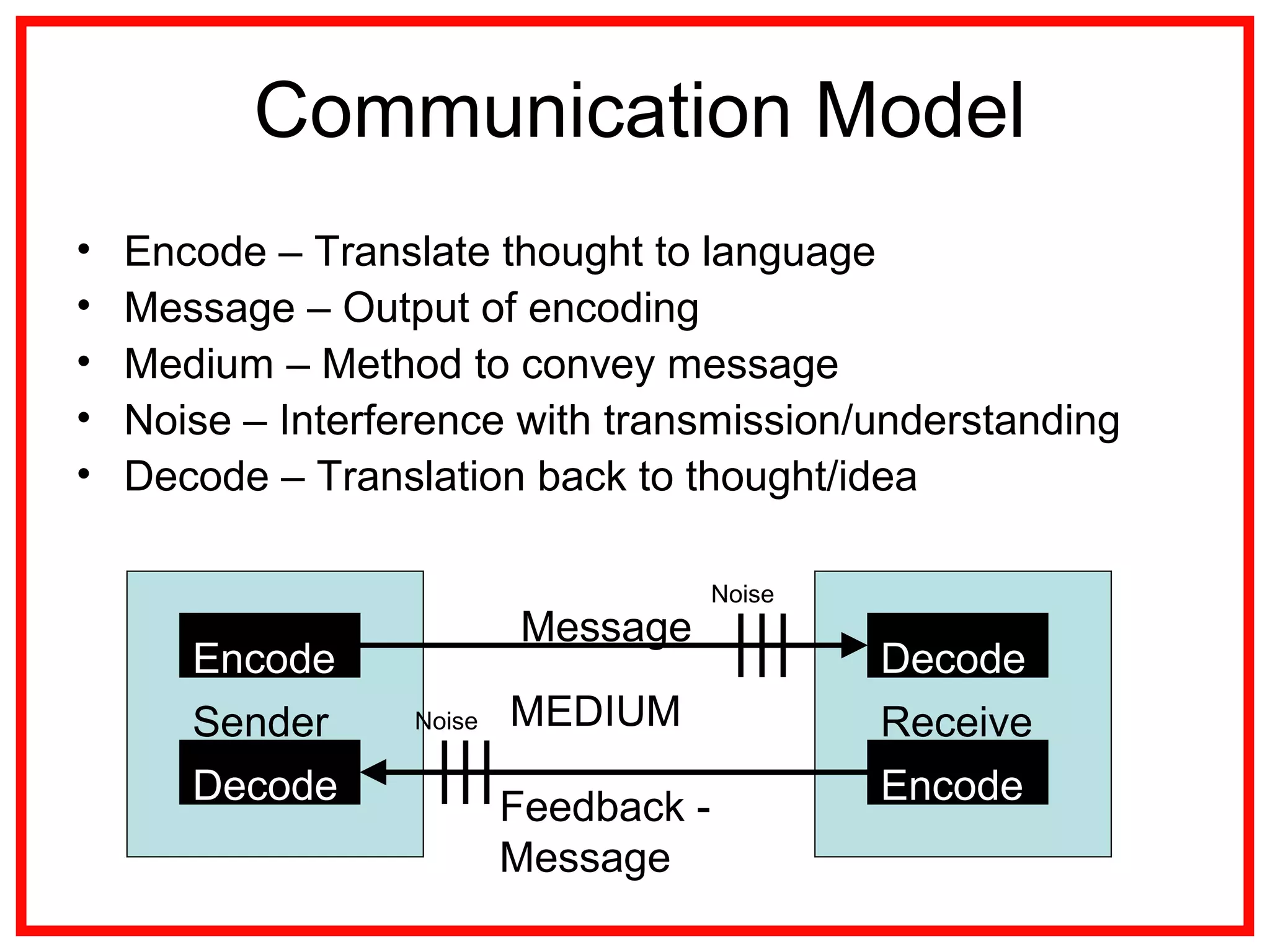
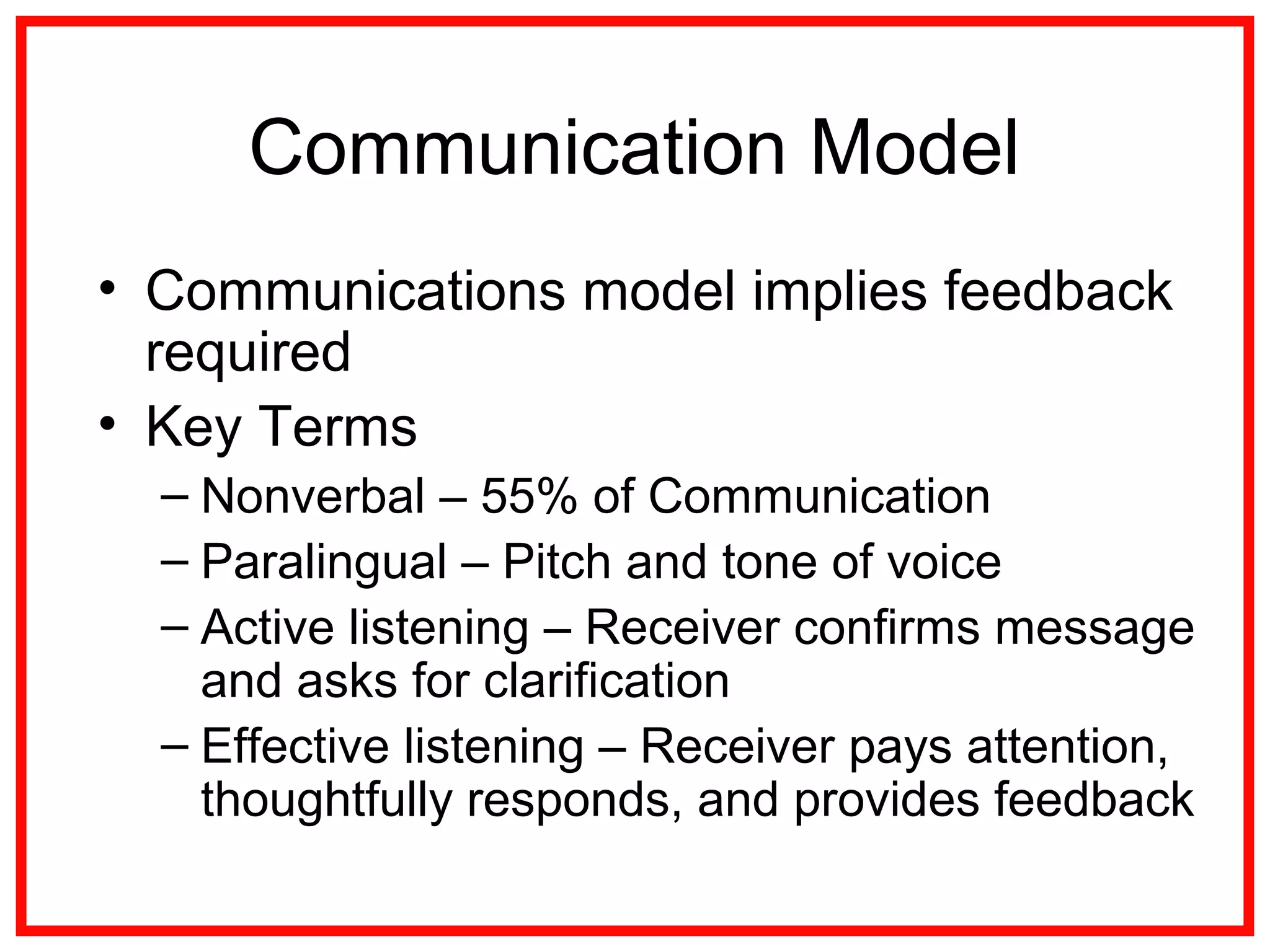
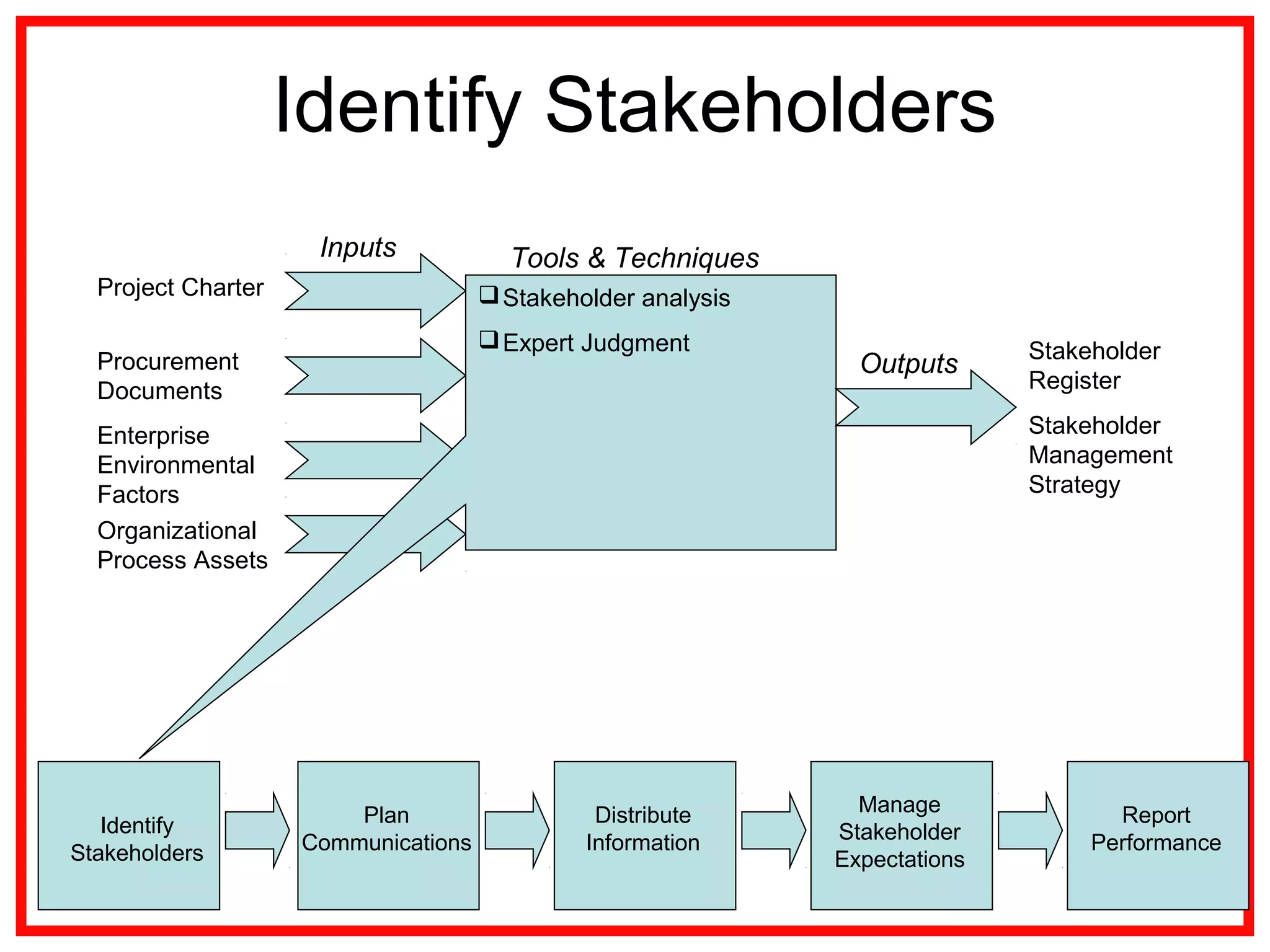
