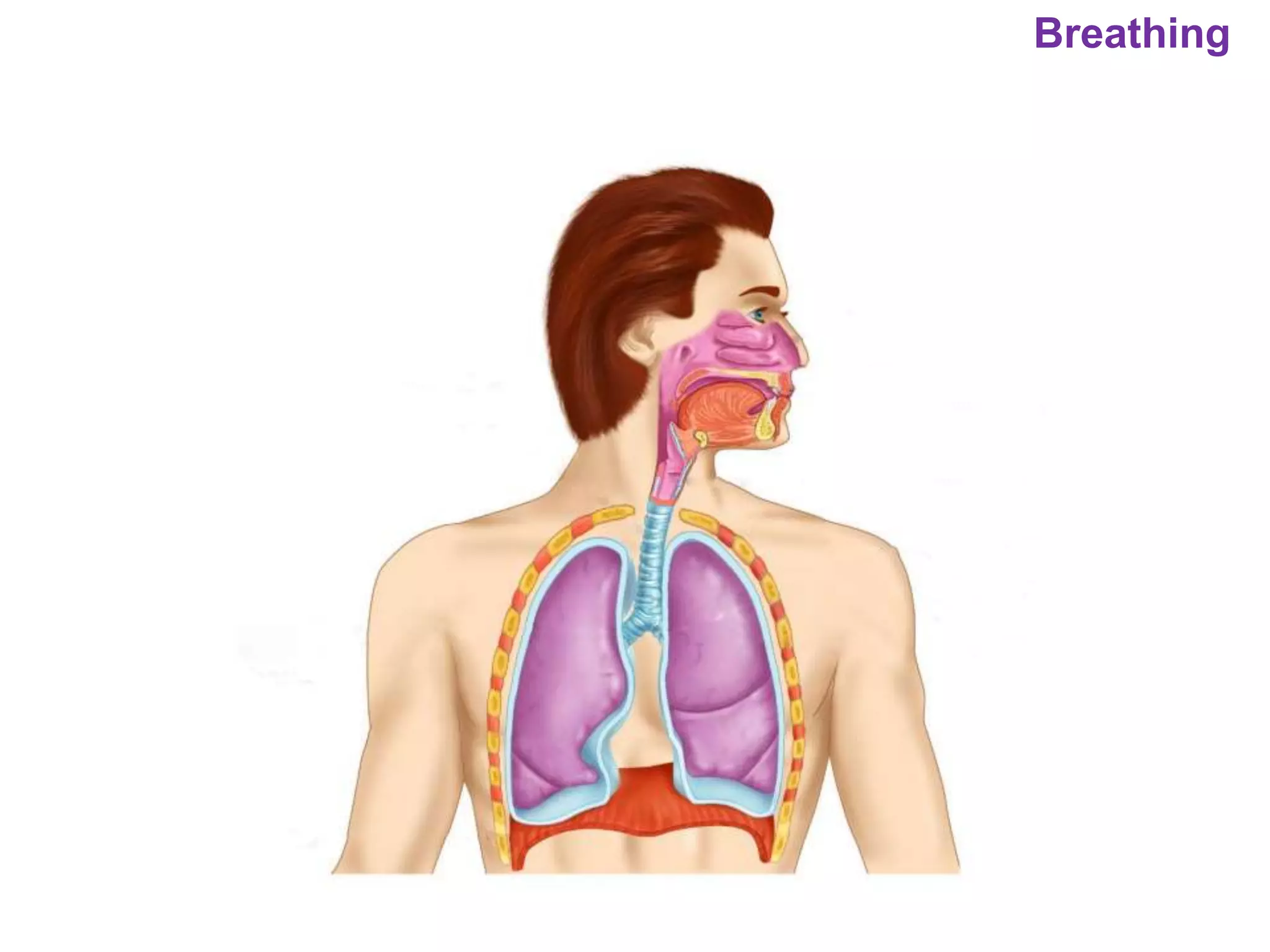
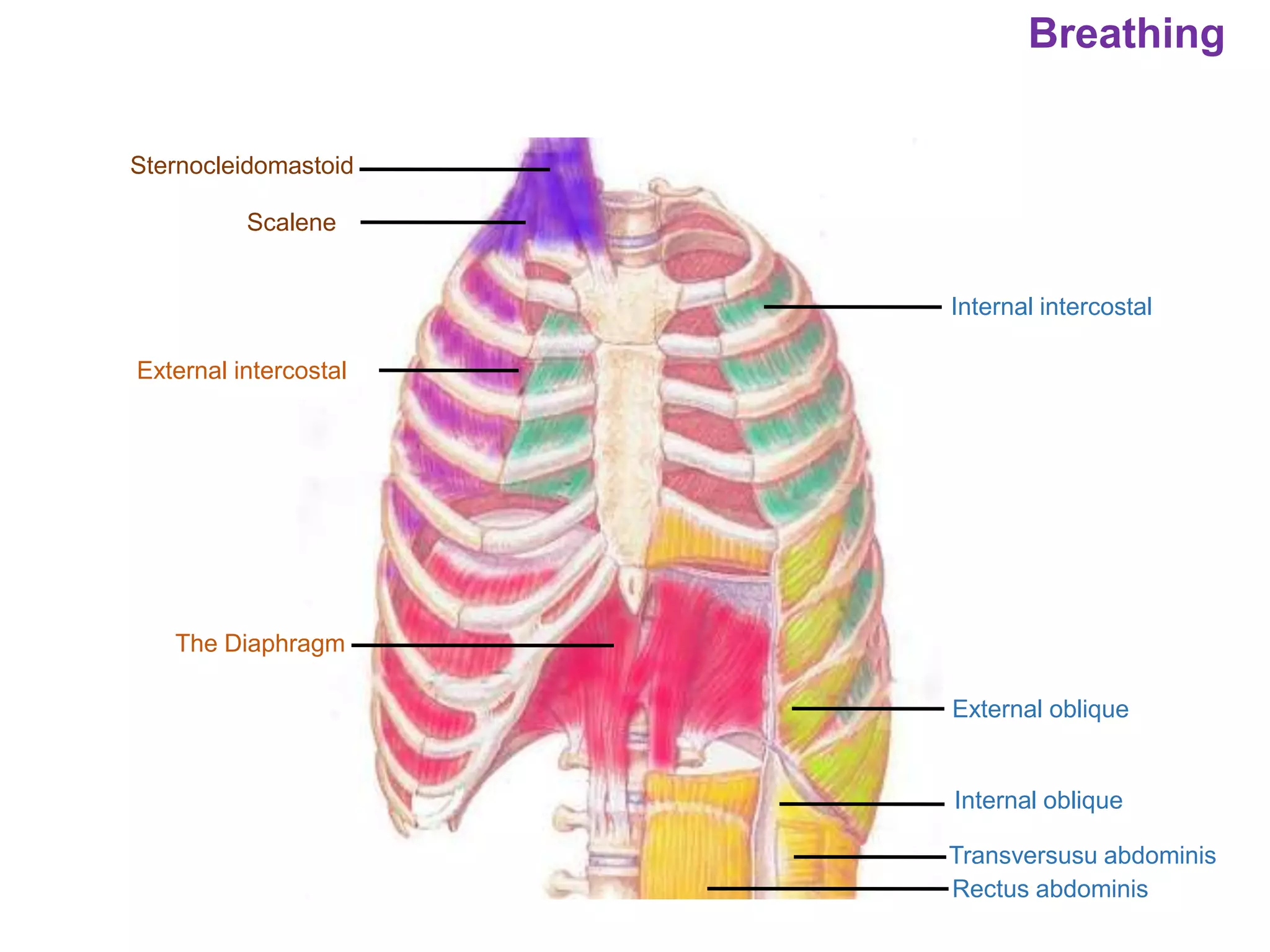
