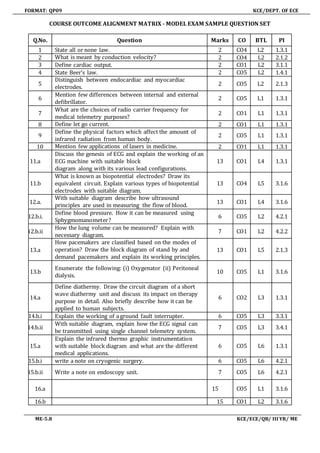
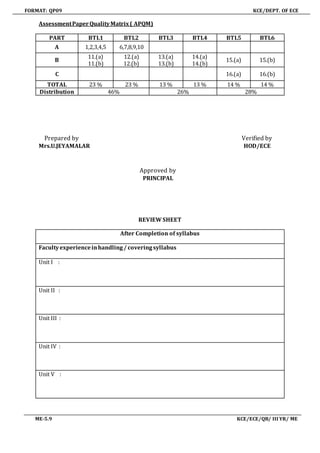
This document contains information related to the course plan and syllabus for Medical Electronics, a third year subject taught in the Electronics and Communication Engineering department.
It includes 5 units covering topics like electrophysiology, biopotential recording, measurement of biochemical and non-electrical parameters, assist devices, physical medicine, and recent trends. Assessment details are provided along with the teaching methodology, references, and web resources for each topic. Course outcomes are listed, ensuring students will understand physiological parameters, measurement techniques, various medical devices, and recent advances.