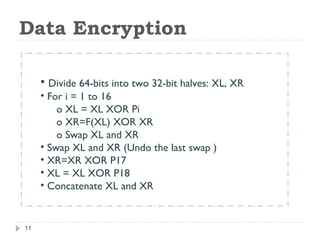
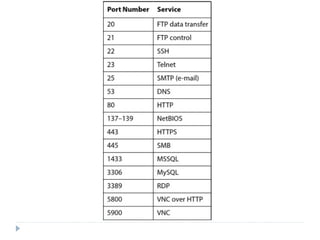
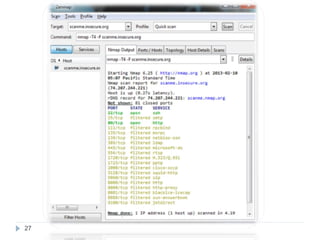
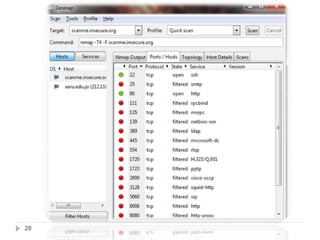
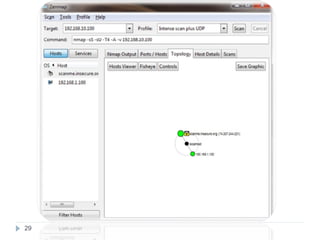
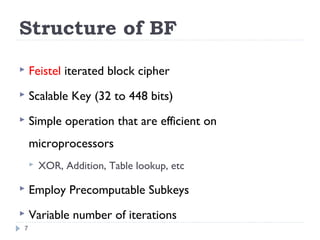
This document discusses the Blowfish encryption algorithm and the Nmap network scanning tool. It begins with an outline of the topics to be covered, which include an introduction to Blowfish, its structure and cryptanalysis, a paper on modifying Blowfish using multiple keys, and an overview of Nmap including its features and usage for port scanning networks. The document provides technical details and code examples for how Blowfish encryption works, discusses its security and comparisons to other algorithms, and outlines how Nmap can be used to detect operating systems, services, and vulnerabilities on targeted systems.






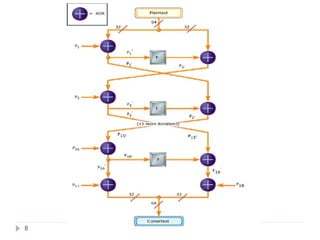
![Implementation: Function F(x(
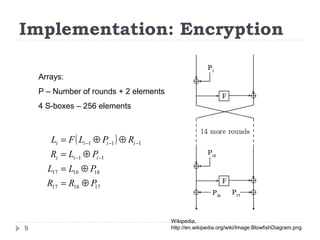
( ) [ ] [ ]( ) [ ]( )
[ ]07
81516232431031
4
321
−
−−−−
+
⊕+=
XS
XSXSXSXF
Wikipedia,
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en
/8/81/BlowfishFFunction.png
Addition is mod 232
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blowfishassig-141223095153-conversion-gate02/85/Blowfish-Cryptosystem-10-320.jpg)