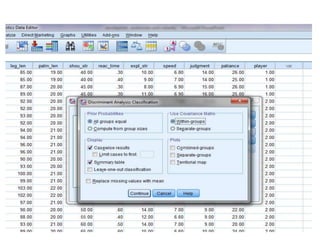
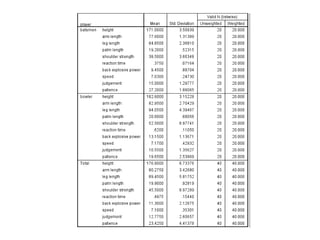
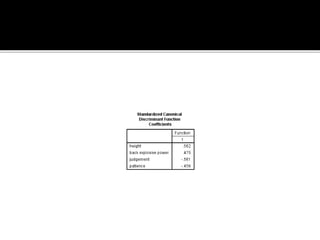
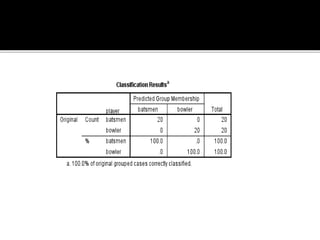
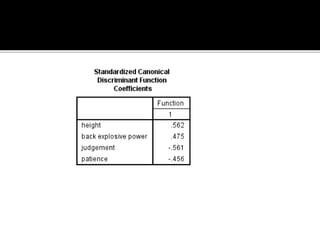
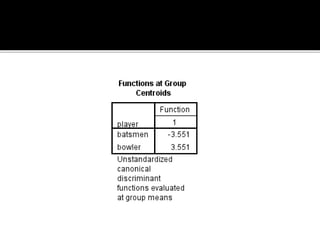
Discriminant analysis is a statistical technique used to classify individuals or cases into groups based on a set of predictor variables. It can be used to determine which variables discriminate between two or more naturally occurring groups and to classify new observations into one of the existing groups. The key steps involve developing a discriminant function using a linear combination of predictors, evaluating the accuracy of classification, and determining the relative importance of predictors in discriminating between groups. Discriminant analysis requires certain assumptions about the data such as normality and equality of group variances to be valid.