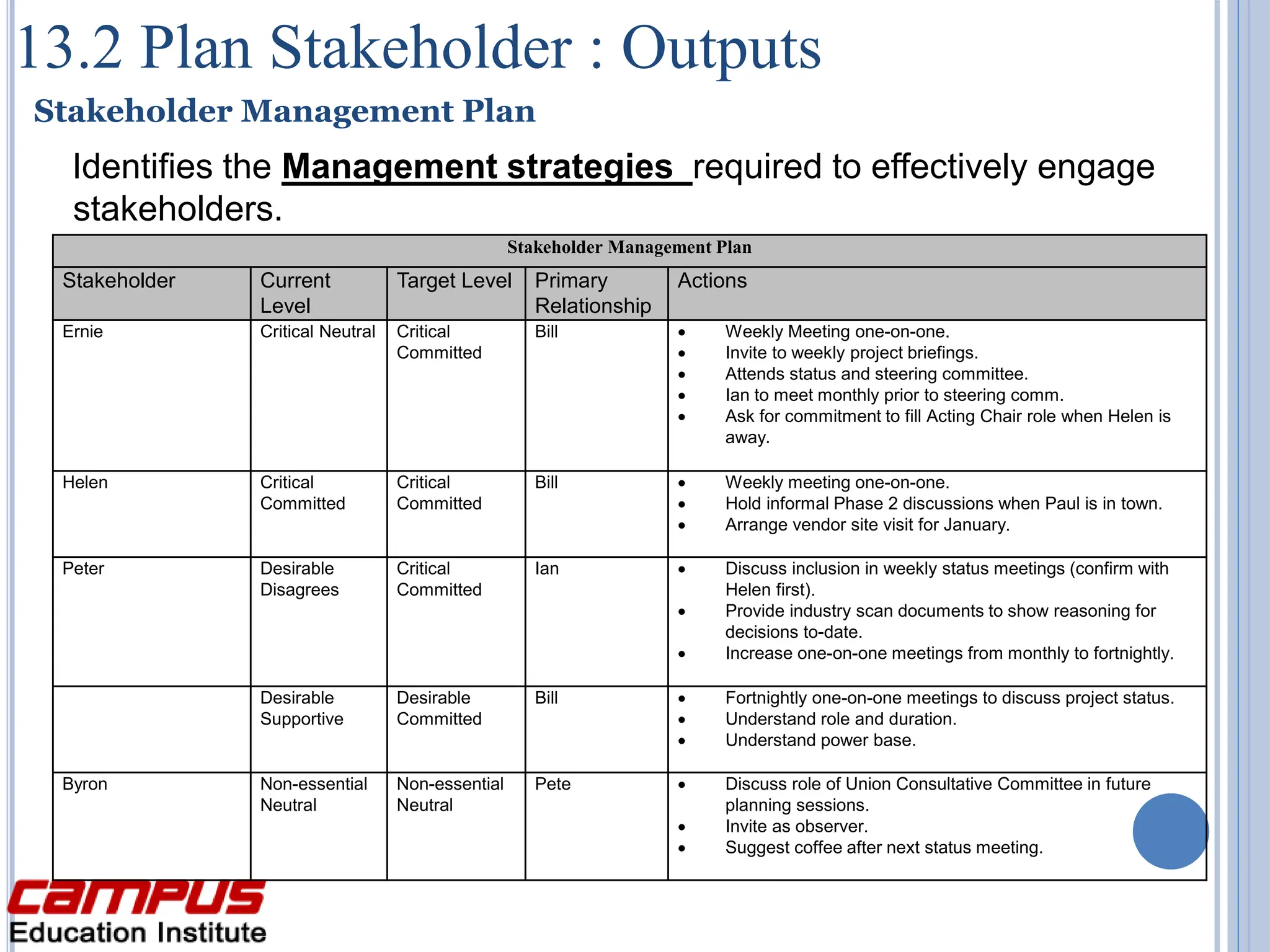
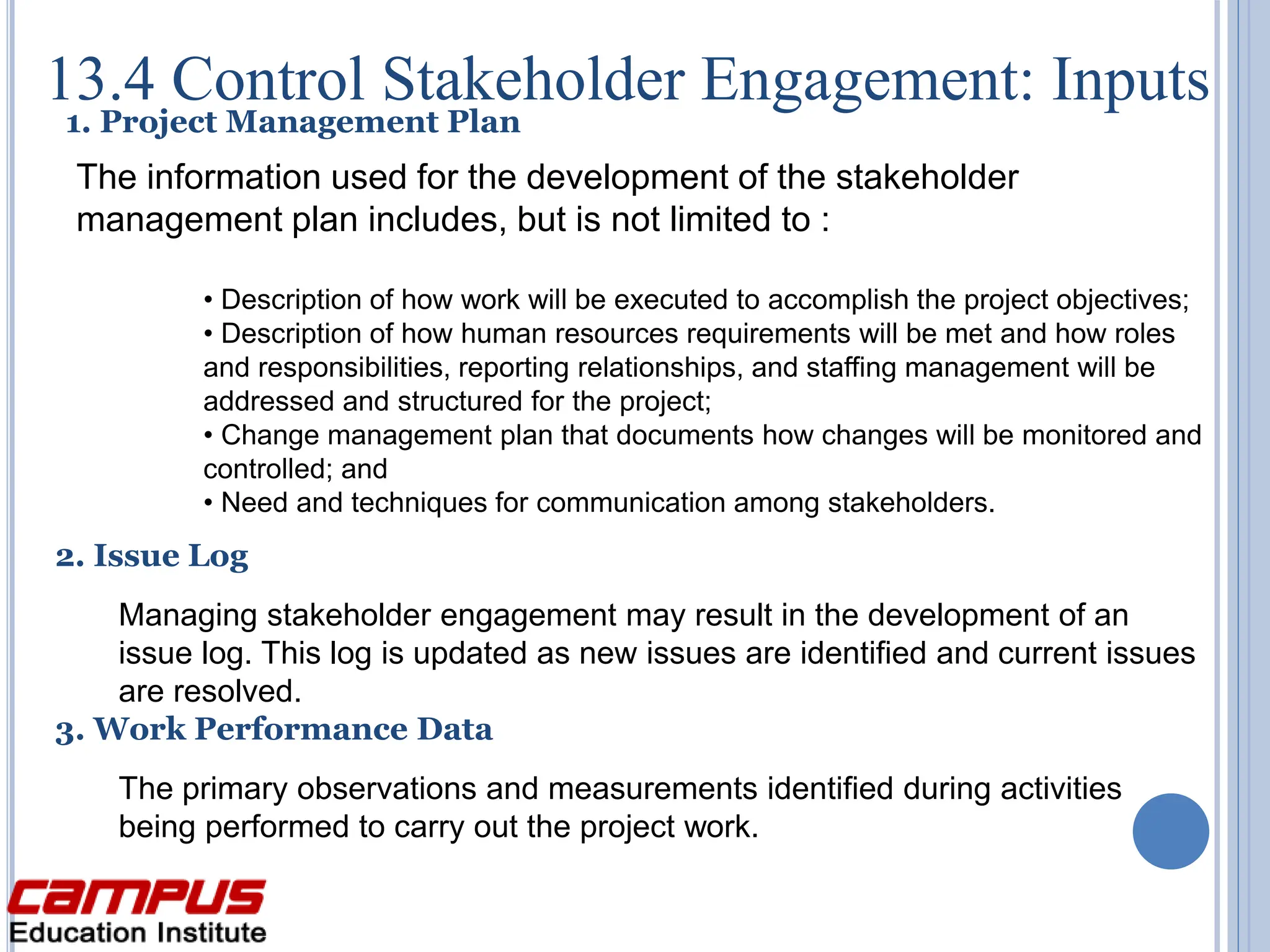
The document discusses stakeholder management in projects. It describes the four key processes:
1) Identify Stakeholders - Involves identifying people impacted by the project and documenting relevant information about their interests and potential impact.
2) Plan Stakeholder Management - Develop strategies to engage stakeholders based on analyzing their needs and interests.
3) Manage Stakeholder Engagement - Communicate with and work with stakeholders to meet expectations, address issues, and ensure engagement throughout the project.
4) Control Stakeholder Engagement - Monitor stakeholder relationships and adjust engagement strategies and plans as needed. Effective stakeholder management is critical to project success.