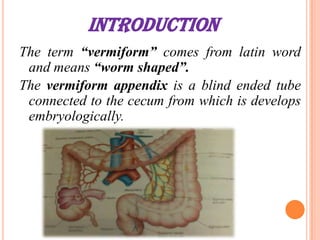
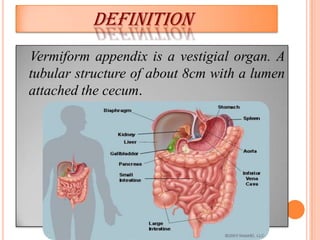
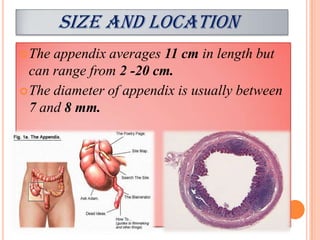
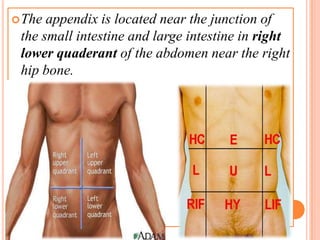
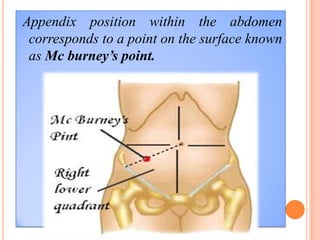
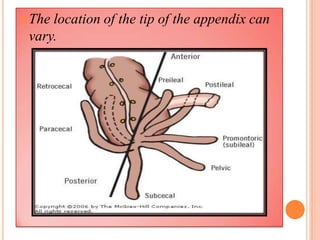
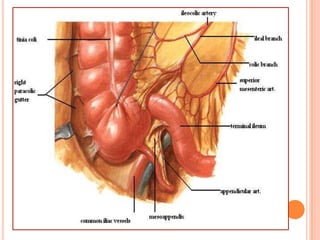
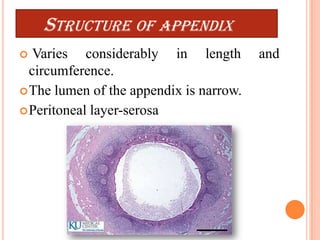
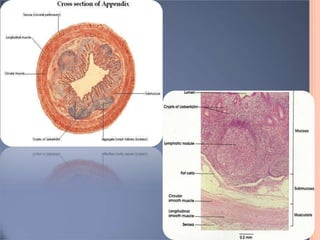
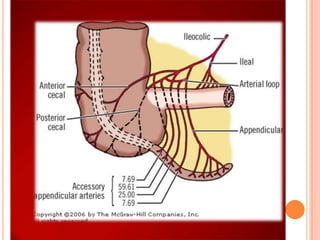
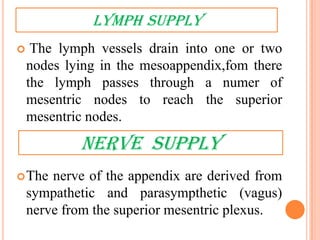
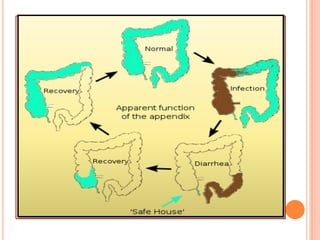
The vermiform appendix is a vestigial organ that is a blind ended tube attached to the cecum. It averages around 11 cm in length and 7-8 mm in diameter. The appendix is located in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen near the junction of the small and large intestines. Though it has lost most of its original function, the appendix still plays a minor role in immunity and housing beneficial gut bacteria.