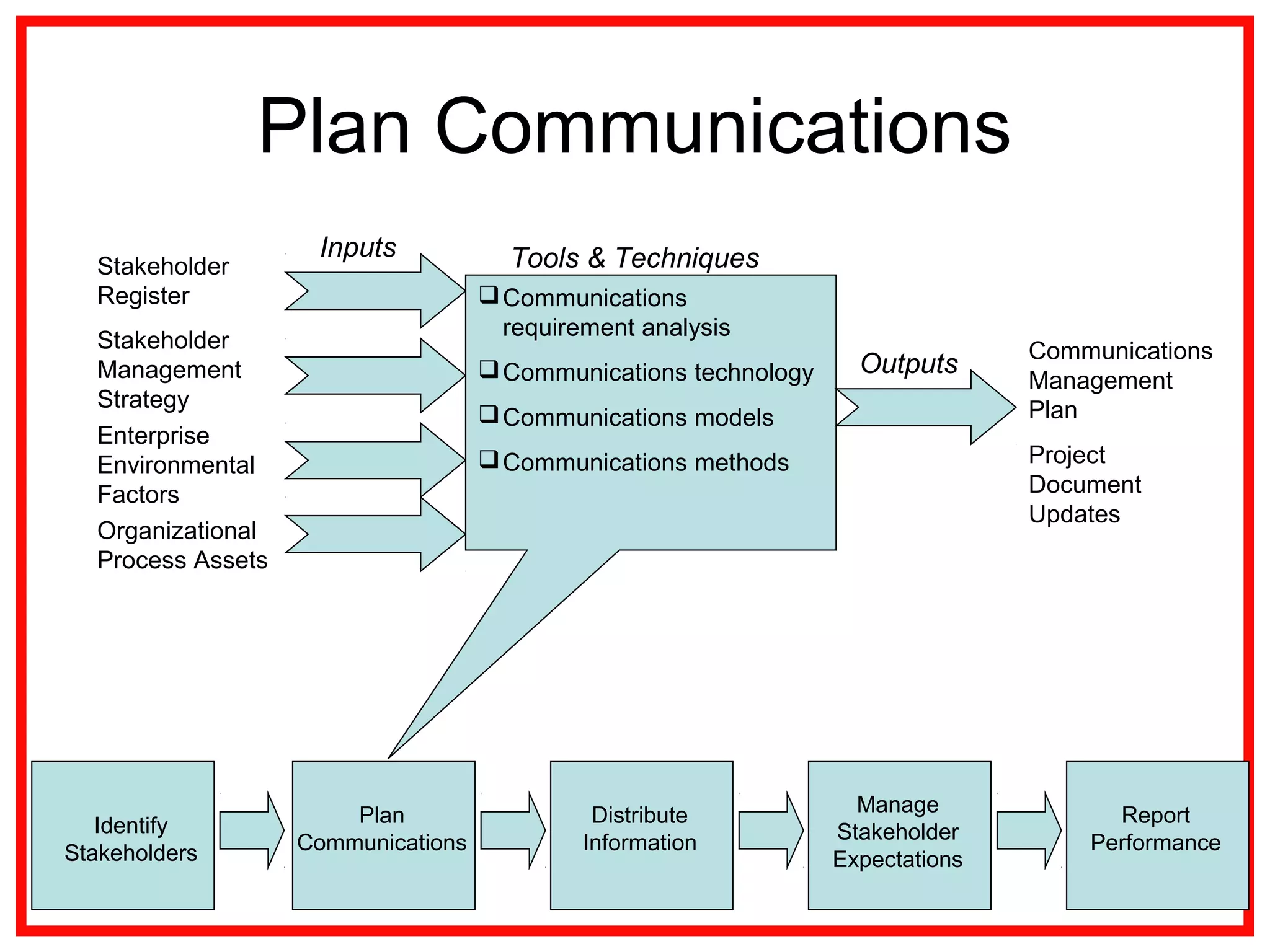
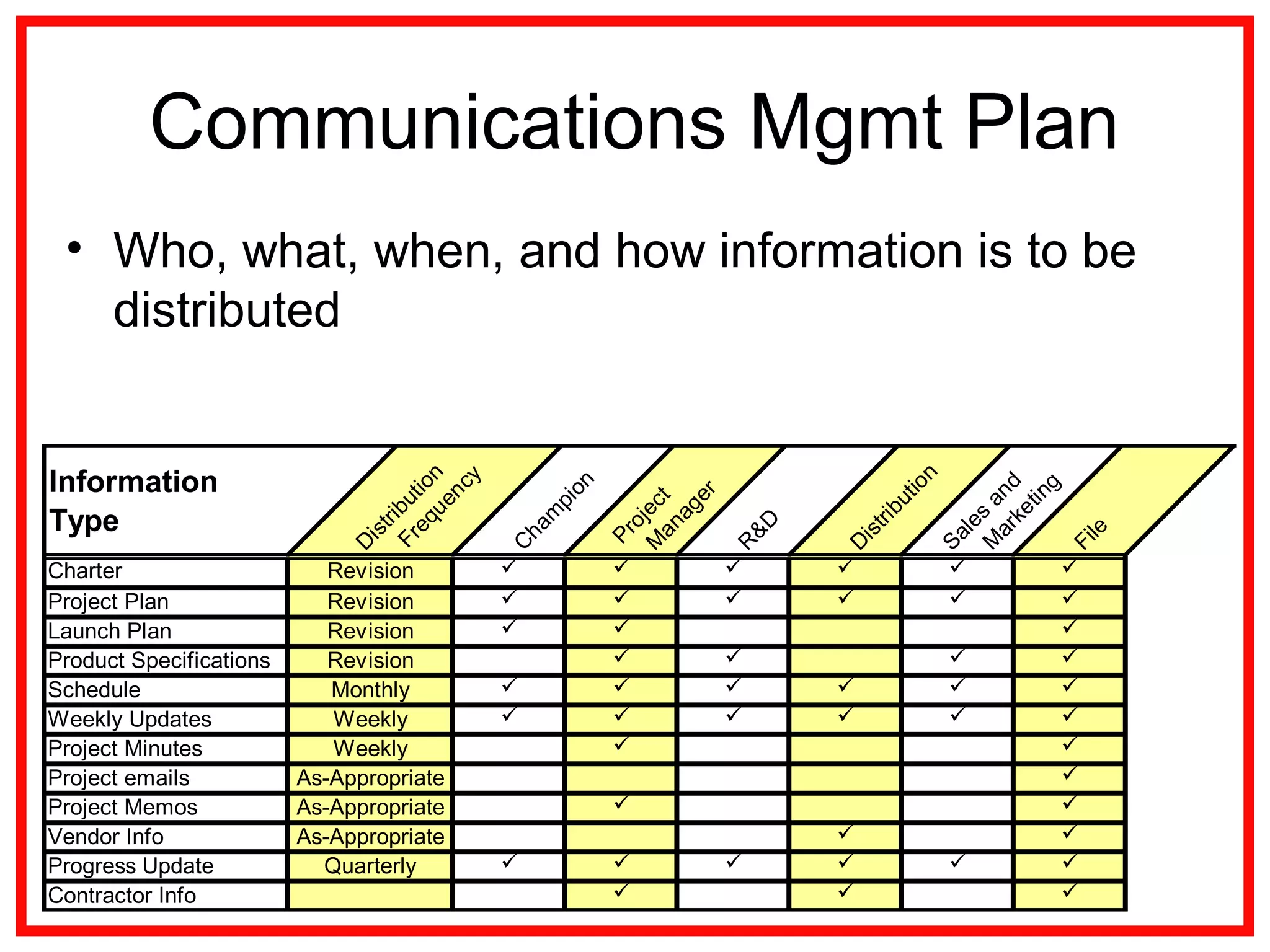
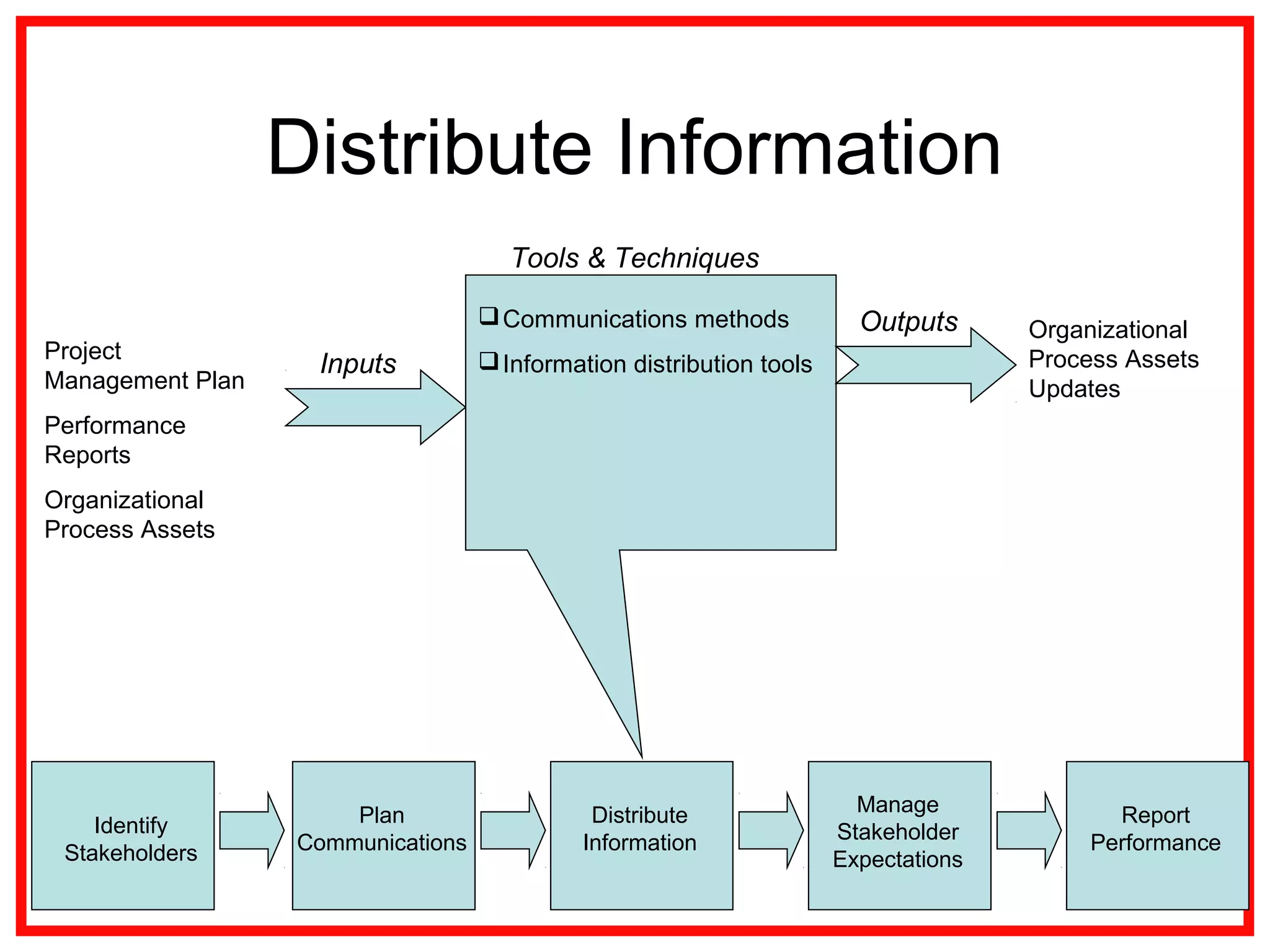
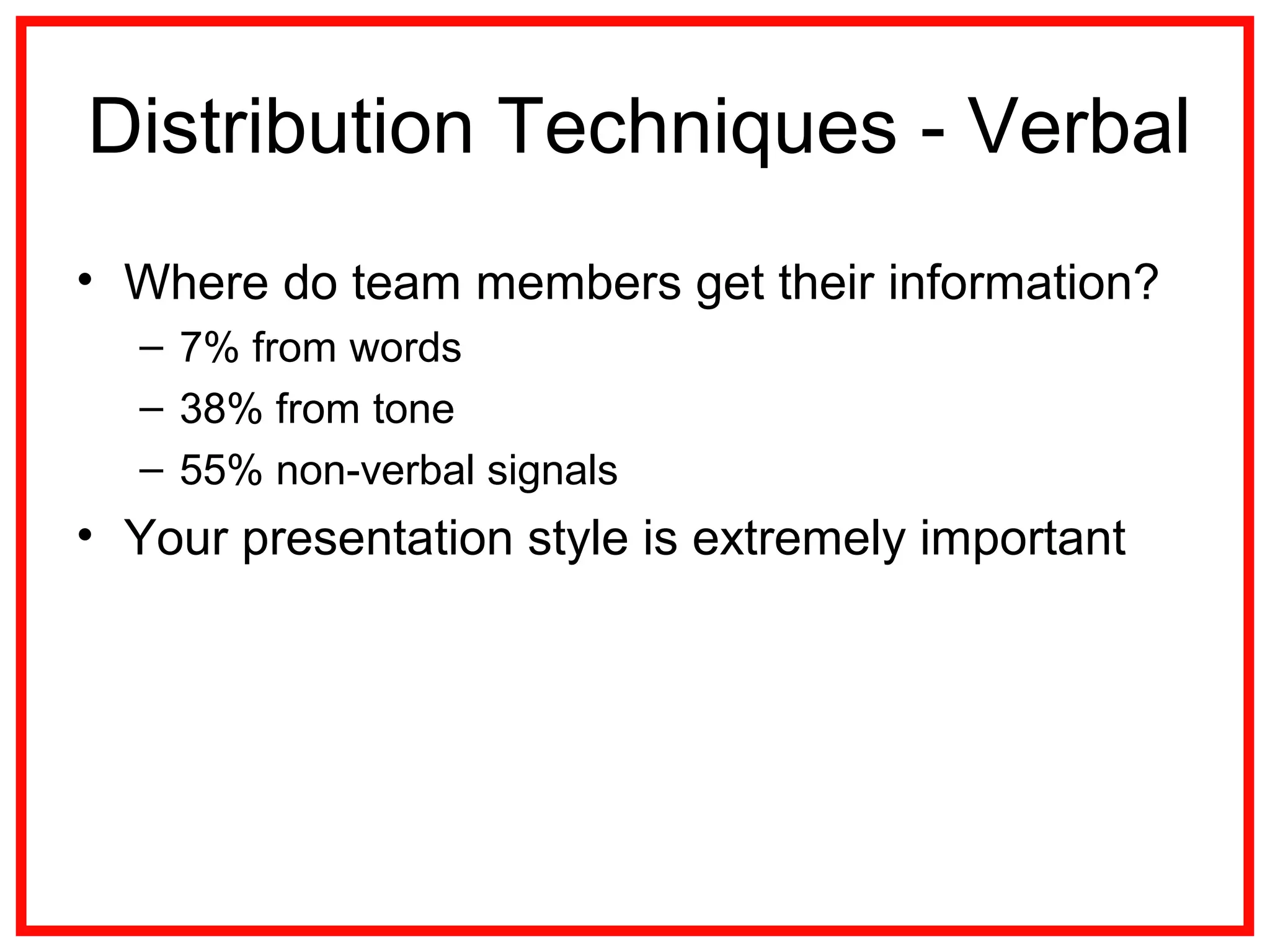
