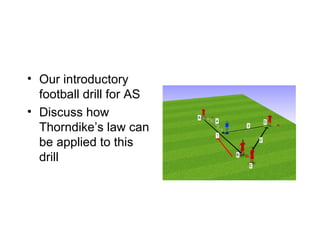
This document discusses several theories relating to learning movement skills:
- Connectionist/associationist theories link a stimulus to a response through reinforcement to strengthen the stimulus-response bond stored in long-term memory.
- Thorndike's laws of effect, exercise, and readiness state that positive reinforcement is most effective for strengthening bonds, which improve with practice when the learner is capable.
- Operant conditioning, based on Skinner's work, also involves strengthening stimulus-response bonds through reinforcement of desired responses shaped through trial and error.
- Cognitive learning theory (Gestalt) focuses on the thinking process of perceiving whole tasks based on past experiences and current knowledge and motivation rather than external stimuli.
- Bandura's