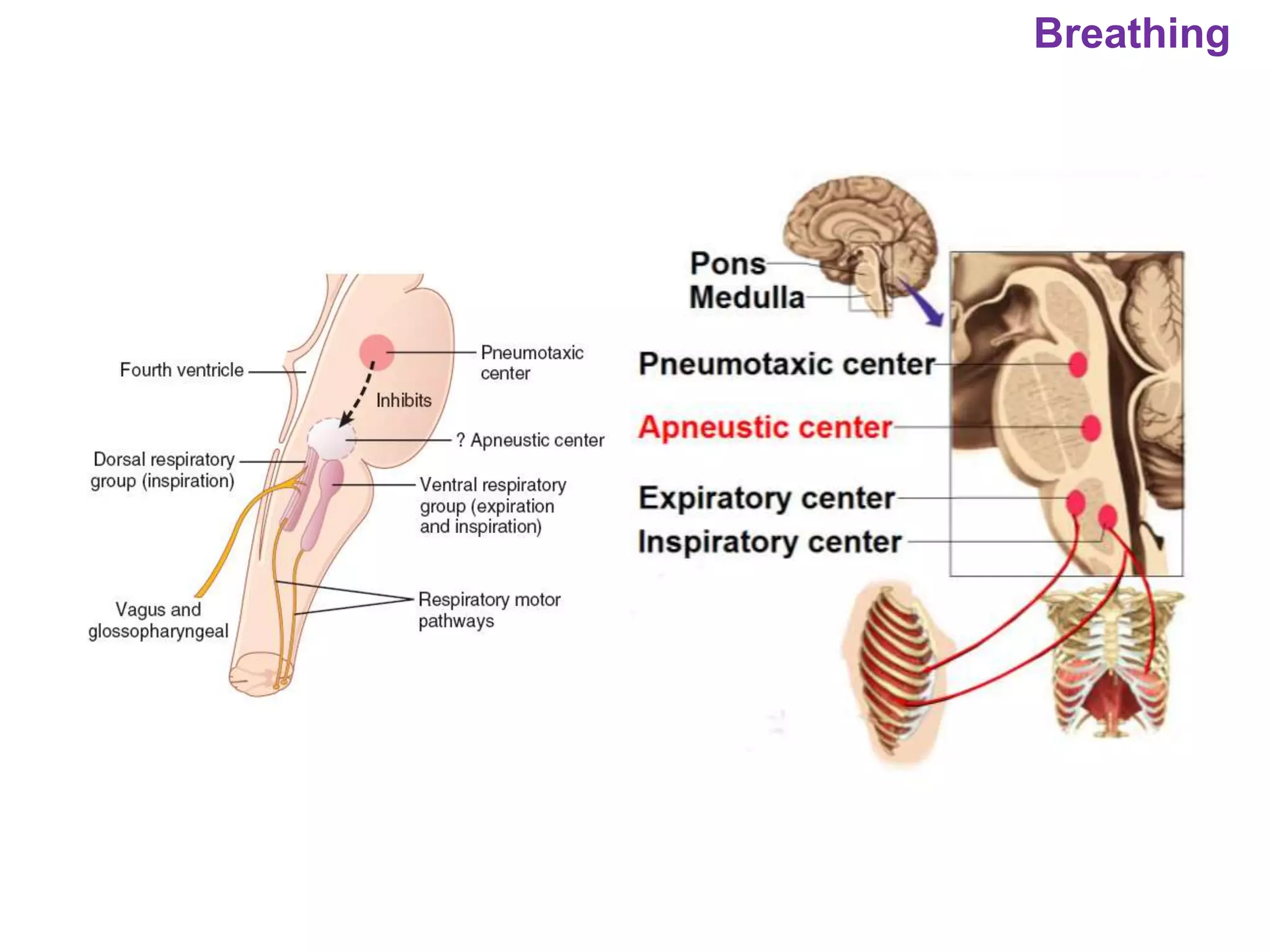
