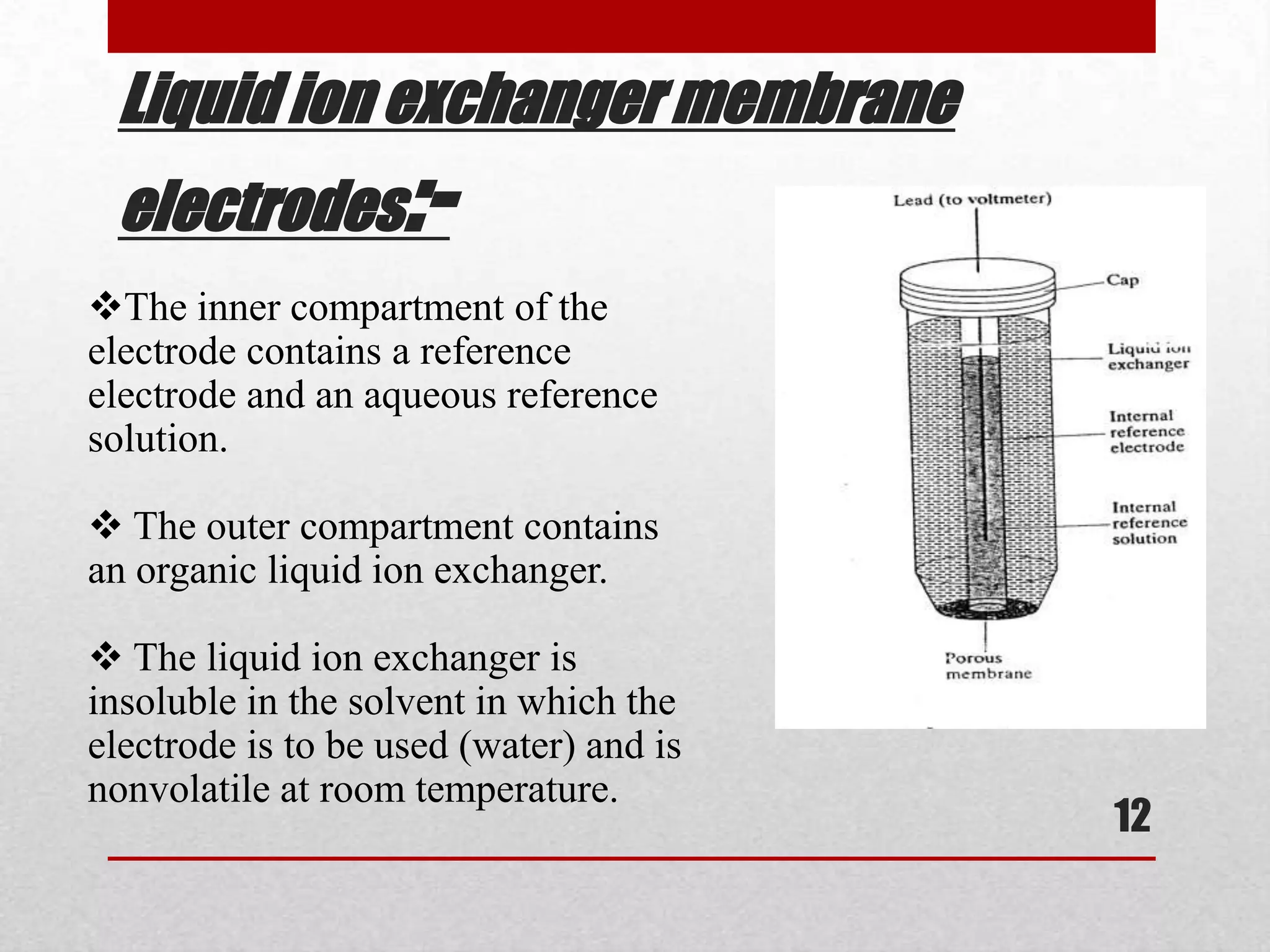
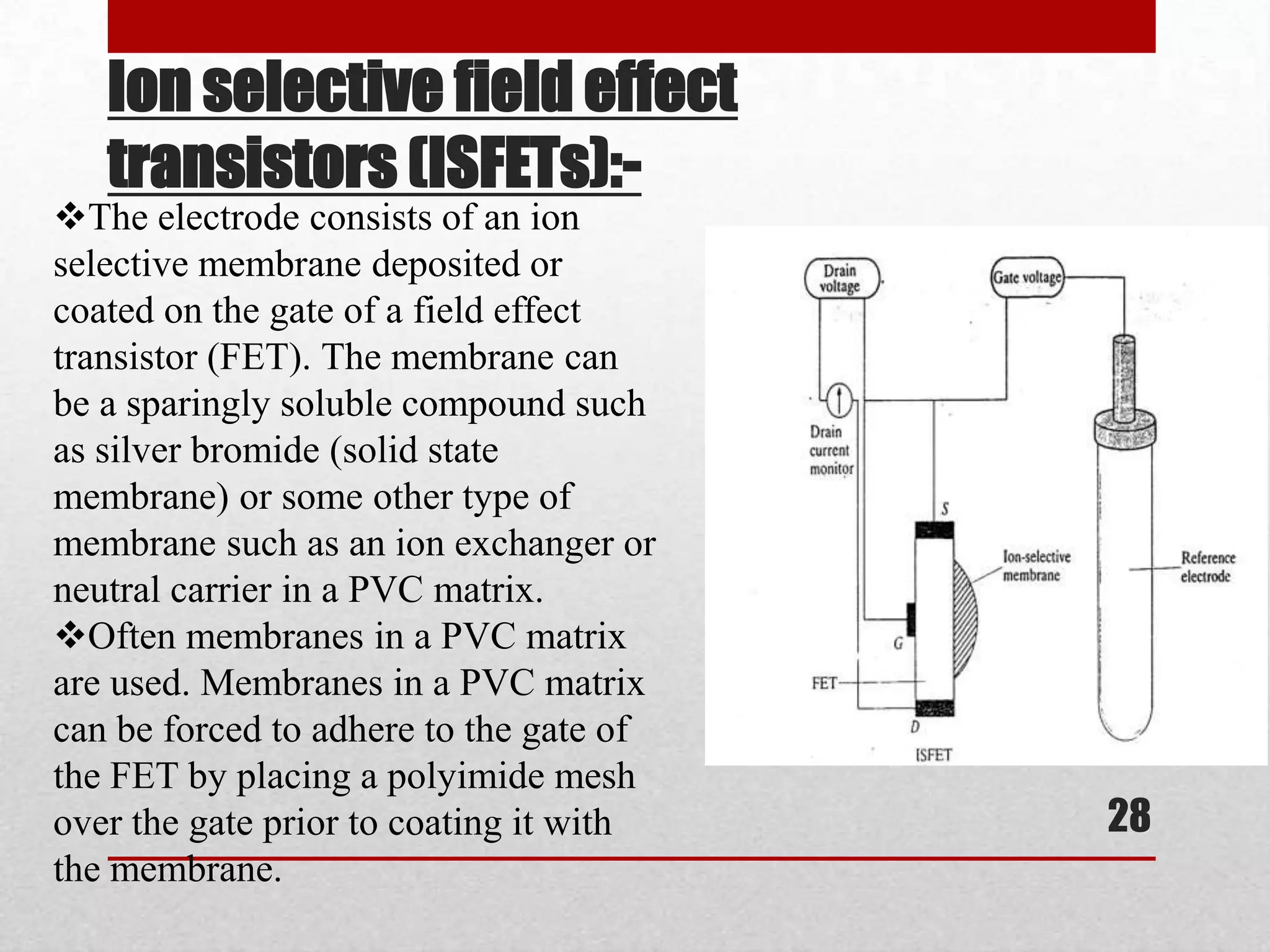
The document discusses ion selective electrodes (ISEs), including:
- The principle of ISEs is that a selective membrane allows only the intended ion to pass through, creating a potential difference.
- Types of ISEs include glass electrodes, liquid ion exchanger membranes, solid state membranes, and coated wire electrodes.
- ISEs have advantages like low cost, wide concentration range, robustness, and fast response times. Limitations include imprecision, interference, and limited lifetime.
- ISEs have many applications in fields, laboratories, medical/biological uses, and industrial processes due to their attributes.