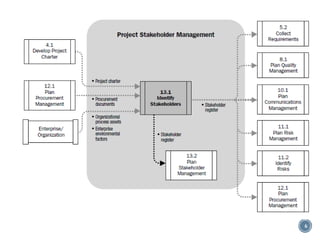
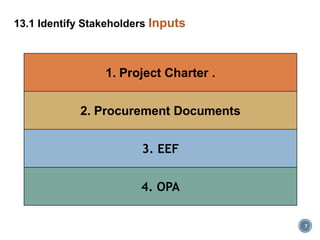
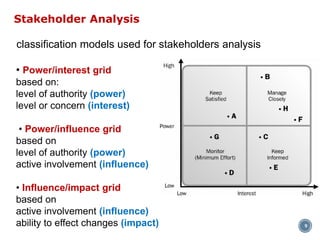
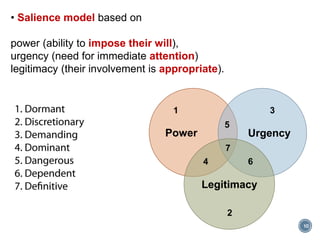
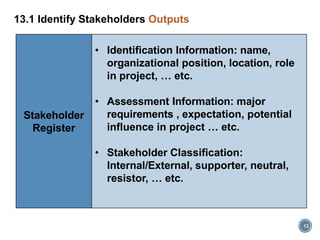
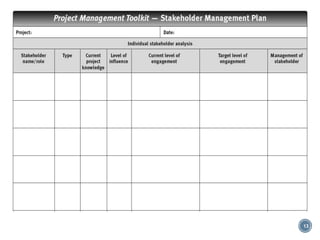
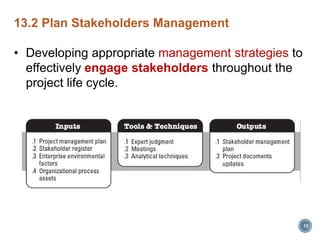
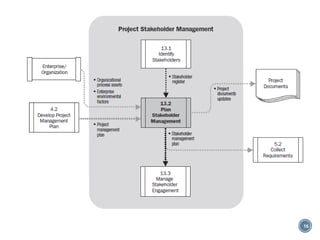
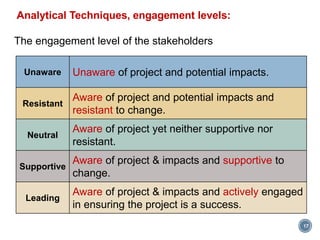
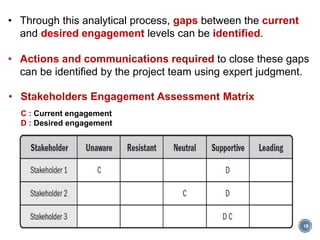
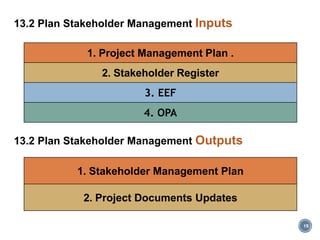
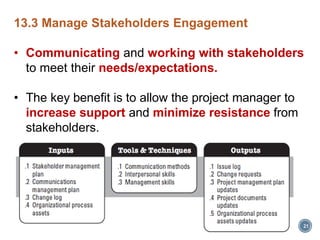
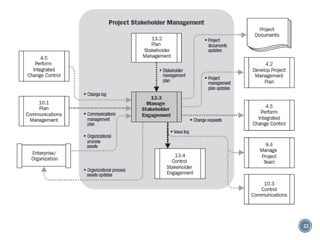
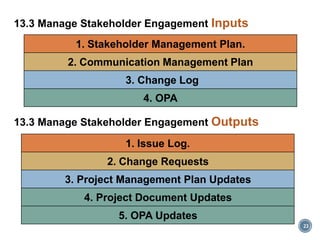
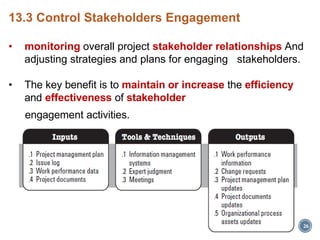
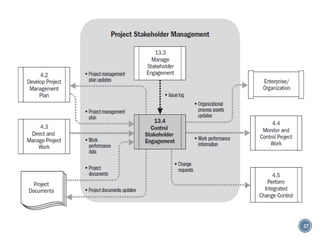
This document discusses project stakeholder management. It covers identifying stakeholders, planning stakeholder management, managing stakeholder engagement, and controlling stakeholder engagement. Stakeholders are identified using stakeholder analysis and expert judgement. A stakeholder register is created. The stakeholder management plan involves assessing current and desired engagement levels to identify gaps. Managing engagement involves communicating with stakeholders and working to meet their needs using various communication methods and interpersonal/management skills. Controlling engagement monitors relationships and makes adjustments to plans.