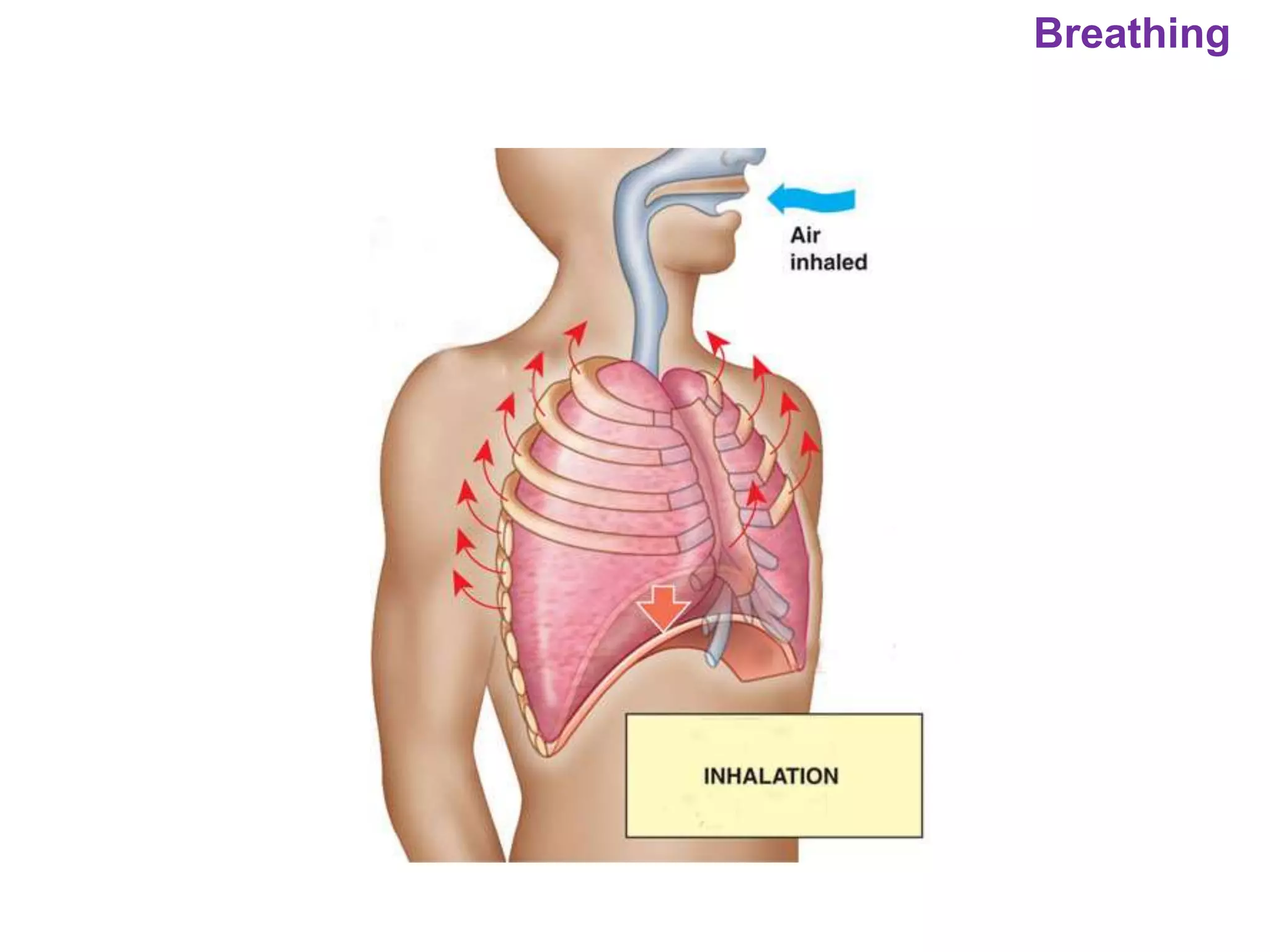
