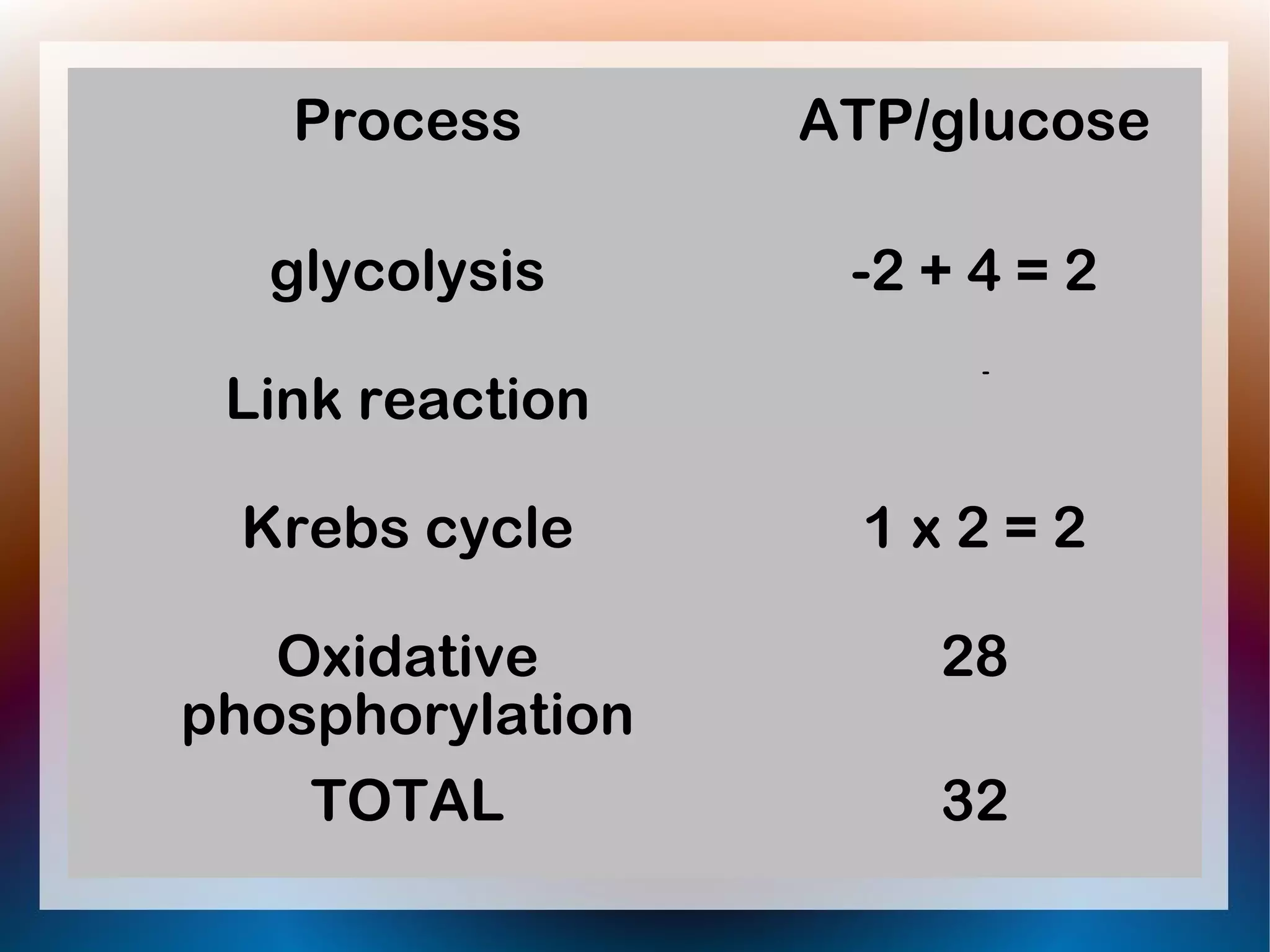
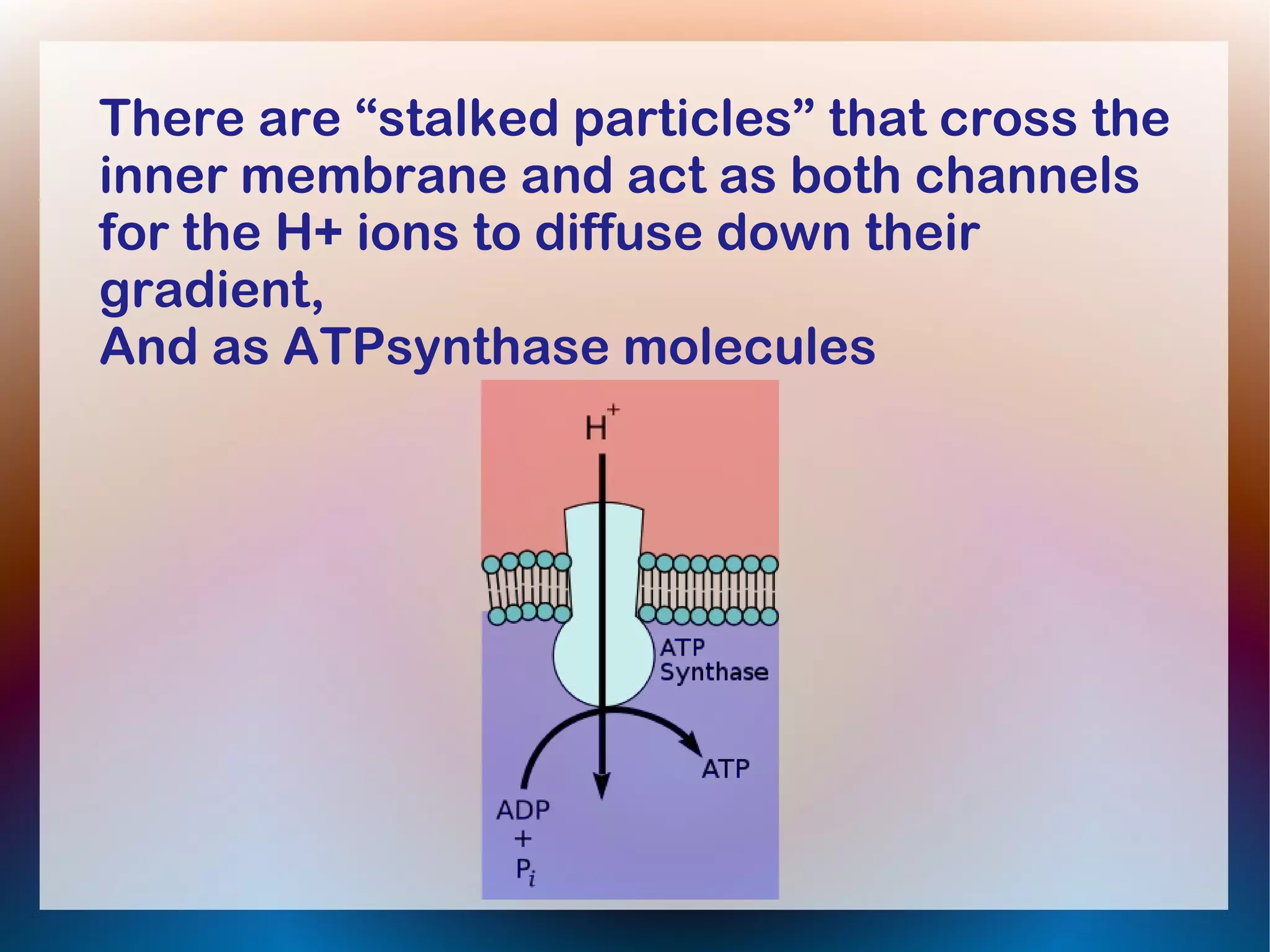
Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane and involves enzymes and carrier proteins that are folded into cristae to increase surface area. Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed along an electron transport chain (ETC), with energy released used to pump hydrogen ions into the intermembrane space. Hydrogen ions diffuse back through ATP synthase enzymes, driving the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP in a process called chemiosmosis. Up to 28-32 molecules of ATP can be generated from each glucose molecule that enters the citric acid cycle through oxidative phosphorylation.