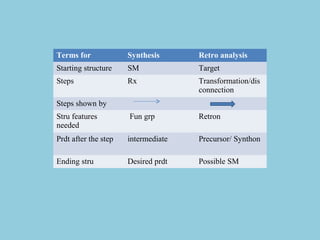
This document discusses retrosynthetic analysis and disconnection strategies for planning the synthesis of drug molecules. It defines key terms like retrosynthesis, synthons, and functional group interconversions. It provides guidelines for disconnecting different types of bonds and functional groups in a molecule, including C-X, C-C, and multiple bonds/groups. The goal is to break down the target molecule into stable and readily available starting materials by applying principles of retrosynthetic analysis.