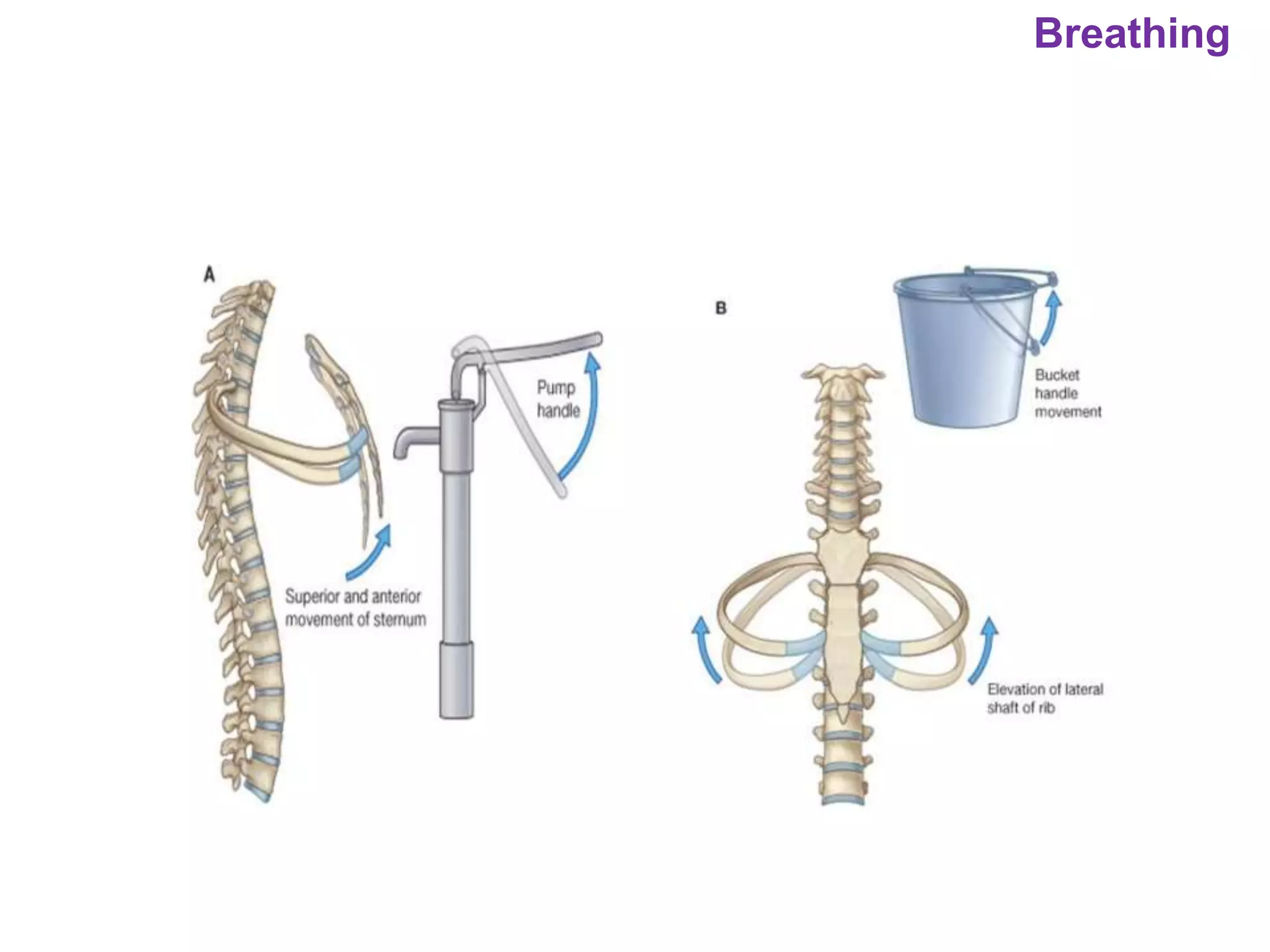
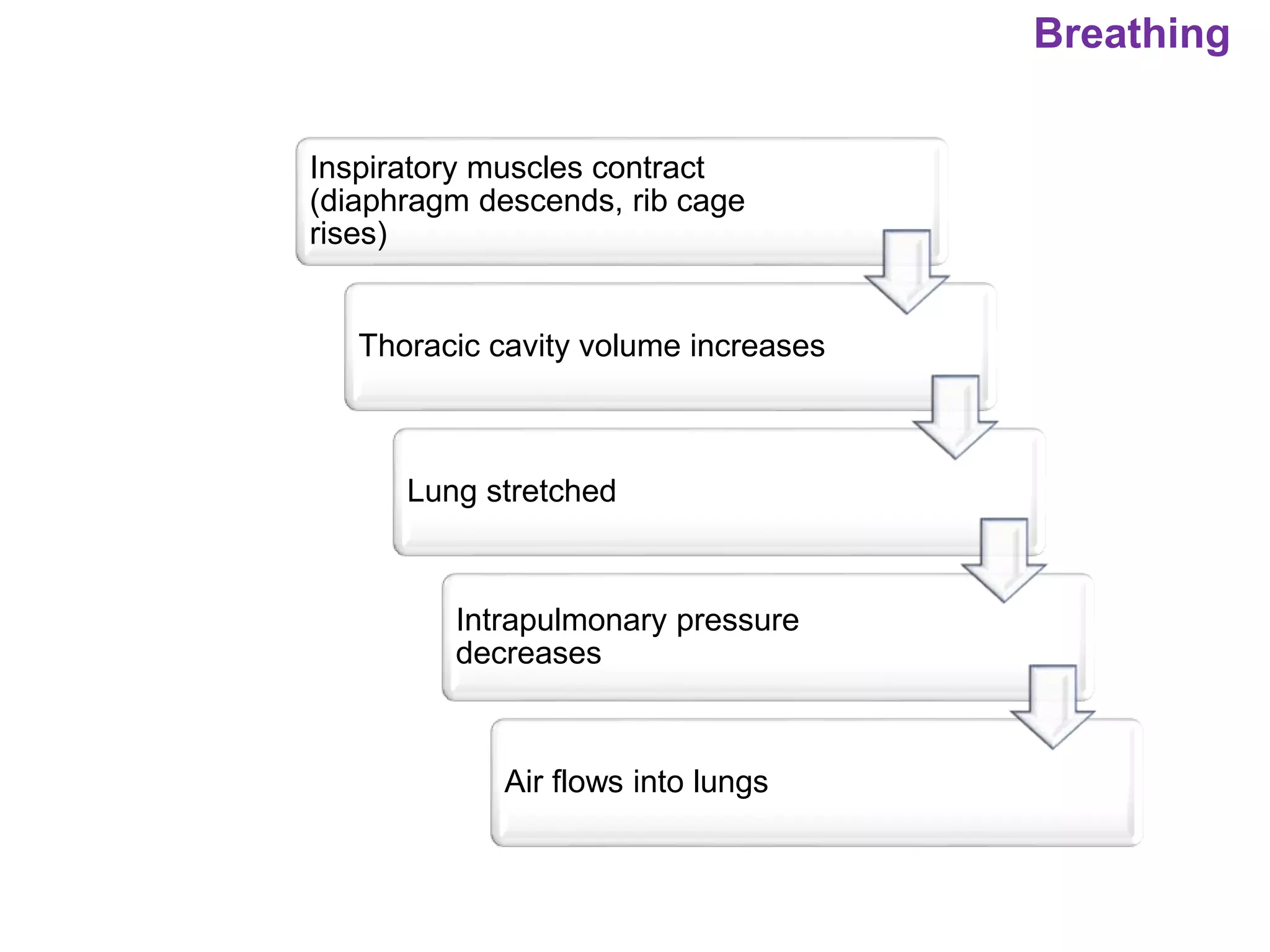
