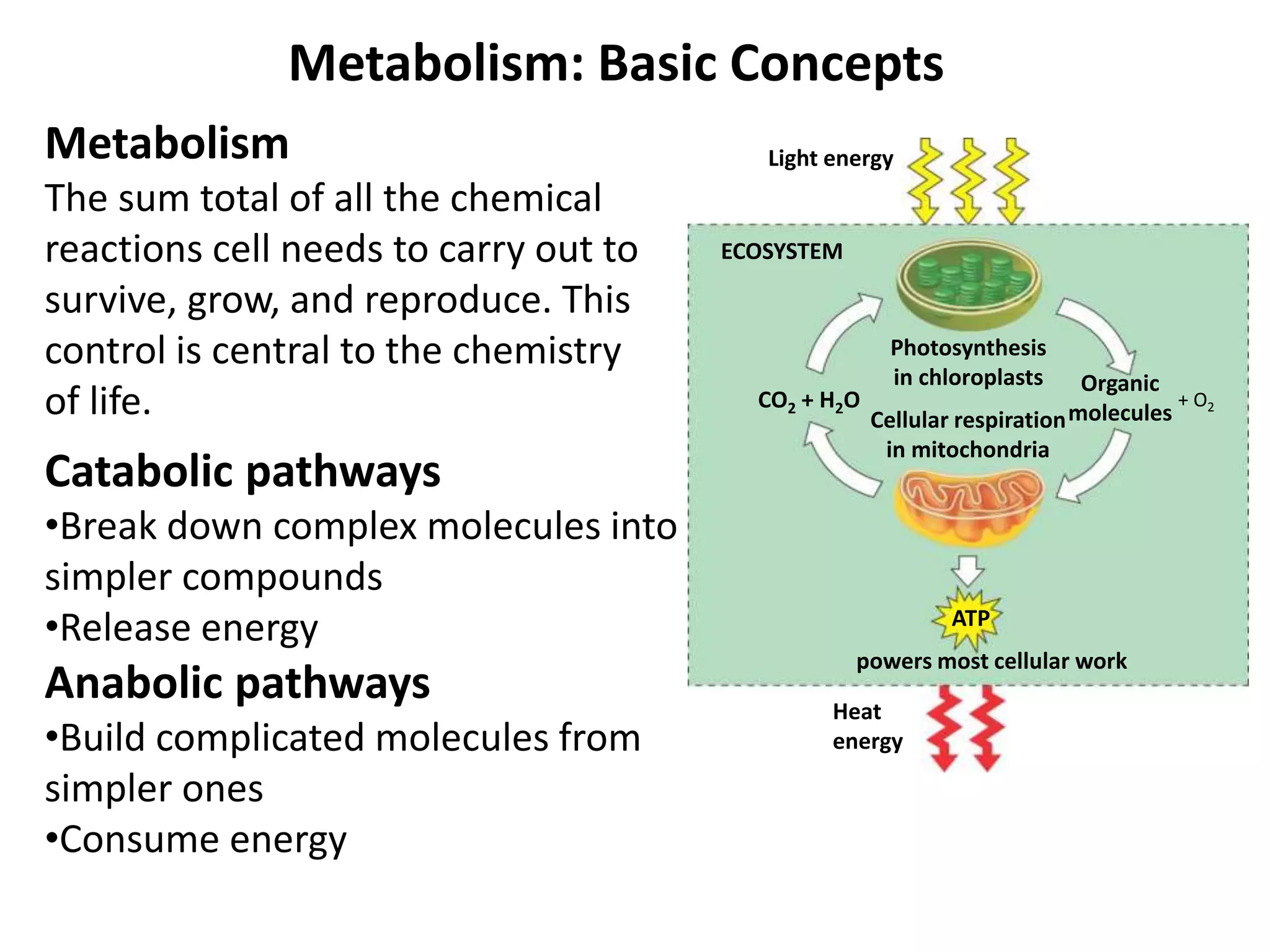
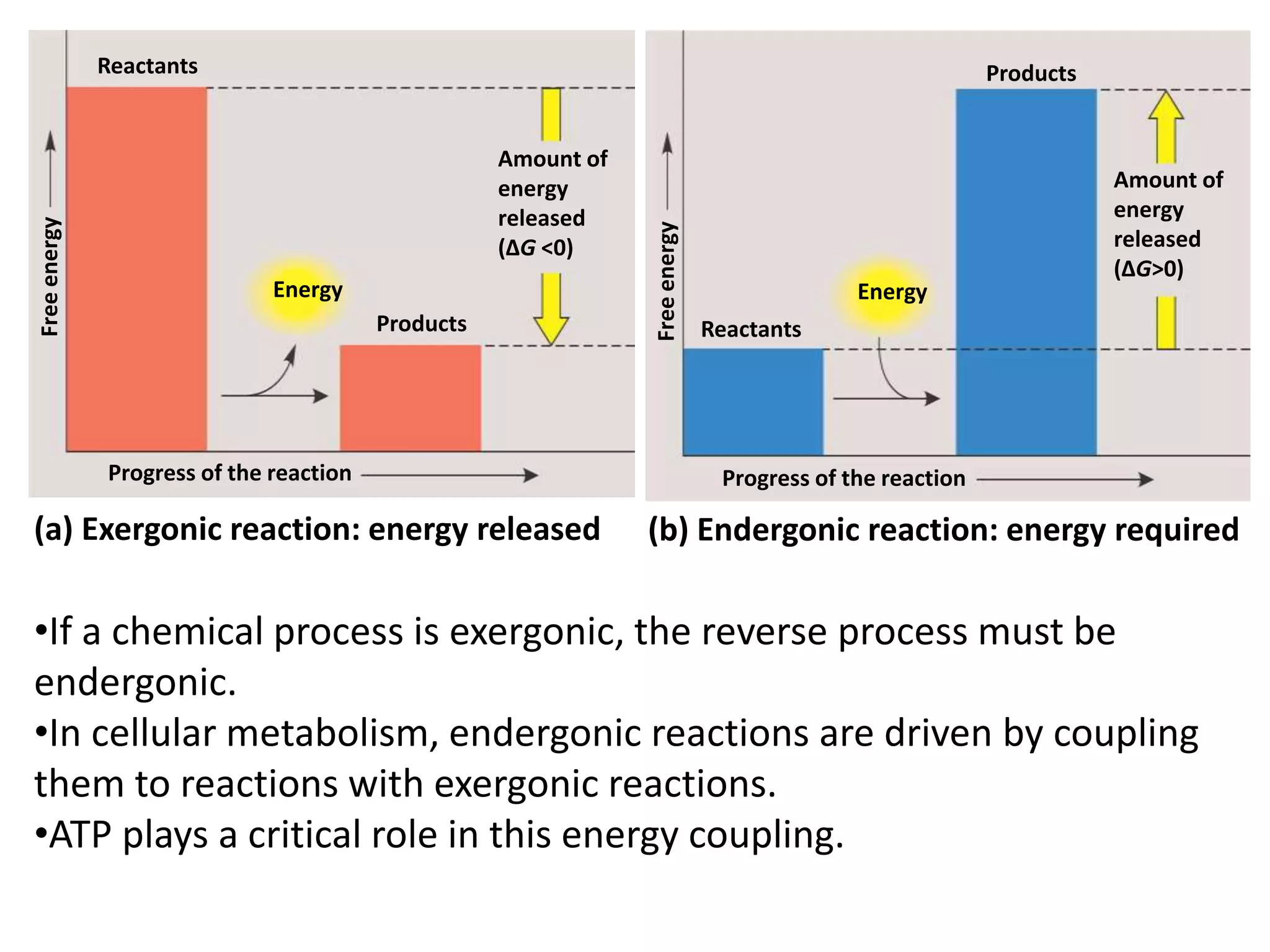
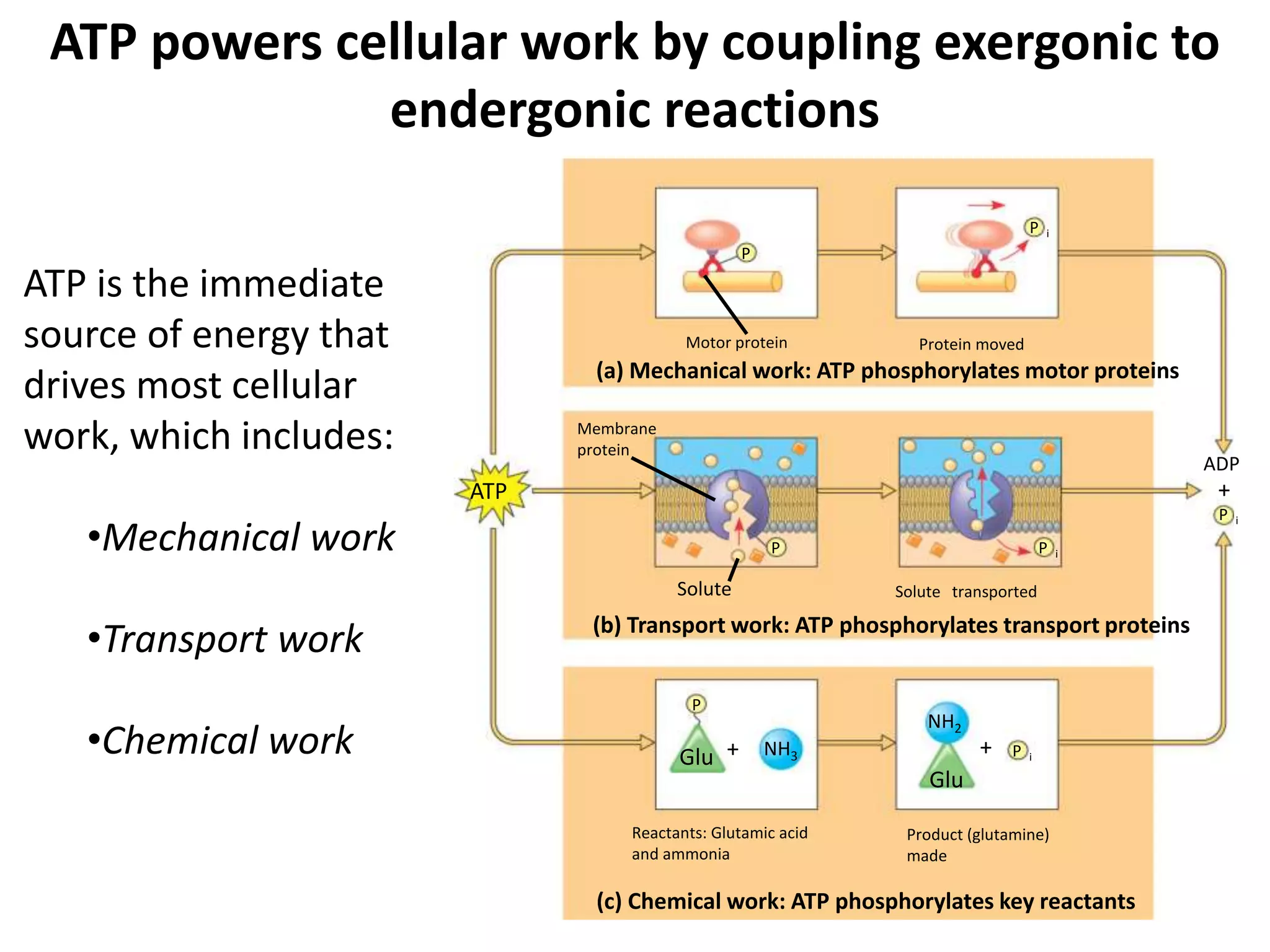
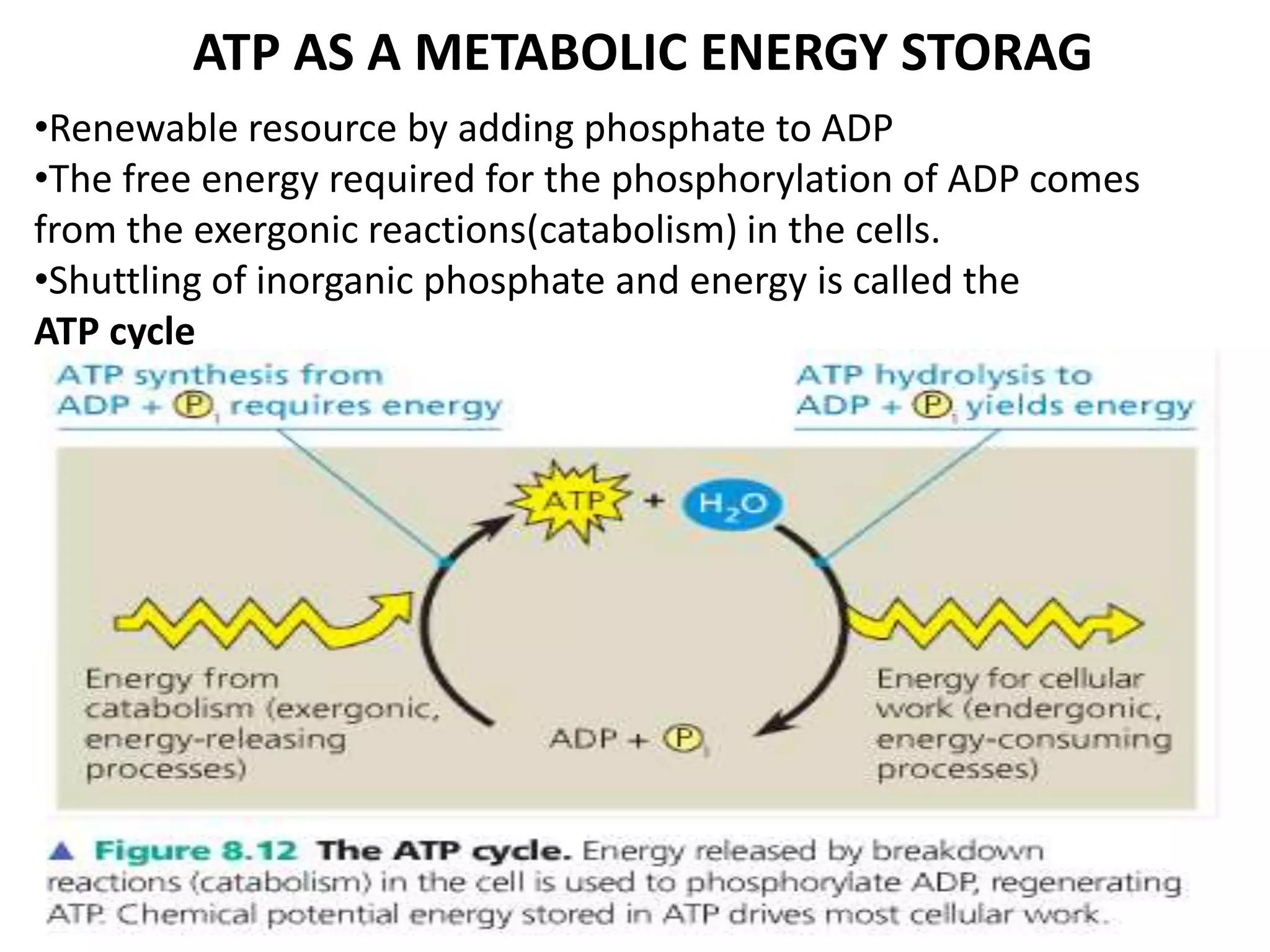
