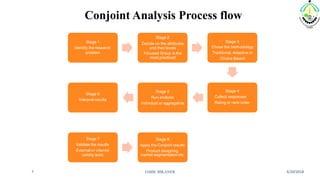
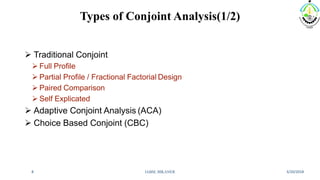
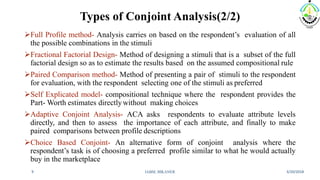
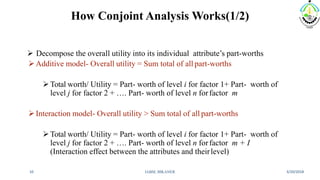
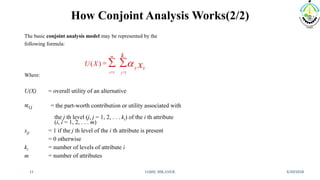
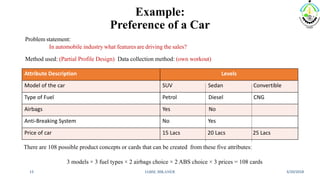
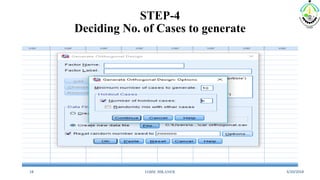
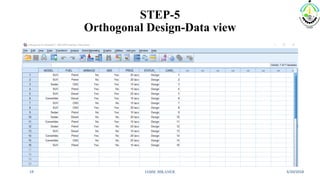
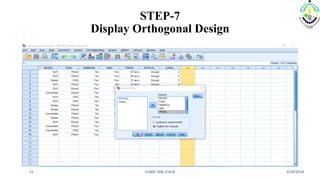
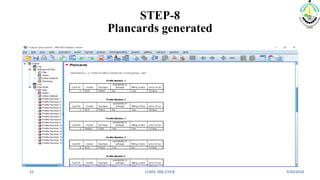
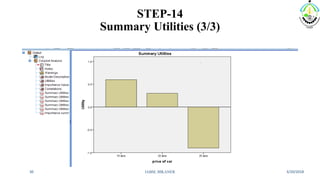
This document discusses conjoint analysis and provides an example using SPSS. It defines conjoint analysis as a technique used to understand how consumers develop preferences for product attributes. The key steps are identified as identifying the problem, attributes and levels, methodology, collecting responses, analysis, interpretation and application. Types include traditional, adaptive choice-based conjoint analysis. An example uses attributes of cars to identify preferred combinations through partial profile surveys and estimating utilities in SPSS. The results show price, fuel type and model have most importance in driving sales.