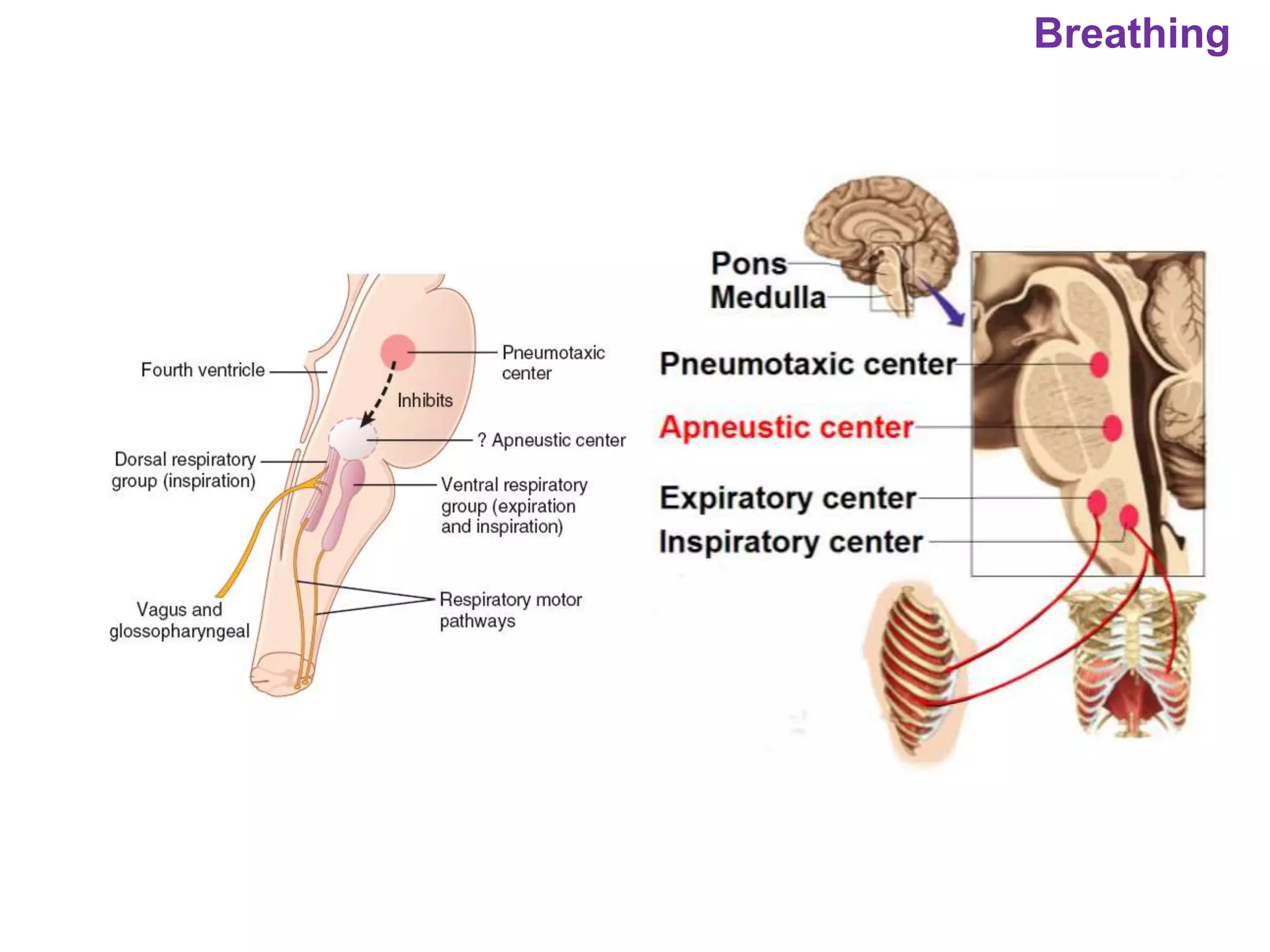
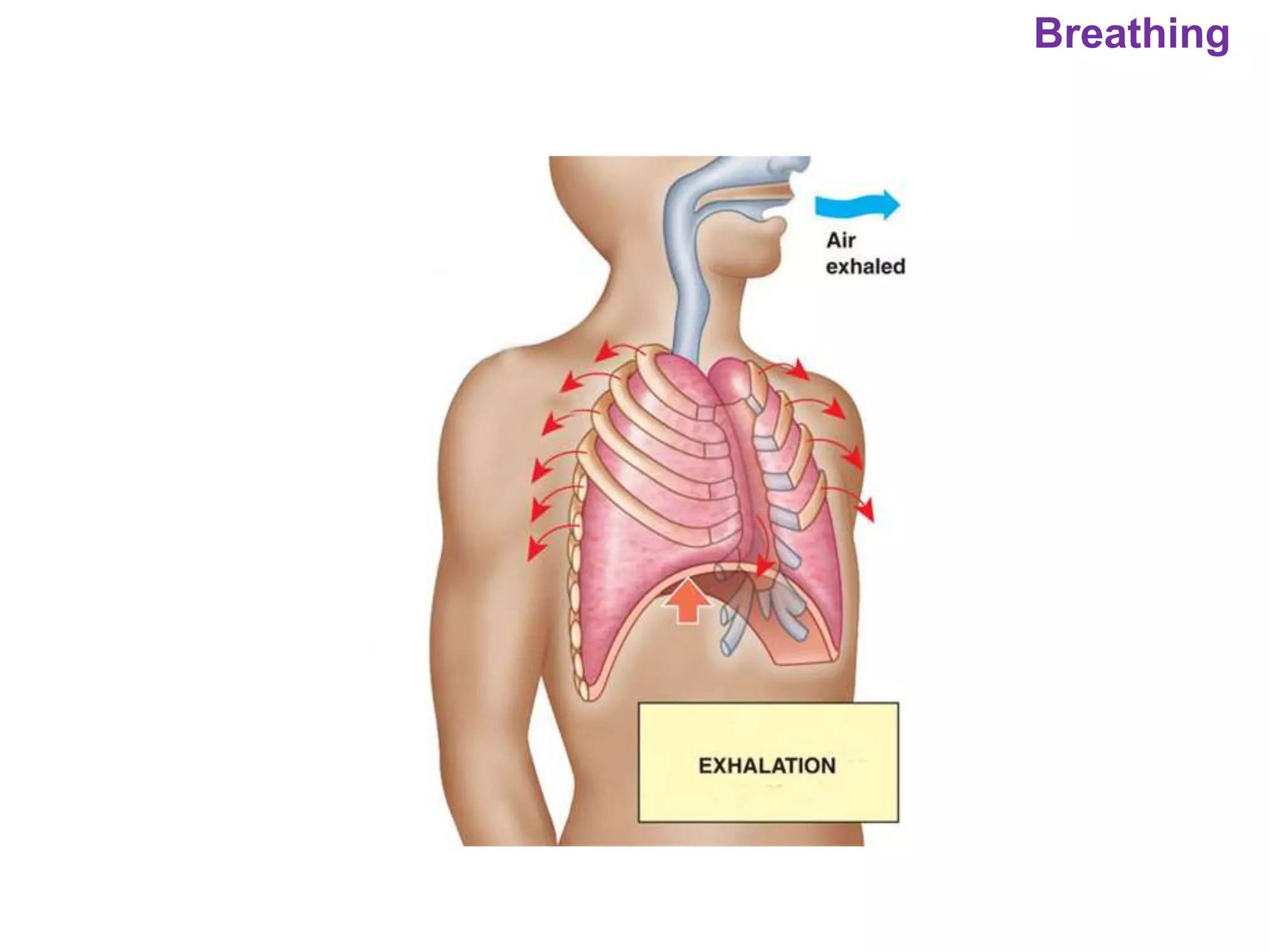
