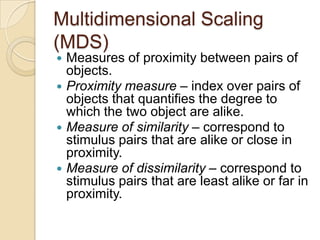
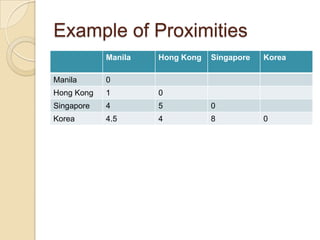
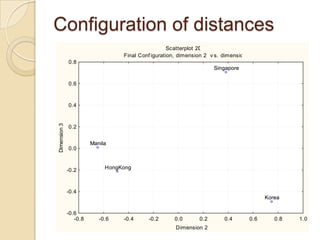
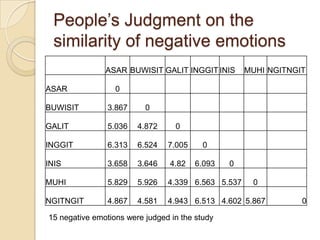
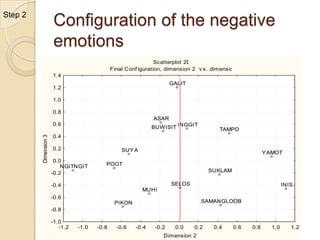
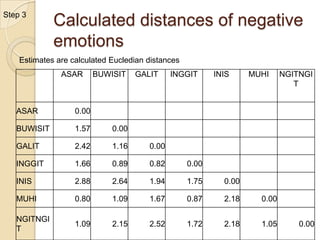
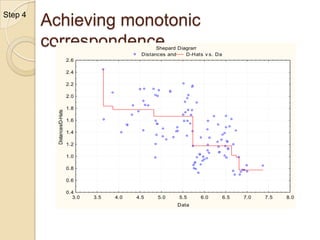
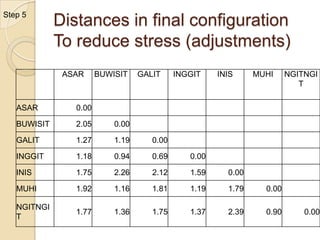
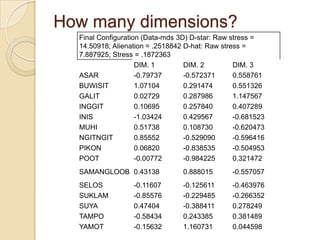
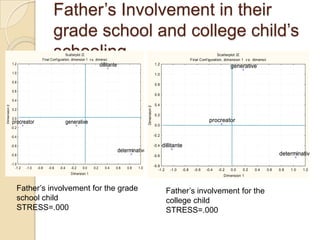
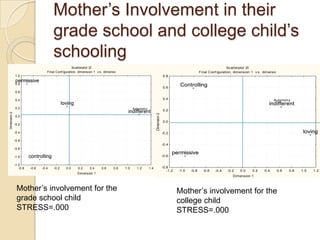
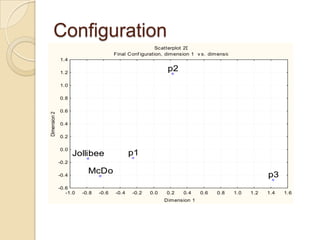
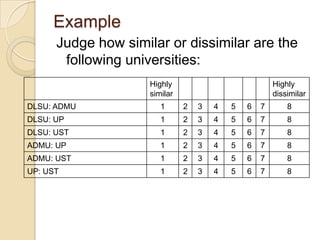
Multidimensional scaling (MDS) is a technique used to analyze proximities or distances between pairs of objects. The goal of MDS is to place objects in a dimensional space such that the distances between objects in that space correspond as closely as possible to the proximities in the original data. There are metric and nonmetric approaches to MDS depending on the level of measurement of the proximities. MDS can be used to visualize perceptions of similarity between objects and allows for further analysis of the dimensional configuration.