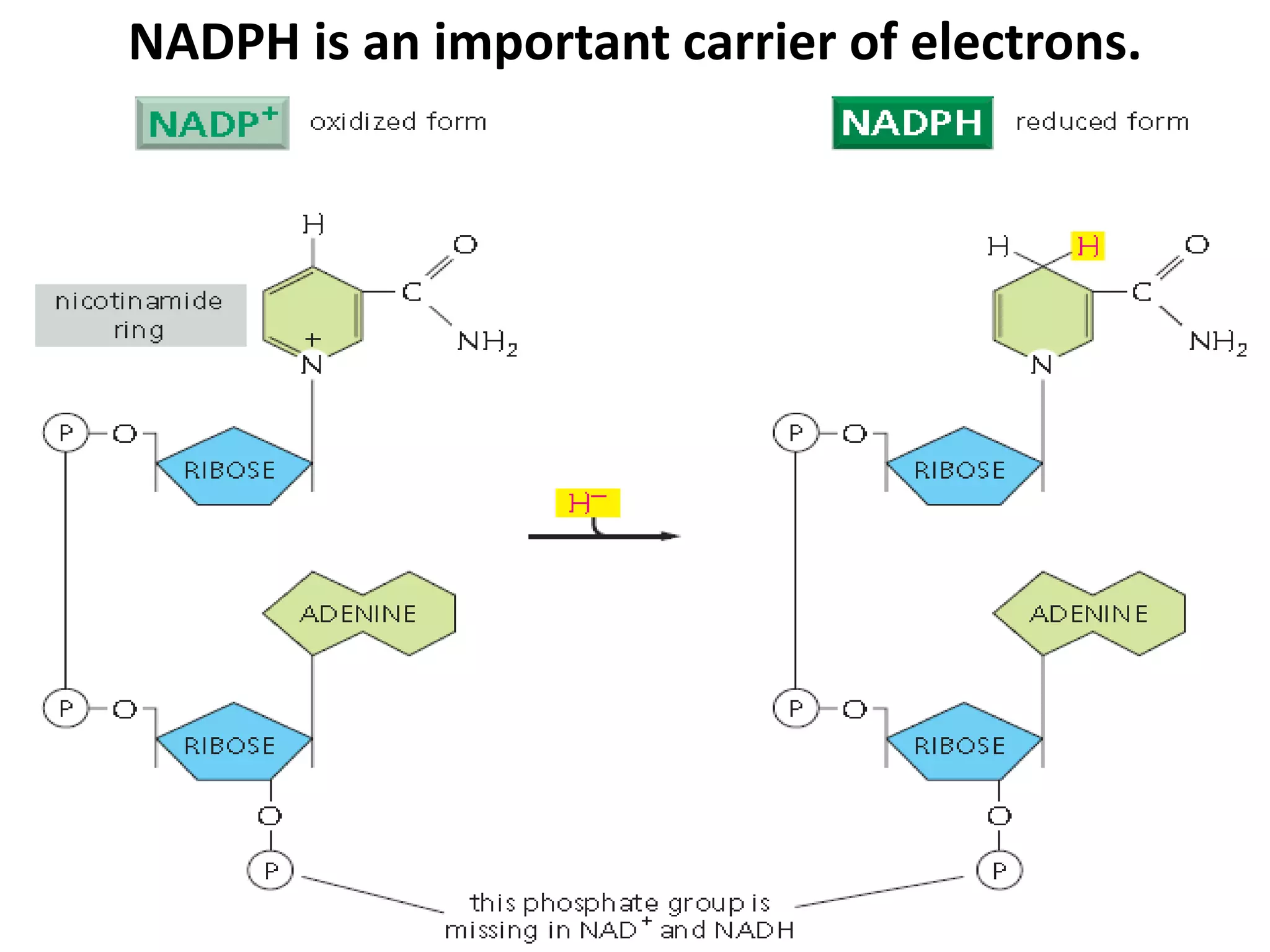
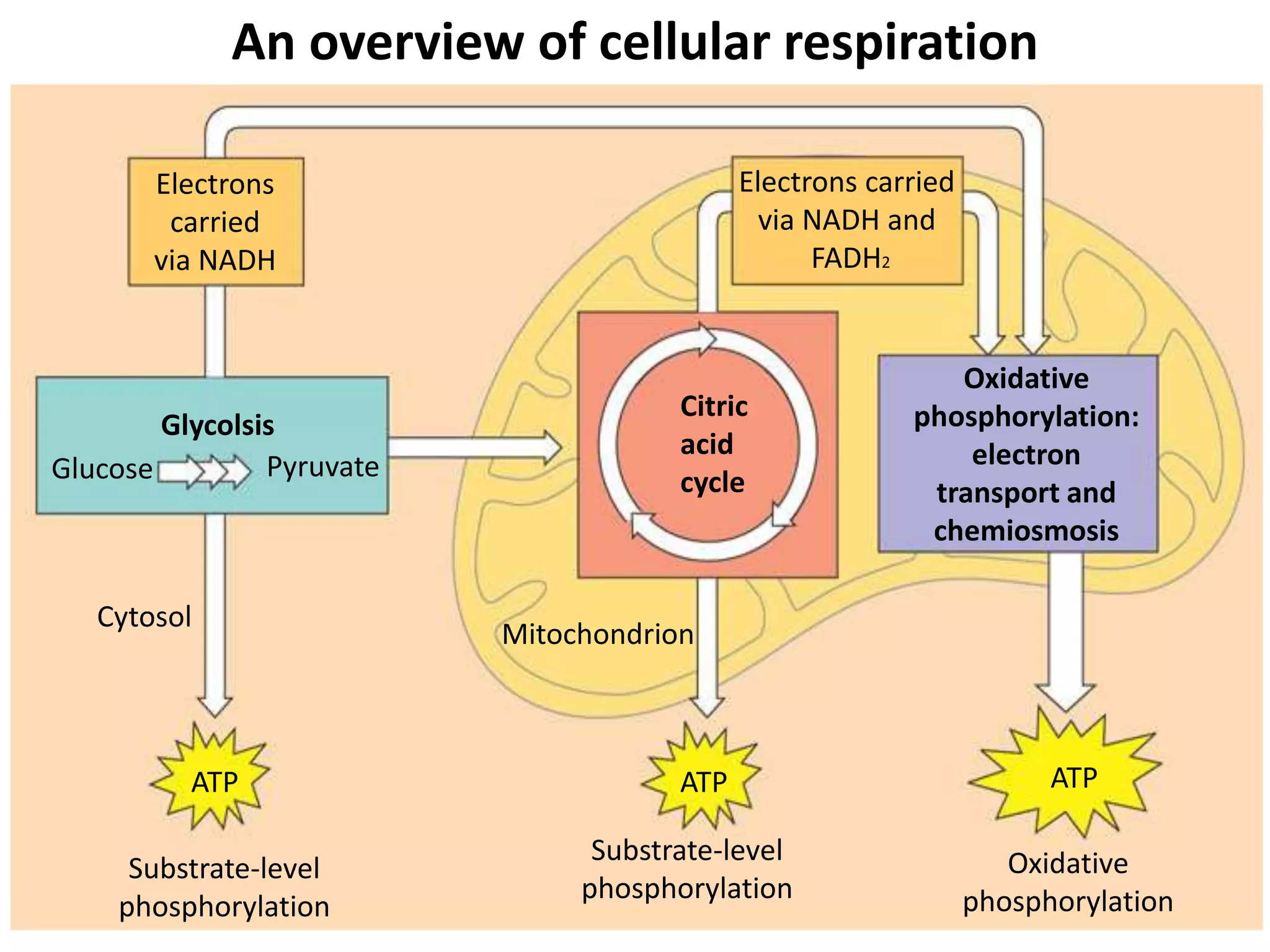
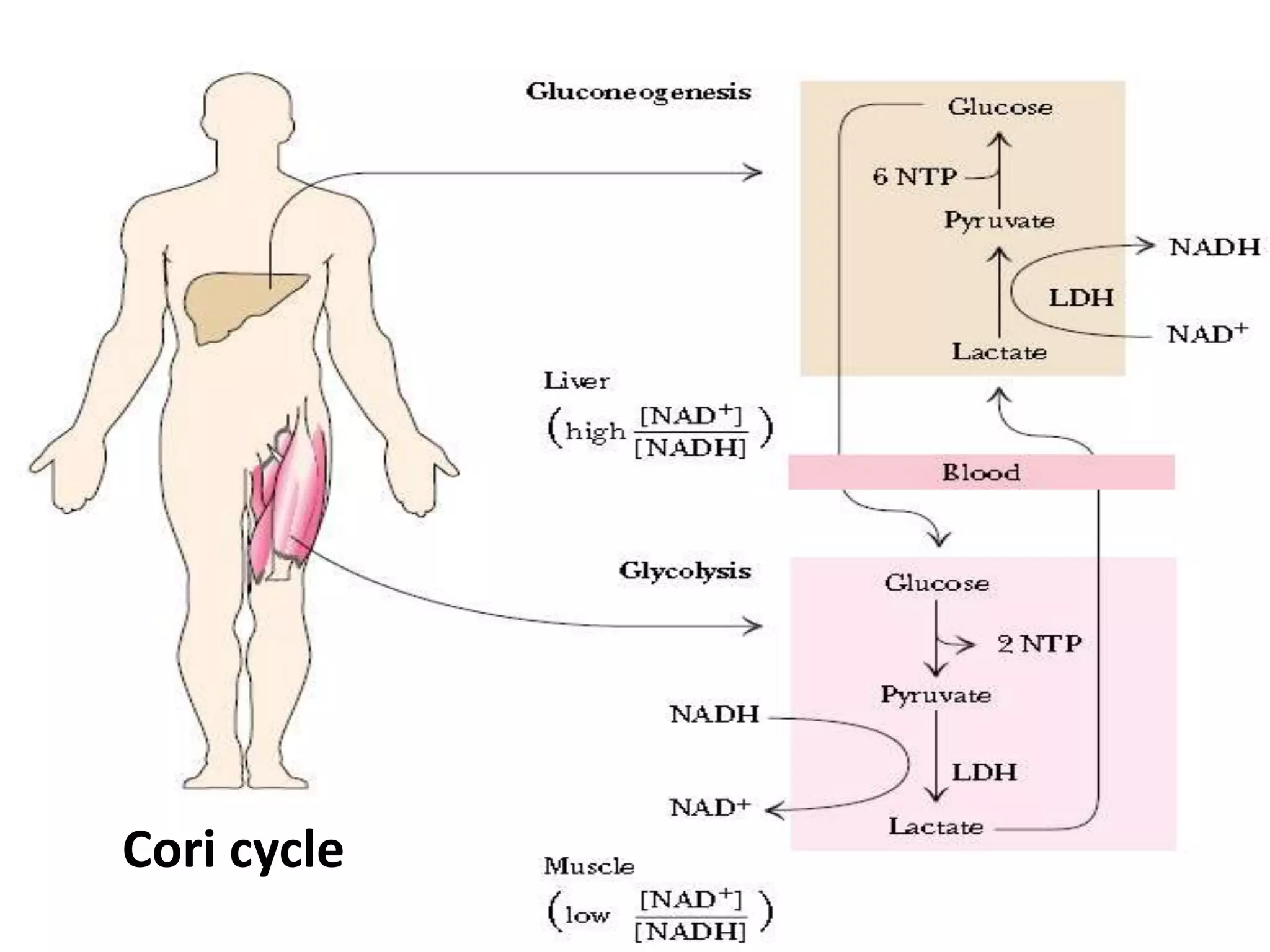
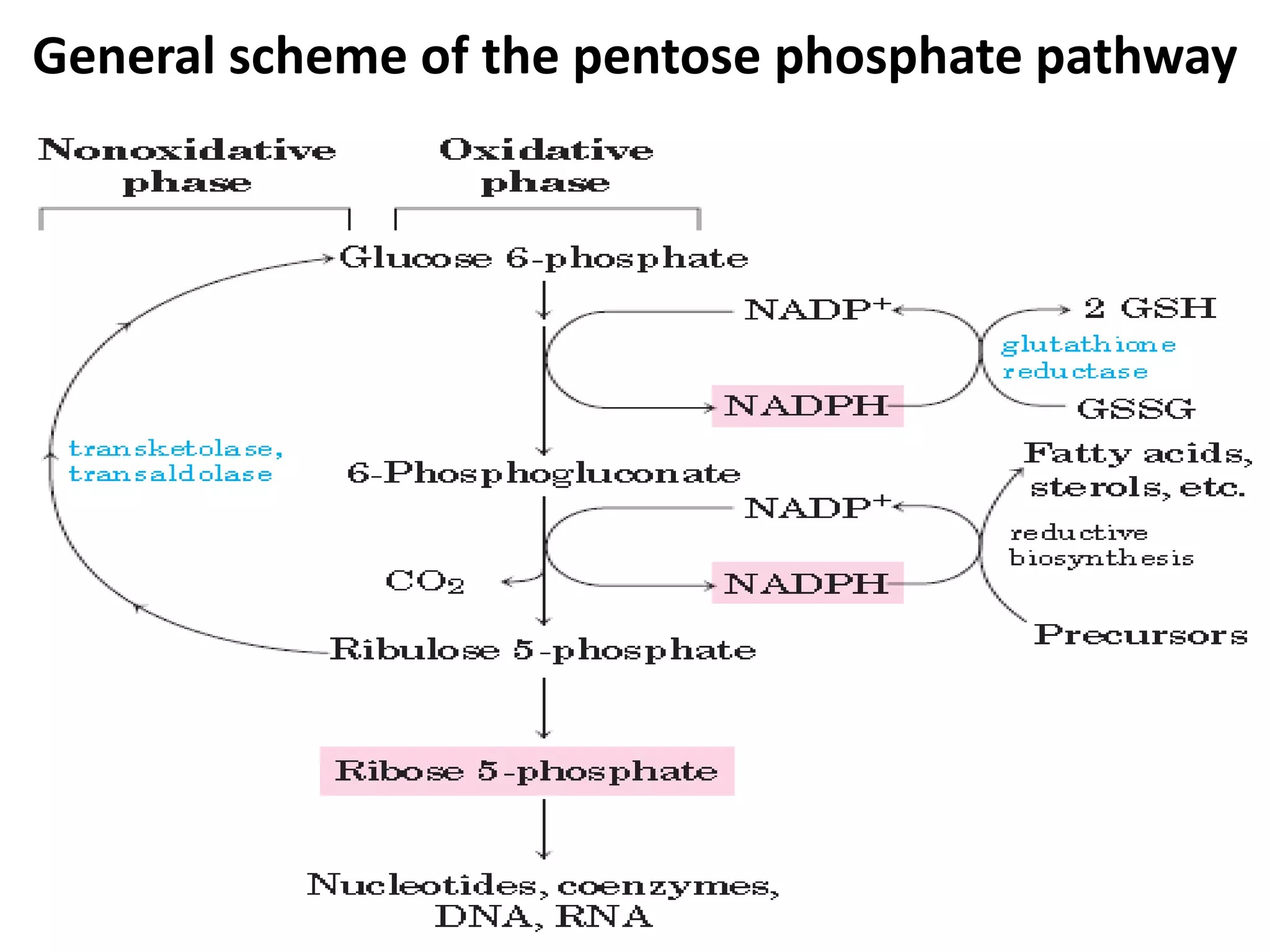