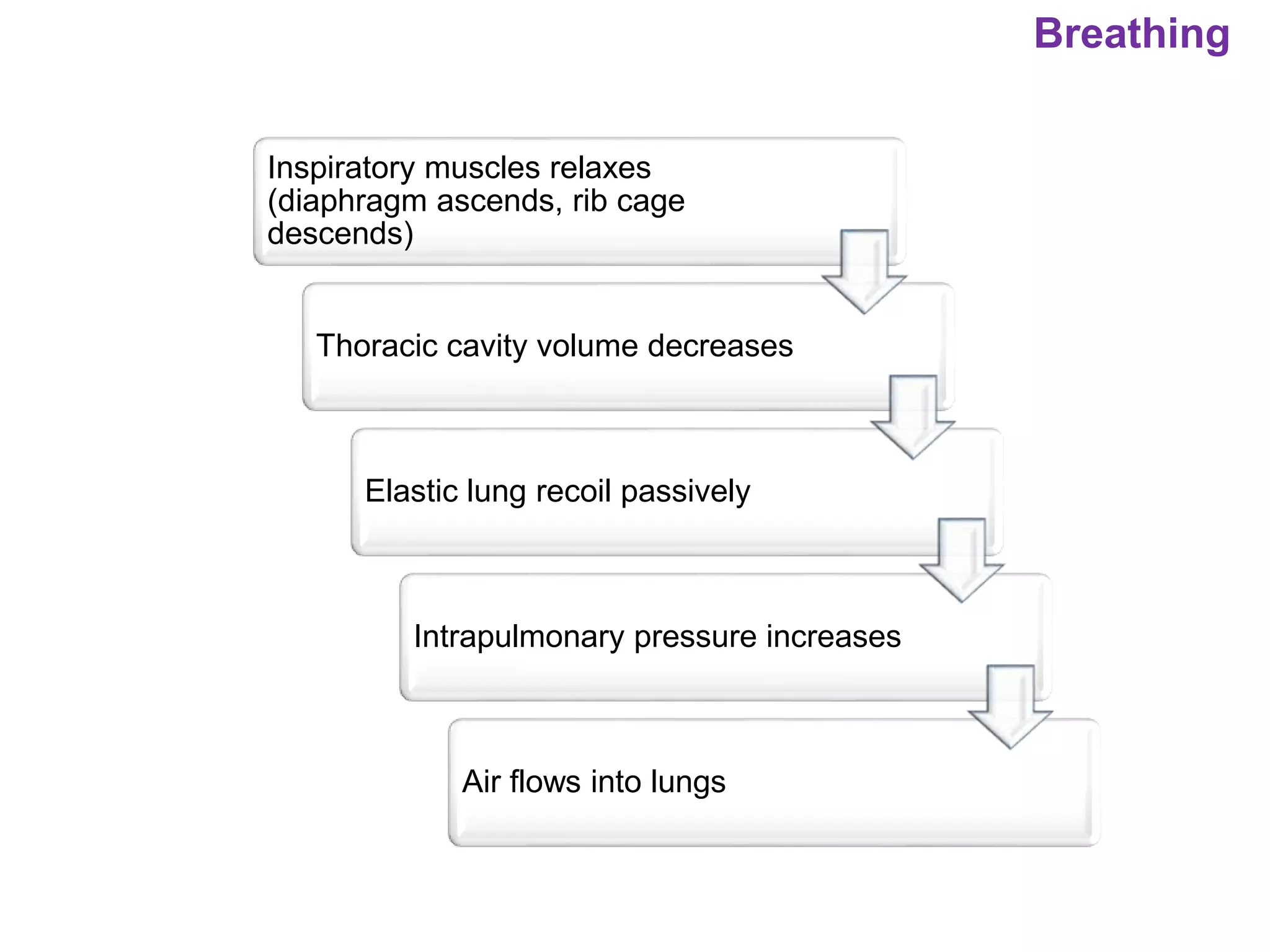
