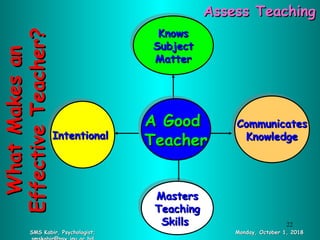
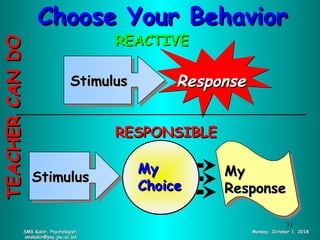
The document discusses the essence of teaching, outlining its processes, purposes, and various methods while emphasizing effective teaching techniques. It highlights the importance of understanding the audience, context, and subject matter for successful teaching and offers strategies for student engagement and assessment. Key points include the significance of lesson planning, effective communication, and fostering a conducive learning environment.