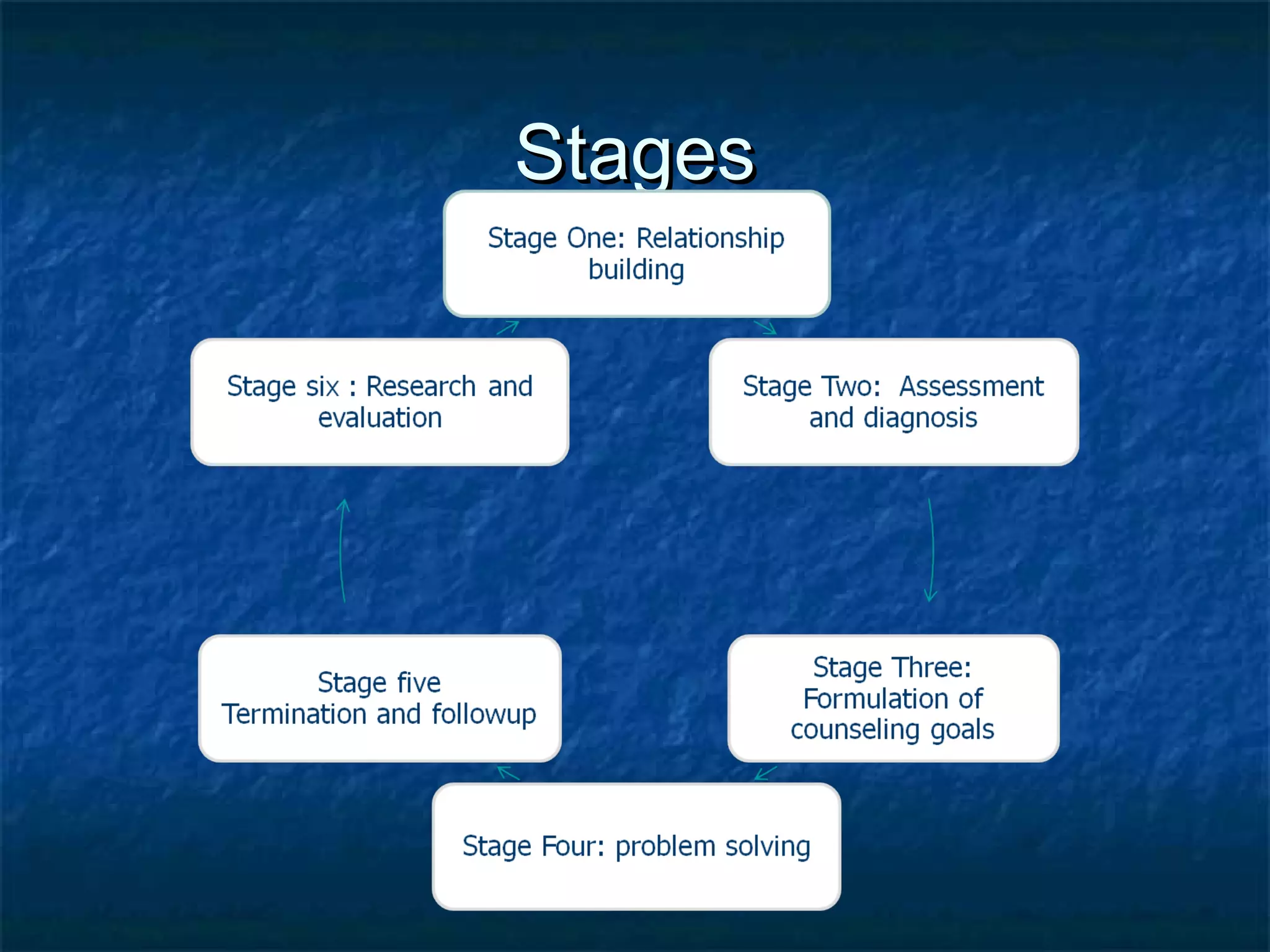
The counseling process involves several stages:
1) Relationship building to establish trust and structure between counselor and client.
2) Assessment and diagnosis where information is gathered about the client's situation and standardized/non-standardized tools are used.
3) Formulation of client goals where the client articulates what they want to achieve in counseling in areas like behavior change, coping, decision-making, or relationships.
4) Problem solving using a treatment plan with clearly defined and achievable goals adapted over time focusing on a positive outcome. Counseling can be directive with the counselor guiding the client, or non-directive with the client driving the process in a supportive environment.