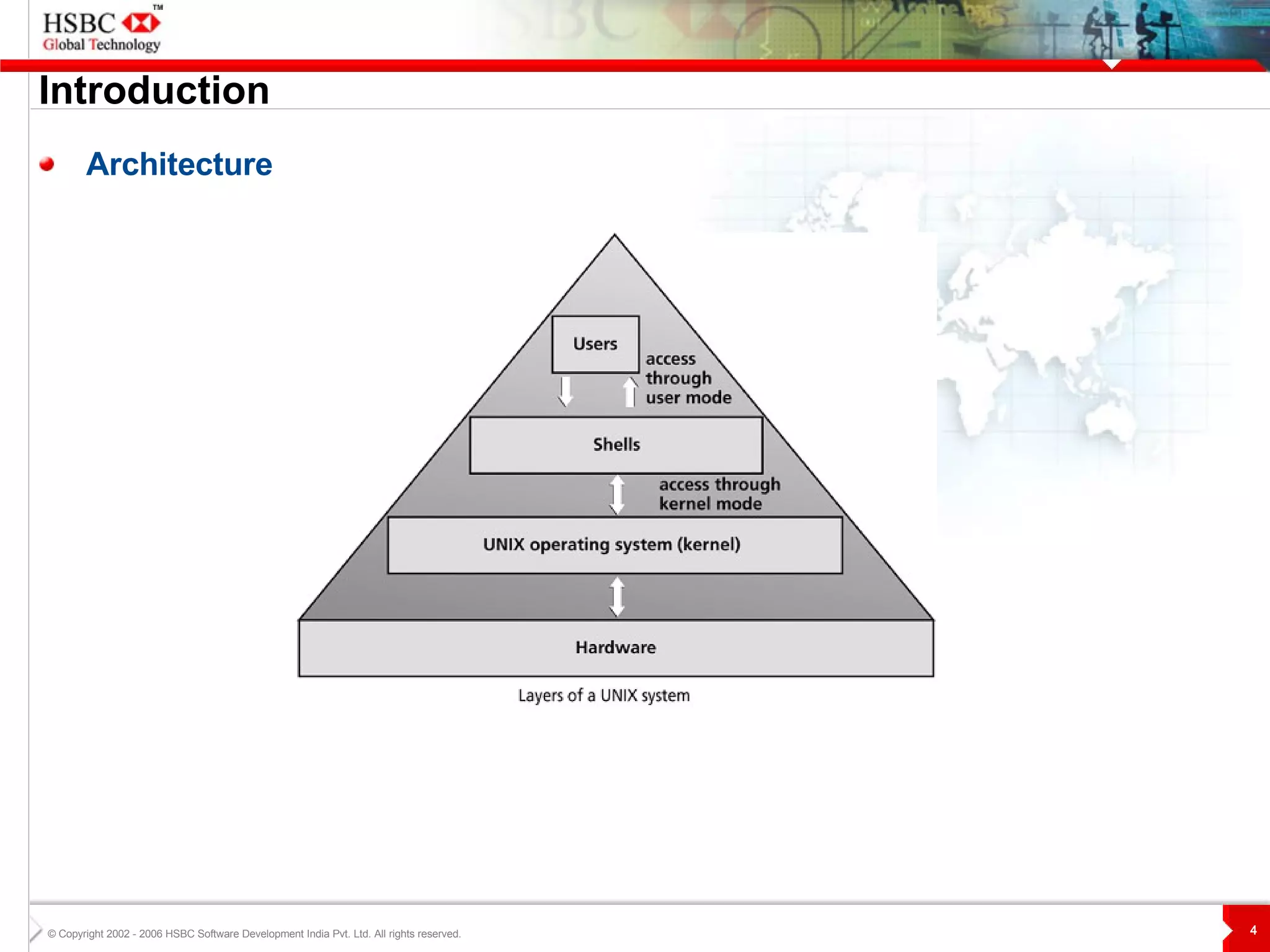
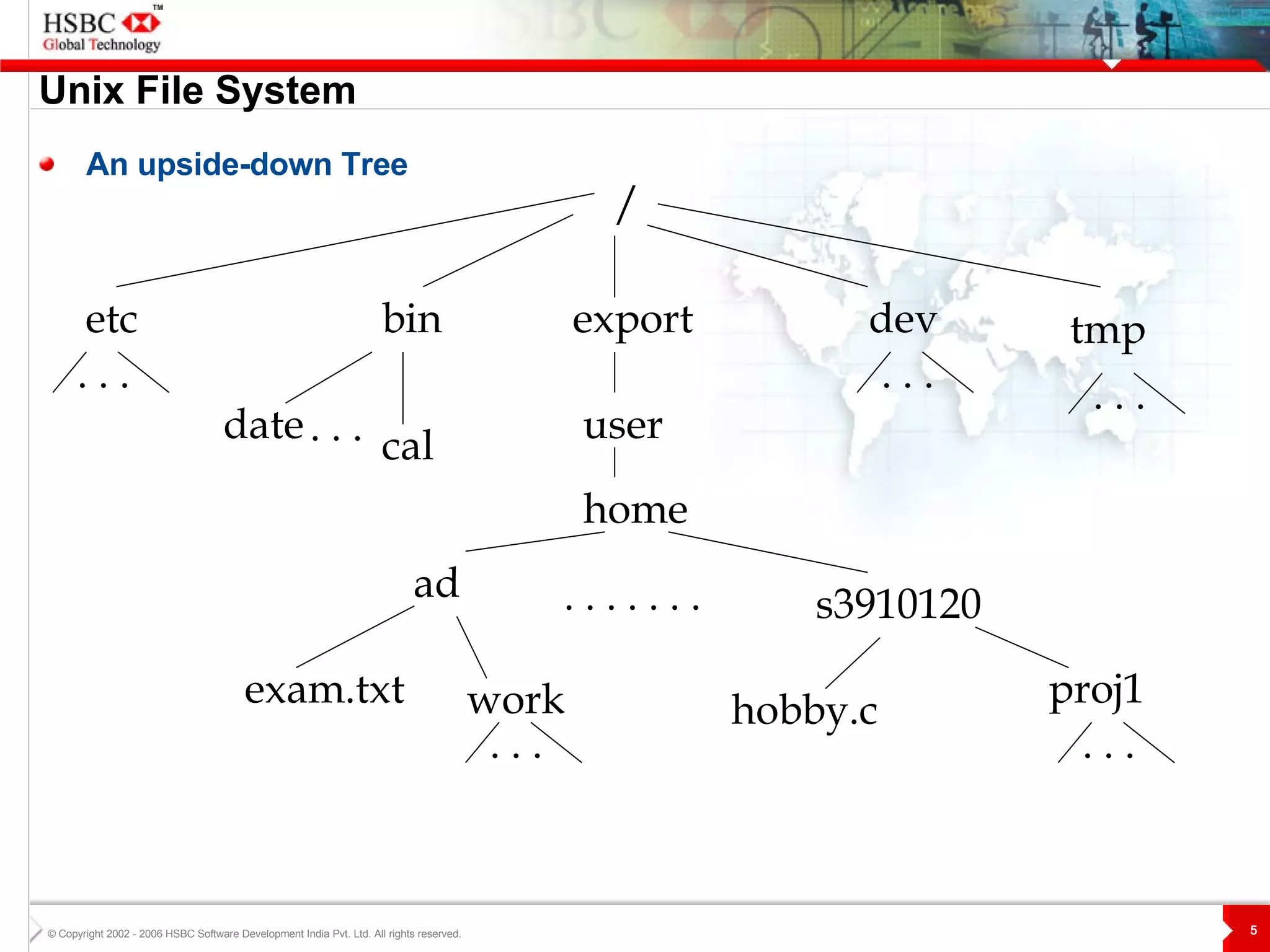
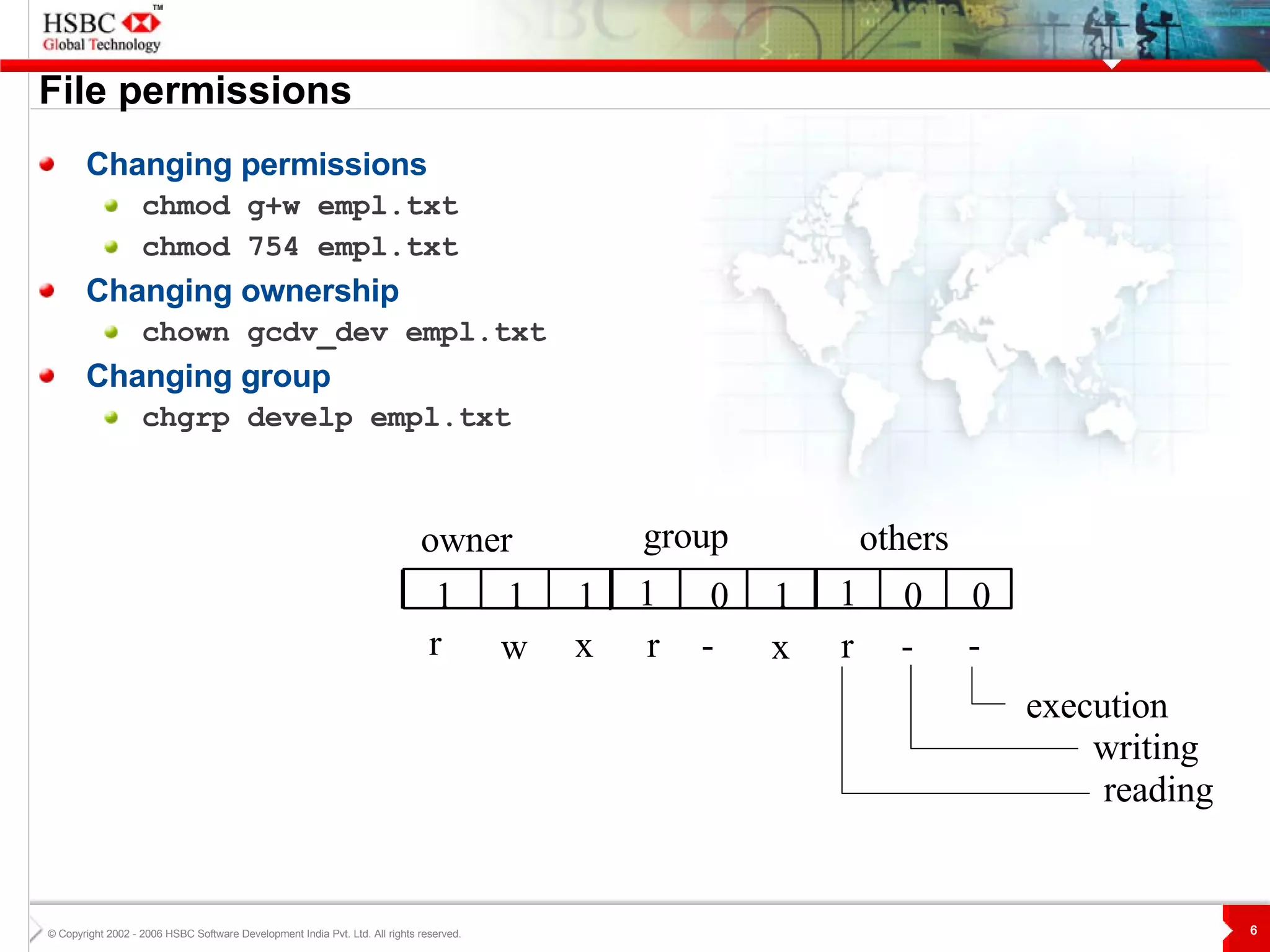
The document discusses various topics related to Unix including the Unix filesystem, file permissions, advanced commands like sort, grep, and tar, shells, shell programming, and AWK. It also includes the speaker's learnings and availability to answer questions.

![Advanced Commands Sort Sorts the contents of a file . sort [-b f n r o t] [file name(s)] Takes the contents of a file(s) and displays it in sorted order. Flags: -b ignores blanks -f change all lower case letter to upper case before comparing -n numeric sort -r reverse usual order -o sends output of command to some file -t field delimiter E.g. To sort the Emp.txt on 2 nd field in reverse order $sort -t, -n -r +2 Emp.txt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unix-1215414593147267-8/75/Unix-7-2048.jpg)