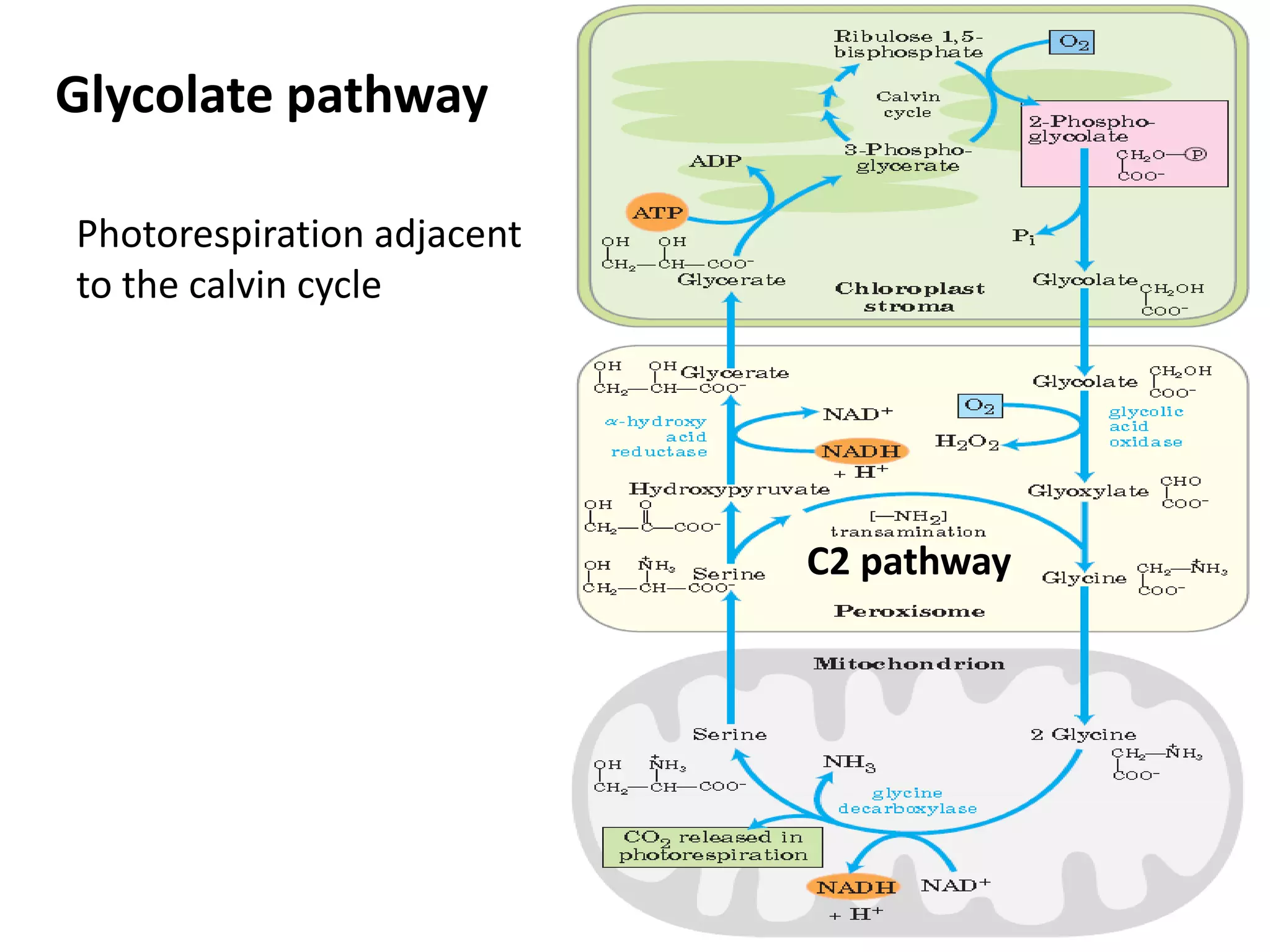
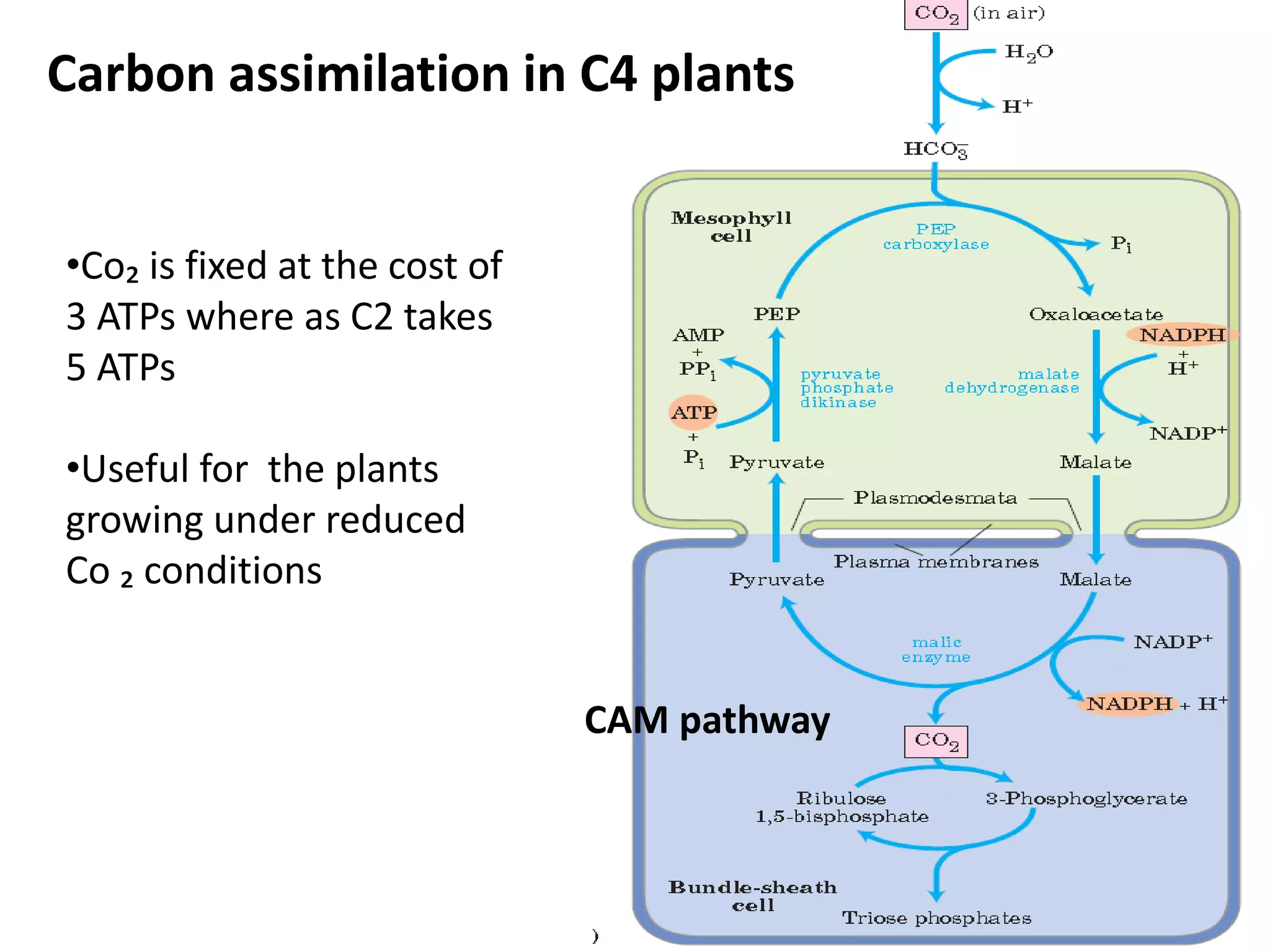
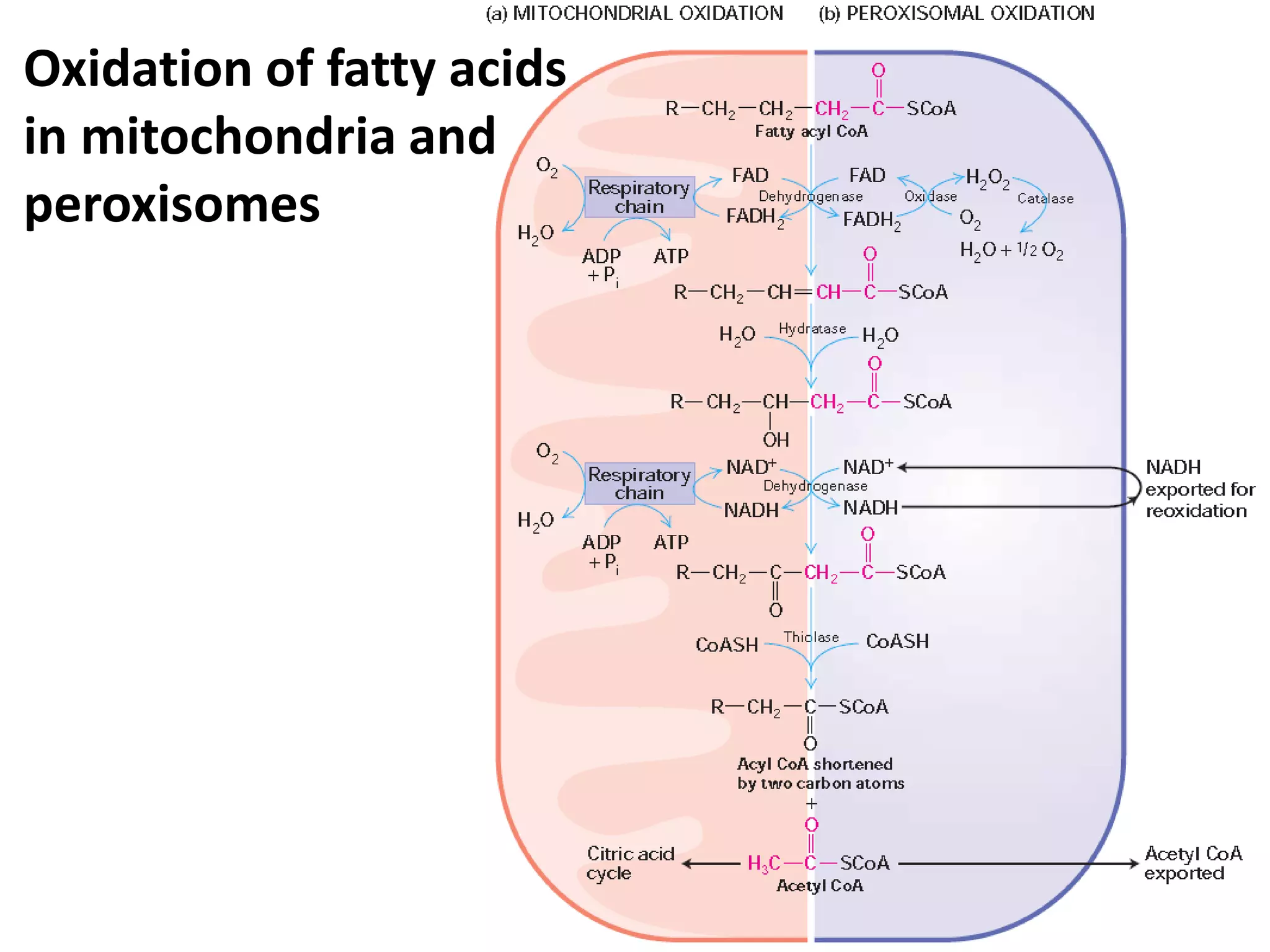
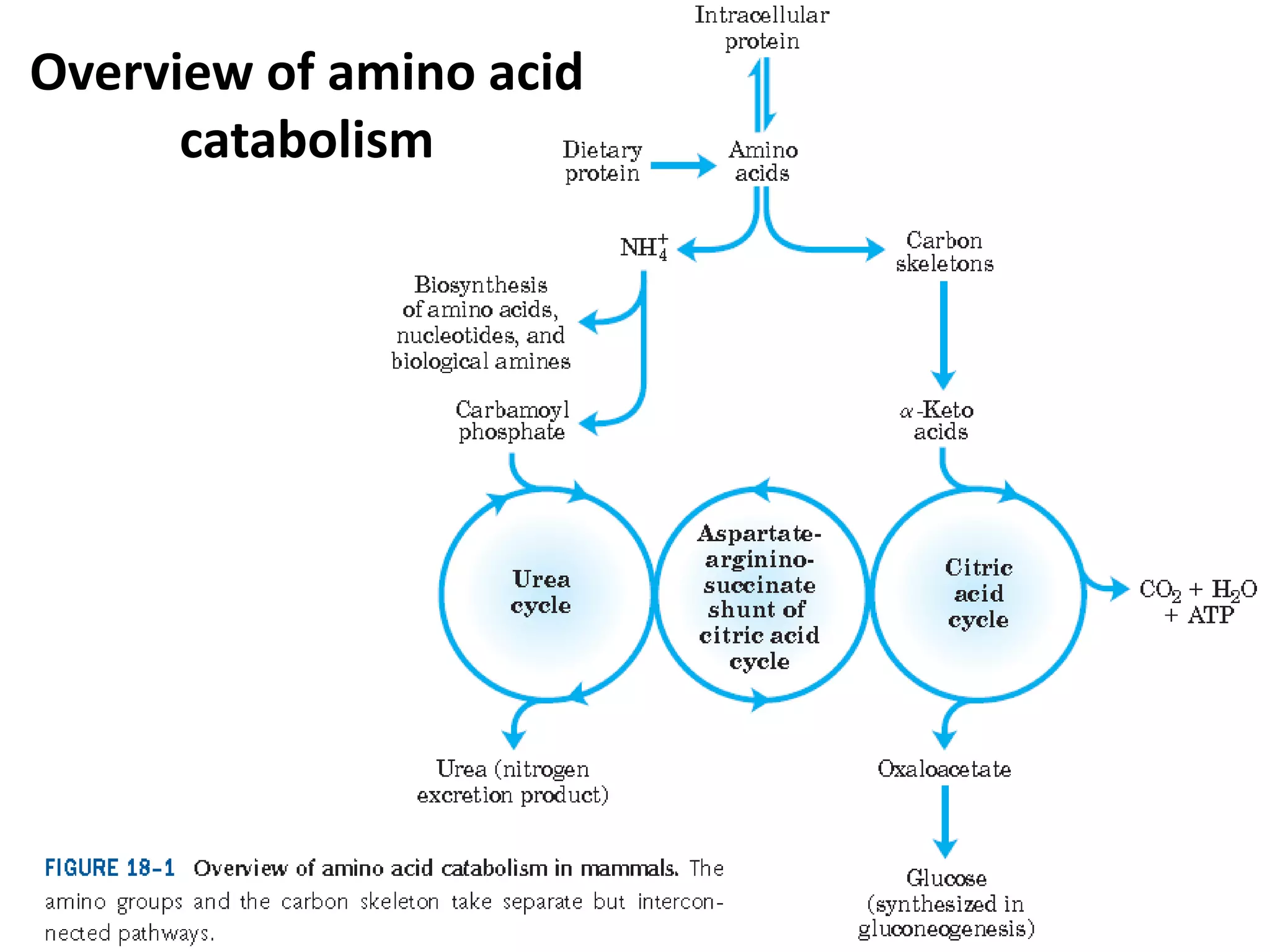
