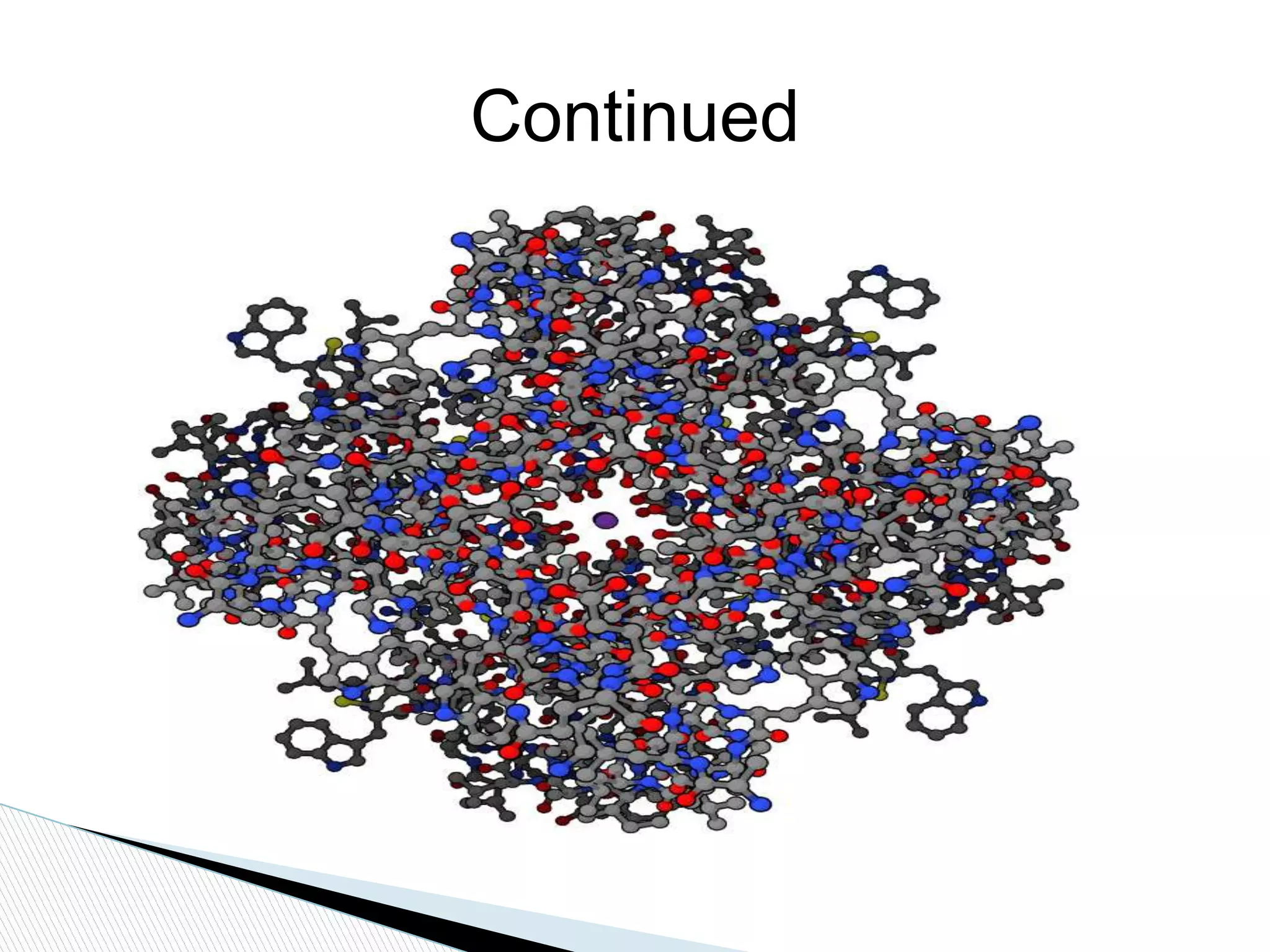
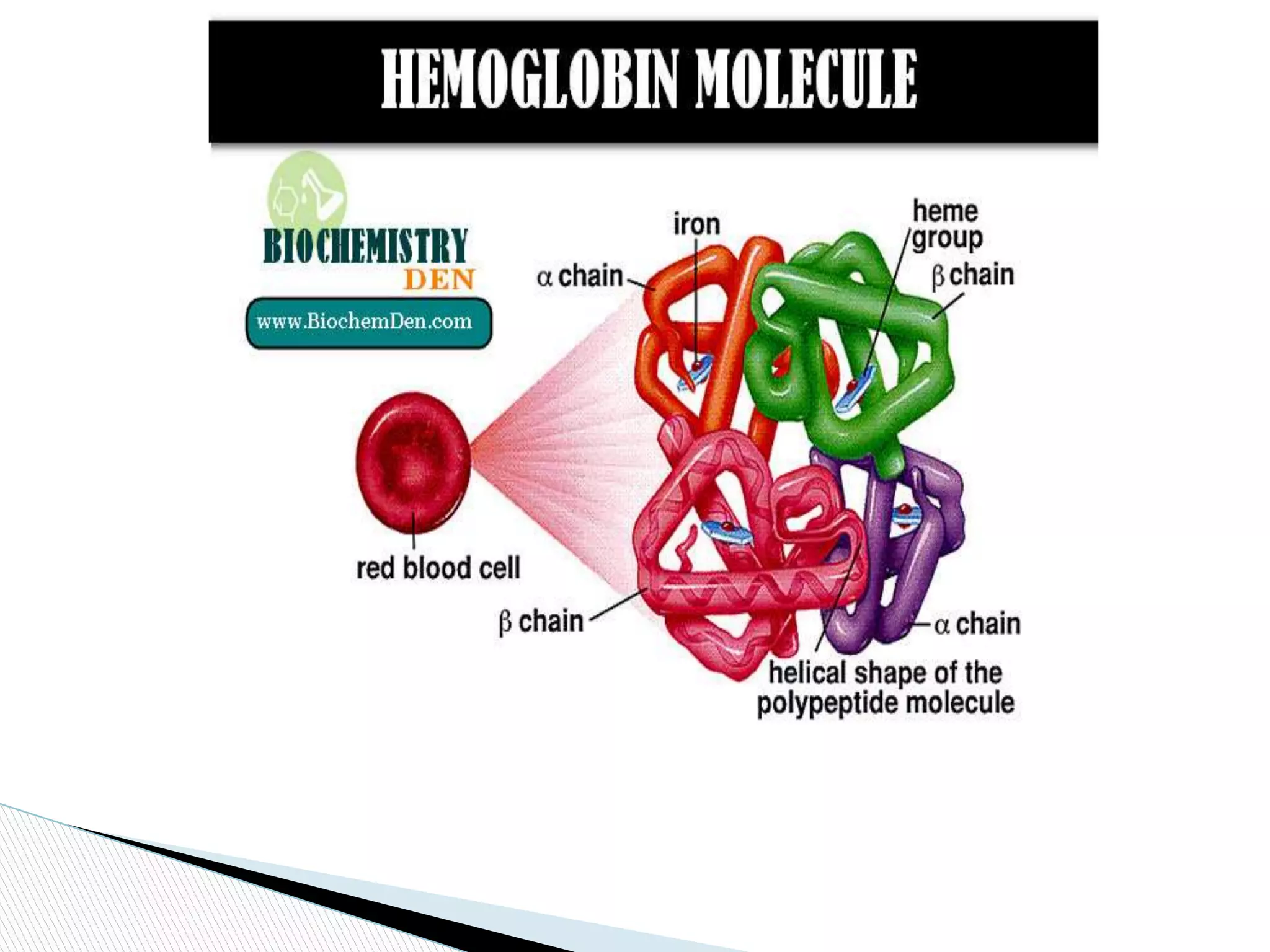
This document provides an overview of globular proteins, including their introduction, structure, factors affecting stability, types of denaturation, and functions. It discusses several examples of globular proteins in depth, including enzymes like hexokinase, hormones like insulin, oxygen carriers like hemoglobin, and structural proteins like actin. Globular proteins are spherical water-soluble proteins that carry out important metabolic, catalytic, and structural functions in cells. Their three-dimensional structure allows them to perform roles like enzyme catalysis, hormone signaling, oxygen transport, and cytoskeleton formation.