![Advanced Commands grep Searches a file for pattern . grep [-c i l v] <pattern> [file name(s)] Takes the contents of a file(s) and displays it in sorted order. Flags: -c displays count of matching lines. -i ignore the case while searching -l lists the names of files that matches pattern -v displays all lines that don’t contain the pattern E.g. To display all lines in the ‘Emp.txt’ that match either the abc or xyz string: $grep "abc|xyz" Emp.txt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unix-1215414593147267-8/75/Unix-8-2048.jpg)
![Advanced Commands tar Compression and decompression of files. tar -(x|c) [ v f r] <tarfile> [file name(s)] Flags: -x extract from file. -c create new extract file. -v displays list files -f name of file follows -r append to old extract. E.g . To compress file Emp.txt $tar -cvf Emp.tar Emp.txt To decompress file Emp.tar $tar -xvf Emp.tar](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unix-1215414593147267-8/75/Unix-9-2048.jpg)







![UNIX S hell Programming if-then and if-then-else The if-then Construct if [ condition ] then true-commands f i The if-then-else Construct if [ condition ] then true-commands else false-command(s) fi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unix-1215414593147267-8/75/Unix-21-2048.jpg)
![UNIX S hell Programming if-then-elif if [ condition1 ] then commands_1 elif [ condition2 ] then commands_2 else commands_n fi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unix-1215414593147267-8/75/Unix-22-2048.jpg)
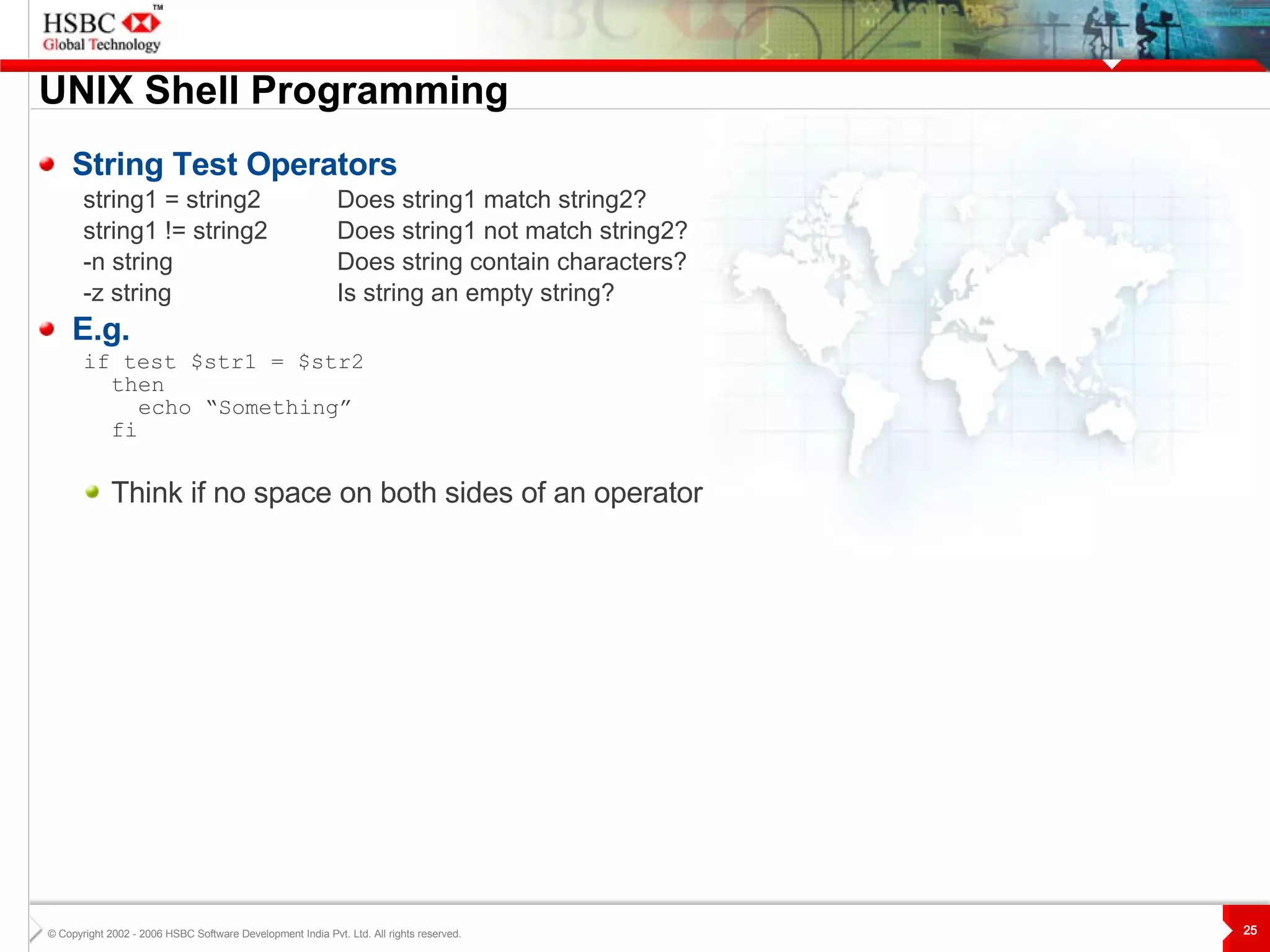
![UNIX S hell Programming test Command The test command is a built-in shell command that evaluates the expression given to it as an argument and return true if the expression is true, if otherwise, false. You can use square brackets ( [ ] ) instead of the word test. Example if test $str1 = $str2 then echo “Something” fi if [$str1 = $str2] then echo “Something” fi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unix-1215414593147267-8/75/Unix-23-2048.jpg)

![UNIX S hell Programming File Test Operators -s file True if File size is greater than 0 -f file True if File exists & not a directory -d file True if file exists & is a directory file. -r file True if file exists & you have read permission on it. -w file True if file exists & you have write permission on it. -x file True if file exists & you have execute permission on it. E.g if [ –f $filename ] then echo “Something” fi Think if no space on both sides of an option.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unix-1215414593147267-8/75/Unix-26-2048.jpg)

![UNIX S hell Programming While Loop while [ condition ] do command(s) done For Loop for variable in list-of-value do command(s) done](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unix-1215414593147267-8/75/Unix-28-2048.jpg)