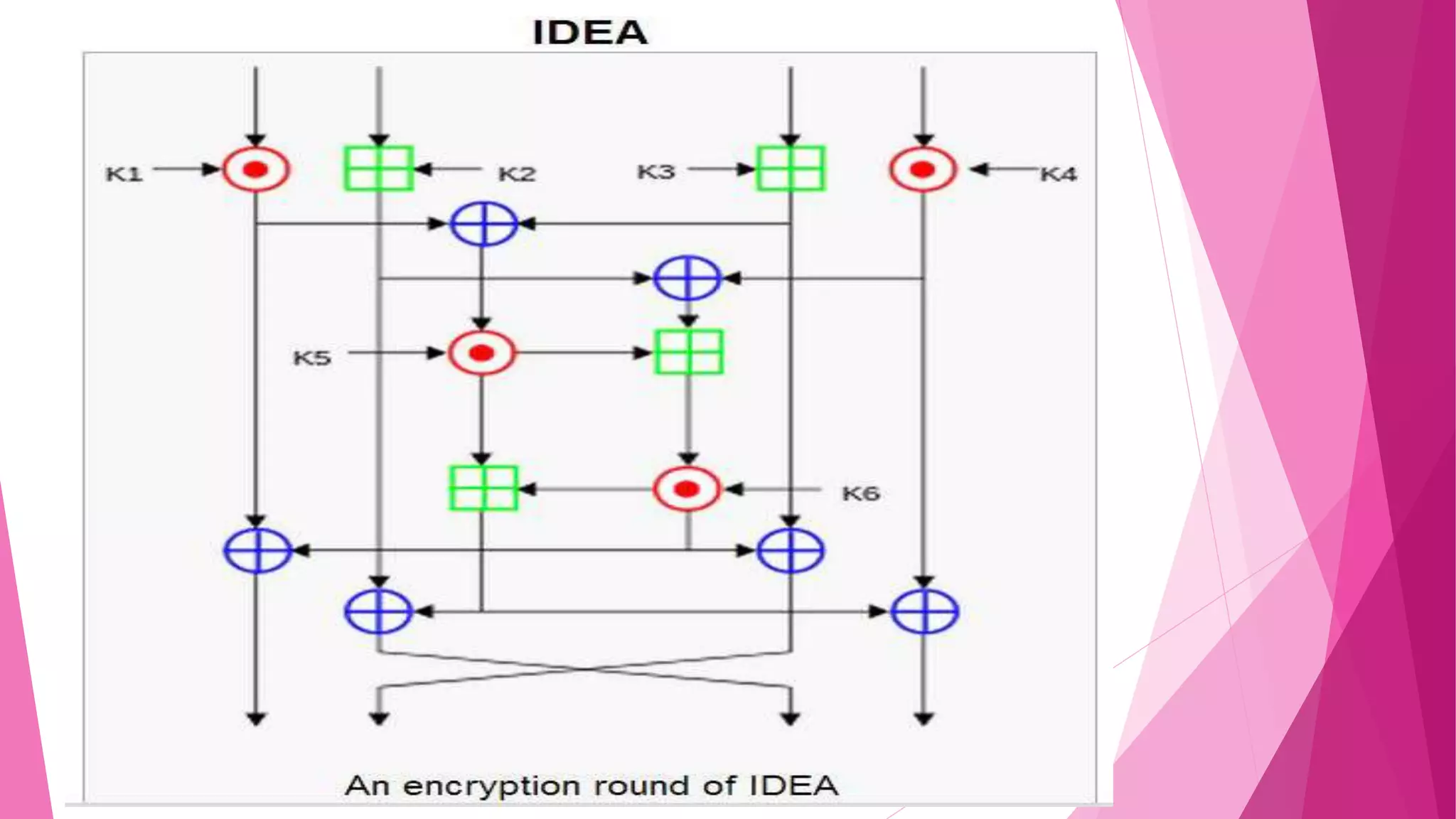
The document discusses the International Data Encryption Algorithm (IDEA). It was developed in 1990 as a replacement for the Data Encryption Standard. IDEA is a symmetric block cipher that uses a 128-bit key to encrypt 64-bit blocks of plaintext into ciphertext. The key is divided into 52 subkeys that are used in 8 rounds of encryption/decryption operations involving XOR, addition, and multiplication. IDEA was used in PGP v2.0 and can encrypt sensitive data for applications like financial services, broadcasting, and government use.