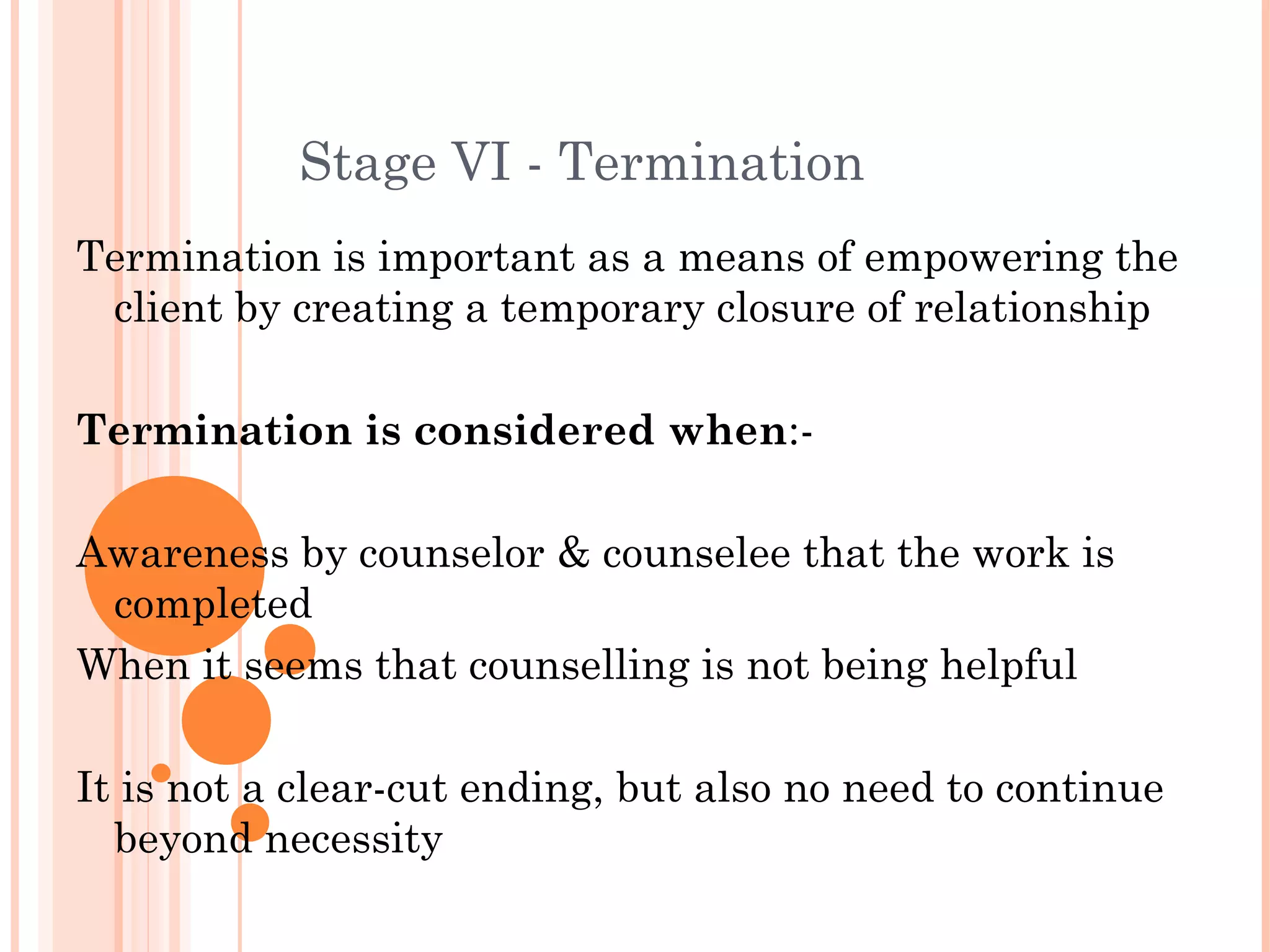
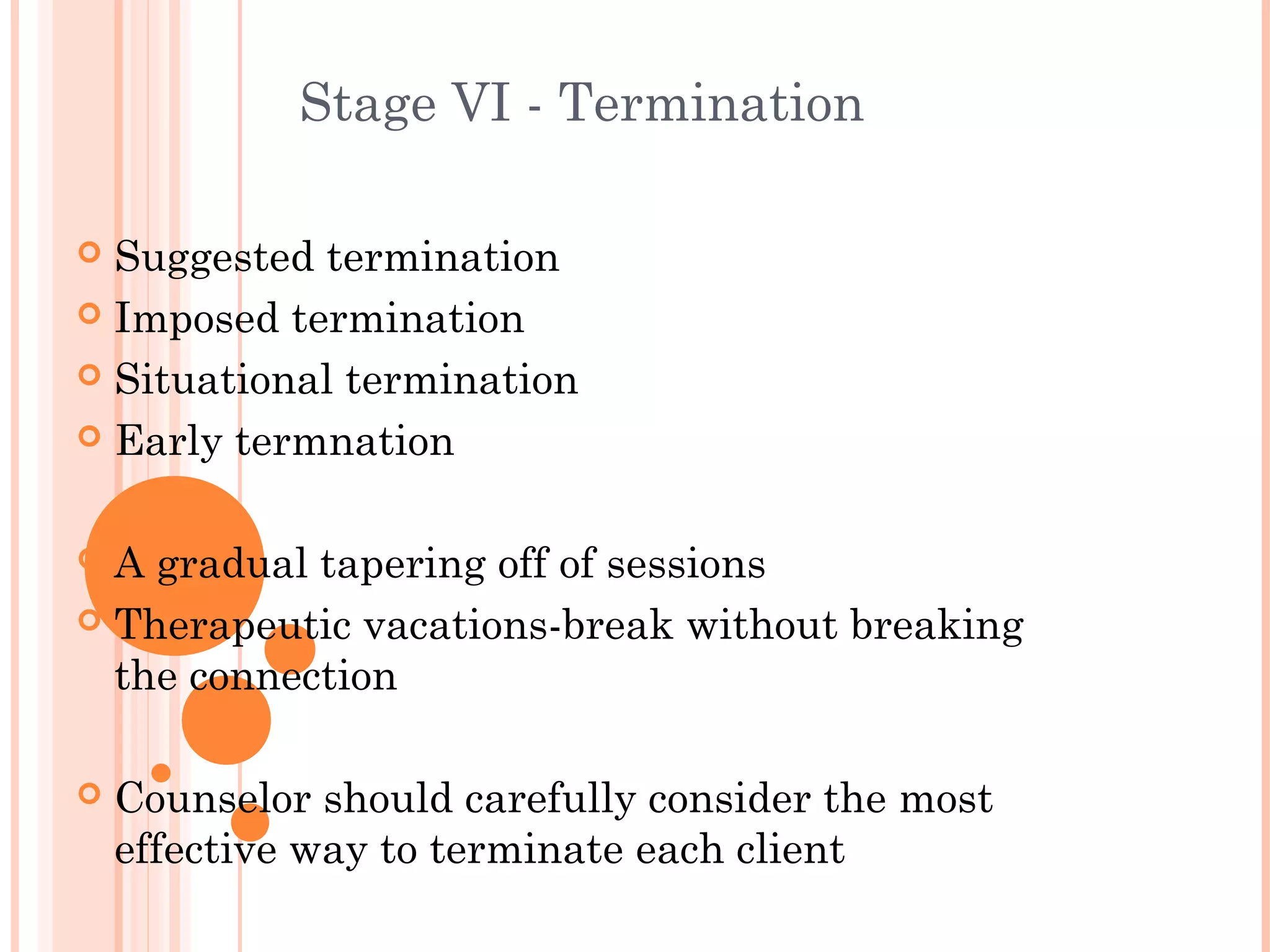
The document outlines the 7 stages of the counselling process: 1) Preparation 2) Pre-counselling session 3) Building rapport 4) Problem definition and goal setting 5) Intervention and problem solving 6) Termination 7) Follow up. It describes the key elements and activities at each stage, including identifying needs, setting goals, implementing action plans, gradually ending sessions, and providing follow up support. The overall aim is to help clients gain a sense of control over their lives by exploring difficulties and developing solutions.