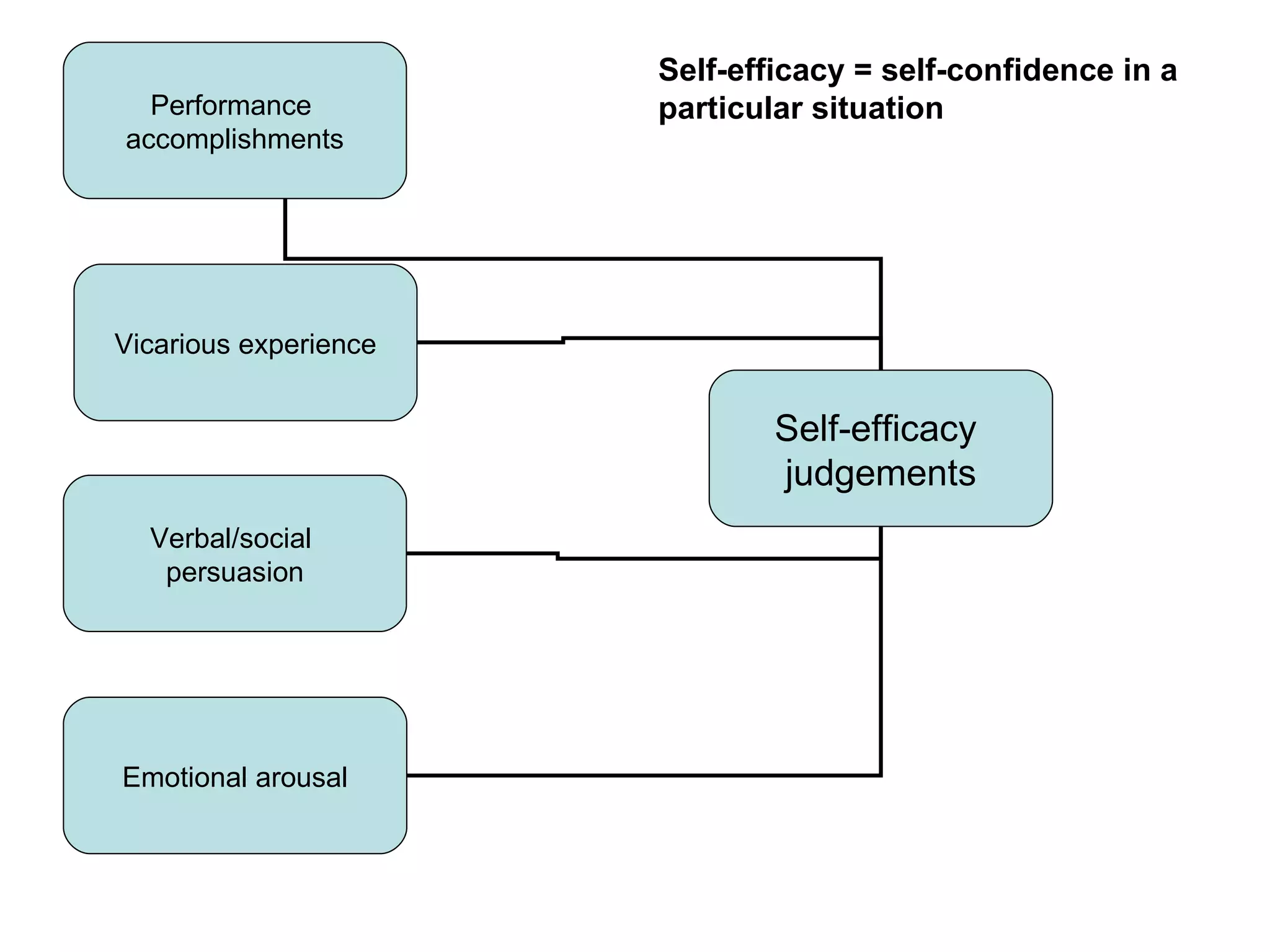
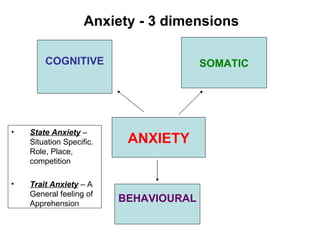
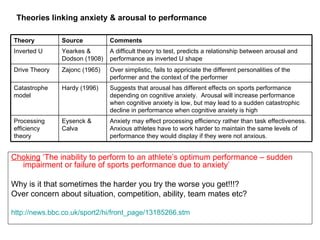
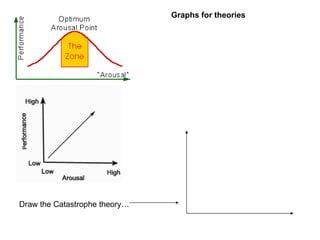
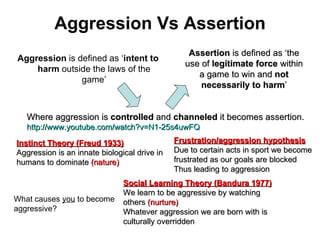
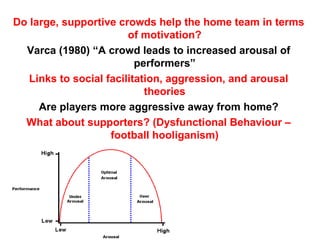
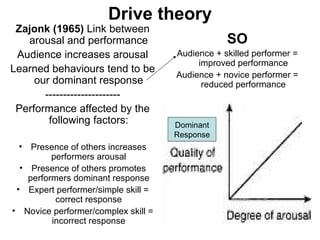
Self-efficacy is influenced by performance accomplishments, vicarious experiences, verbal persuasion, and emotional arousal. Anxiety can be state-specific or a general trait and theories link anxiety levels to an inverted-U relationship with performance. Coaches can help raise self-efficacy through goal setting, imagery, positive self-talk, and simulating competitive situations in practice.