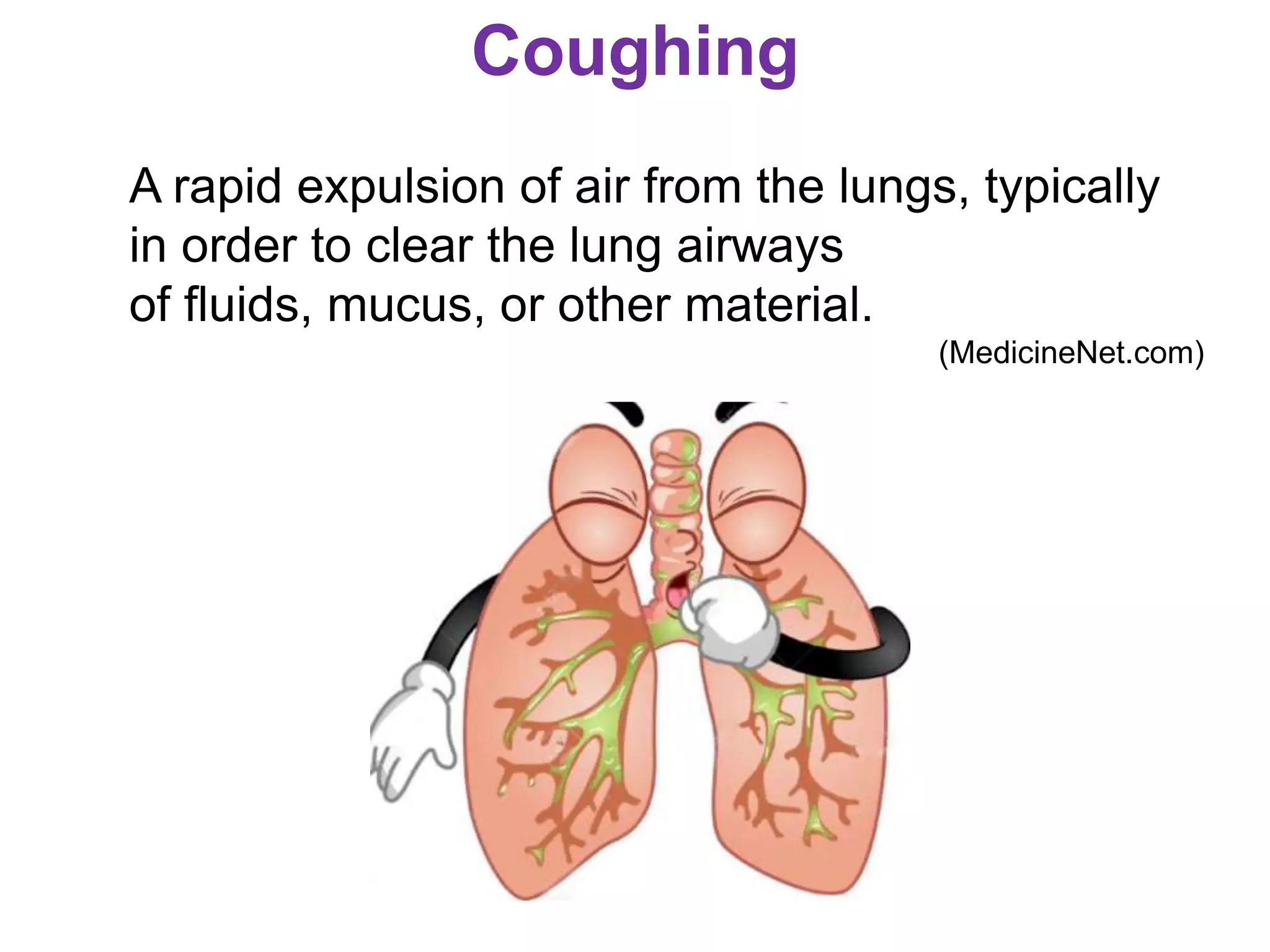
