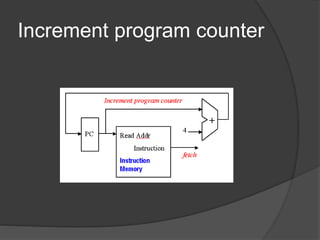
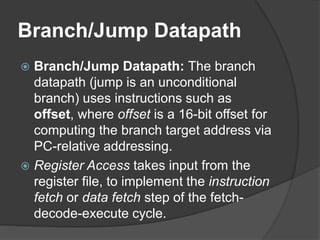
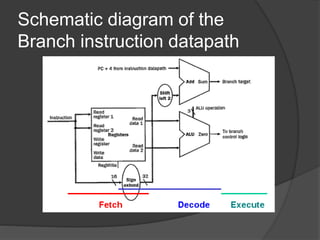
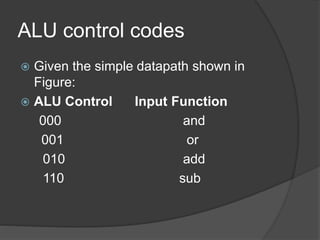
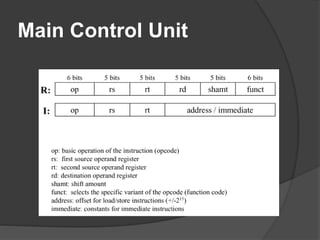
A datapath is a collection of functional units like ALUs and registers that perform data processing along with a control unit to form the CPU. There are three general steps to datapath design: 1) determine instruction classes, 2) design components for each class, and 3) combine the components. Common datapaths include load/store which uses memory addressing and branch/jump which uses instruction addressing. The ALU performs operations like addition and subtraction. The main control unit identifies instruction fields and controls the datapath. Multiplication can be done with combinational or sequential circuits while division similarly uses subtraction and shifting. Floating point uses separate exponent and mantissa fields.