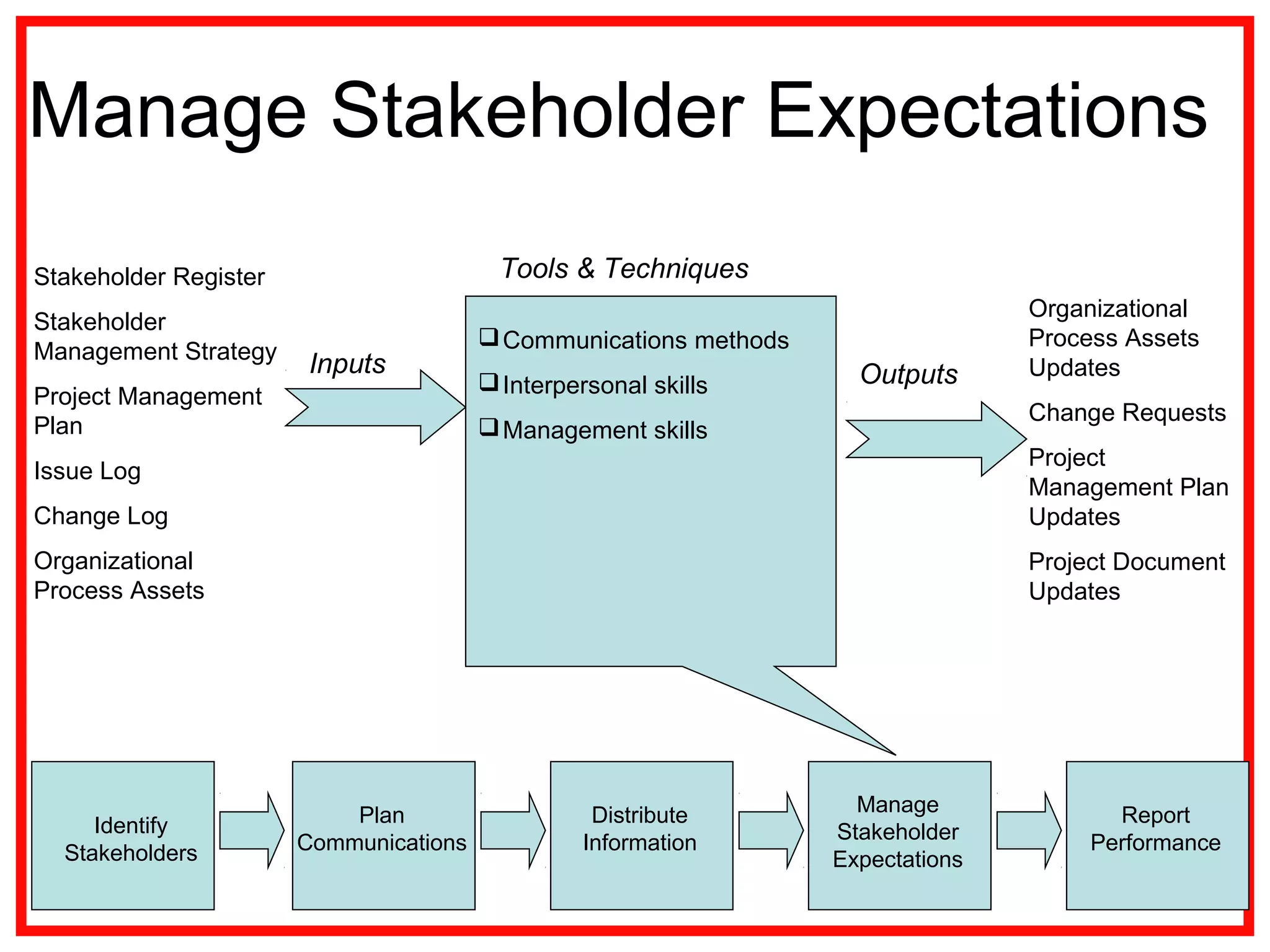
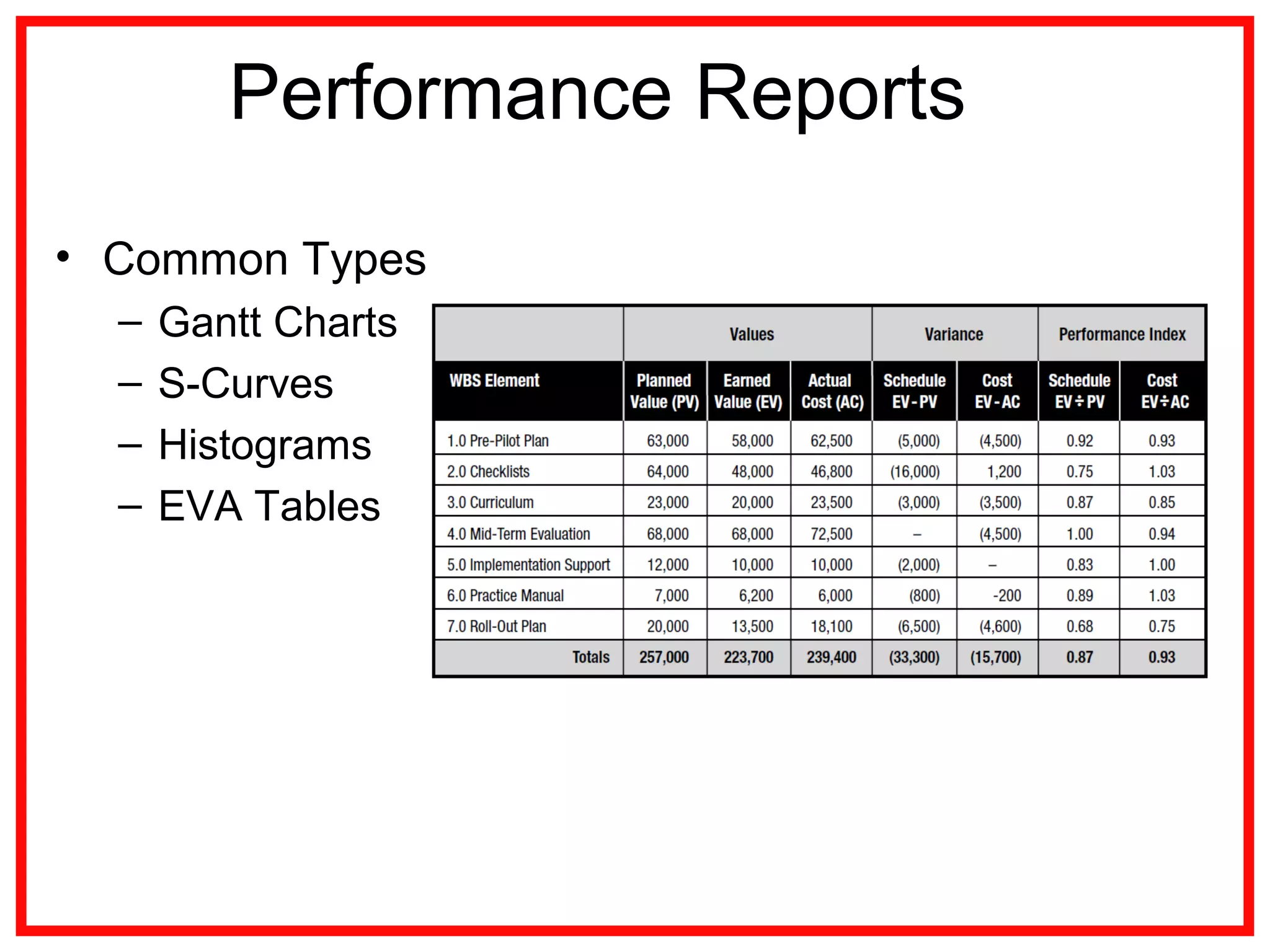
Project communications management involves identifying stakeholders, planning communications, distributing information, managing stakeholder expectations, and reporting performance. Effective communication is key, as project managers spend most of their time communicating. The communication process includes encoding messages, transmitting messages through a medium which can include noise, and decoding the message. Planning communications involves analyzing requirements, selecting communication methods and models. Information is then distributed according to the plan using various written and verbal techniques. Stakeholder expectations are managed through applying communication and interpersonal skills. Performance is reported using tools like Gantt charts and S-curves.