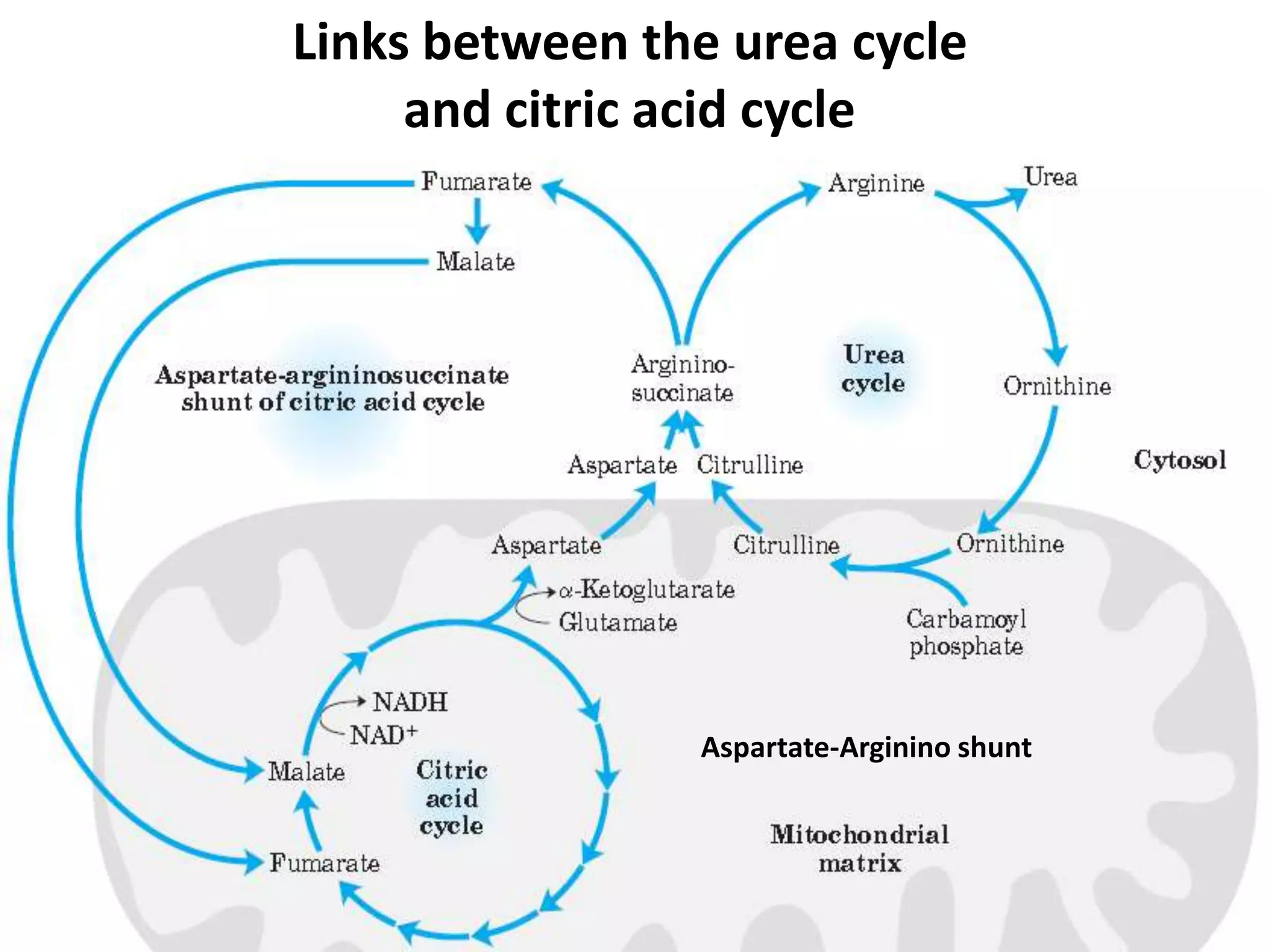
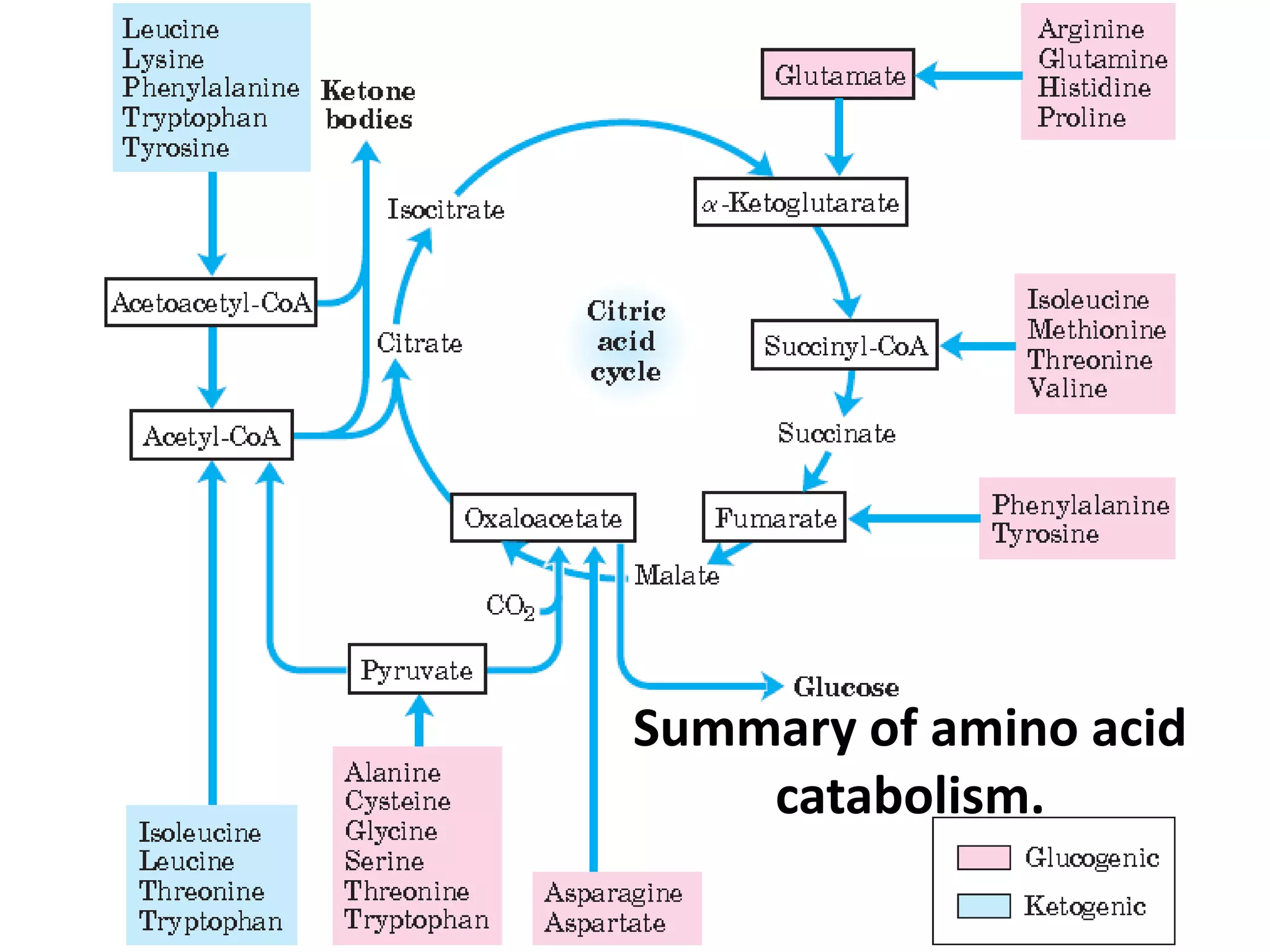
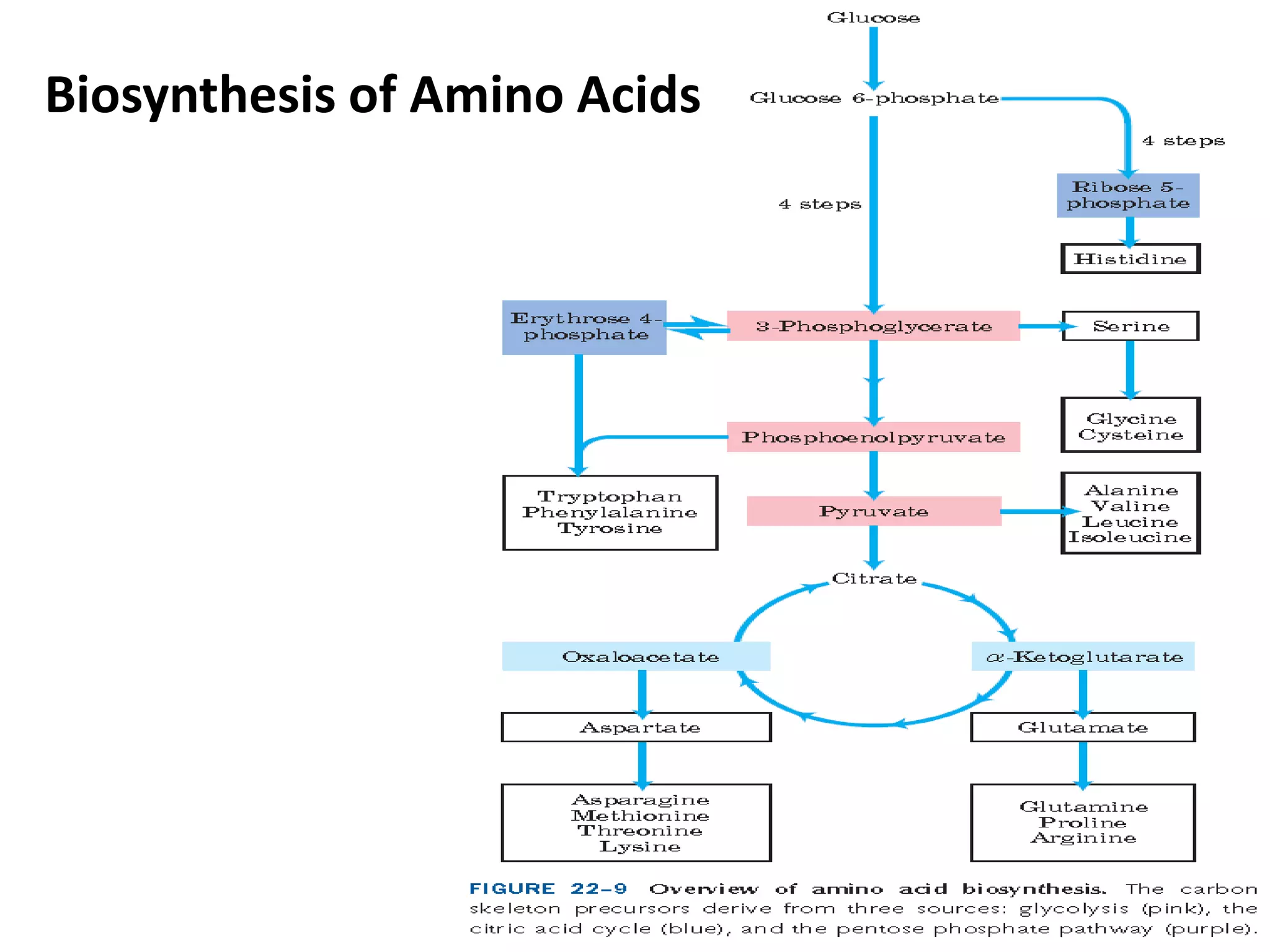
The document discusses key concepts in metabolism including photosynthesis, cellular respiration, ATP, and free energy. Photosynthesis uses light energy to convert CO2 and H2O into organic molecules and oxygen. Cellular respiration in mitochondria converts organic molecules back into CO2 and uses the energy released to produce ATP, which powers most cellular work. Metabolic pathways are classified as either catabolic, which breaks down molecules and releases energy, or anabolic, which builds molecules and requires energy. ATP acts as the main energy carrier in cells by coupling exergonic reactions to endergonic reactions like chemical work, transport work, and mechanical work.