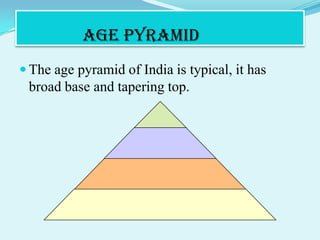
Demography is the study of human populations focusing on population size, composition, and distribution. It deals with 5 demographic processes: fertility, mortality, marriage, migration, and social mobility. Demography can be static, focusing on population structure, or dynamic, focusing on changing patterns of mortality, fertility, and migration. India's population growth rate is the net of crude birth and death rates. India's population is young with 34.33% under 15 and growing elderly population above 60 years. Sex ratio is females per 1000 males and is adverse to women in India. Dependency ratio considers under 15 and over 65 as dependent on 15-64 age group. India's age pyramid is broad at the base and tapering at the top.