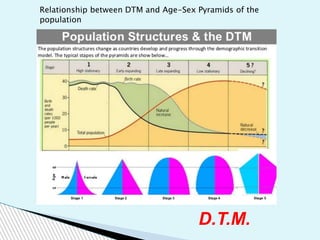
The document discusses the age-sex pyramid as a key tool for illustrating demographic characteristics of a population, including gender and age distribution. It outlines the different stages of the demographic transition model (DTM) that explain how birth and death rates change over time, from high rates in developing countries to low rates in developed ones. Additionally, factors influencing population pyramids are identified, such as fertility, migration, and health care advancements.