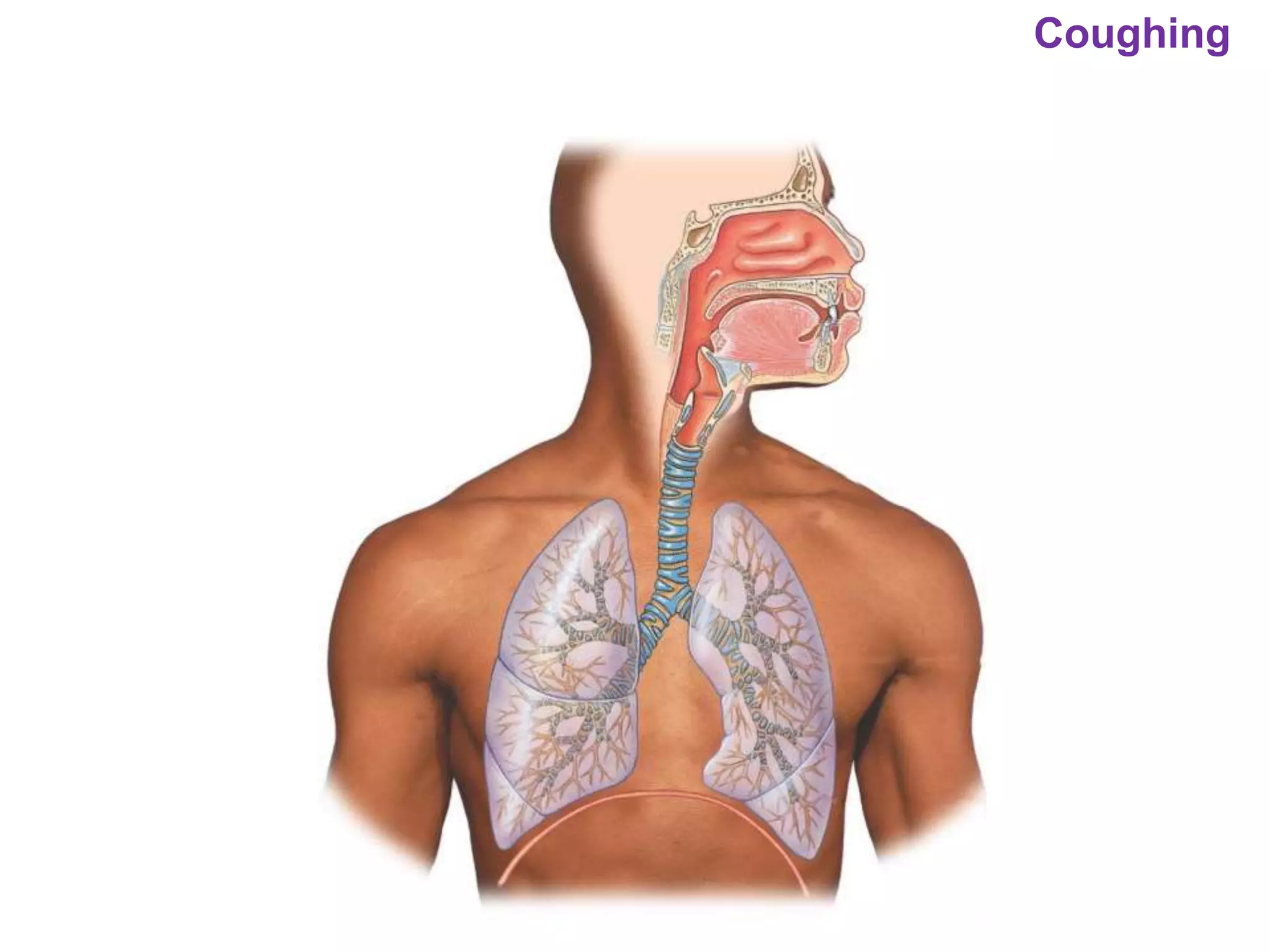
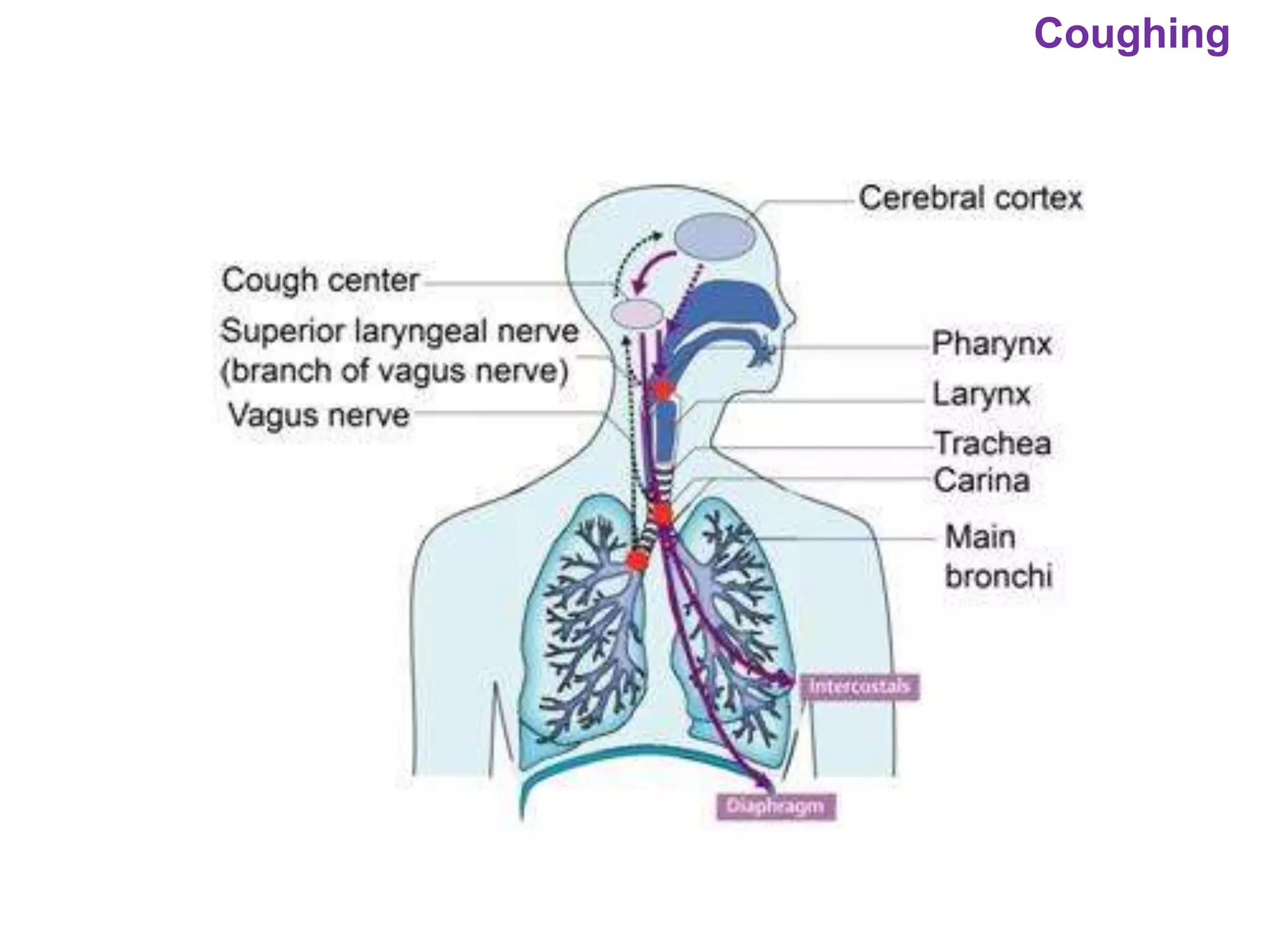
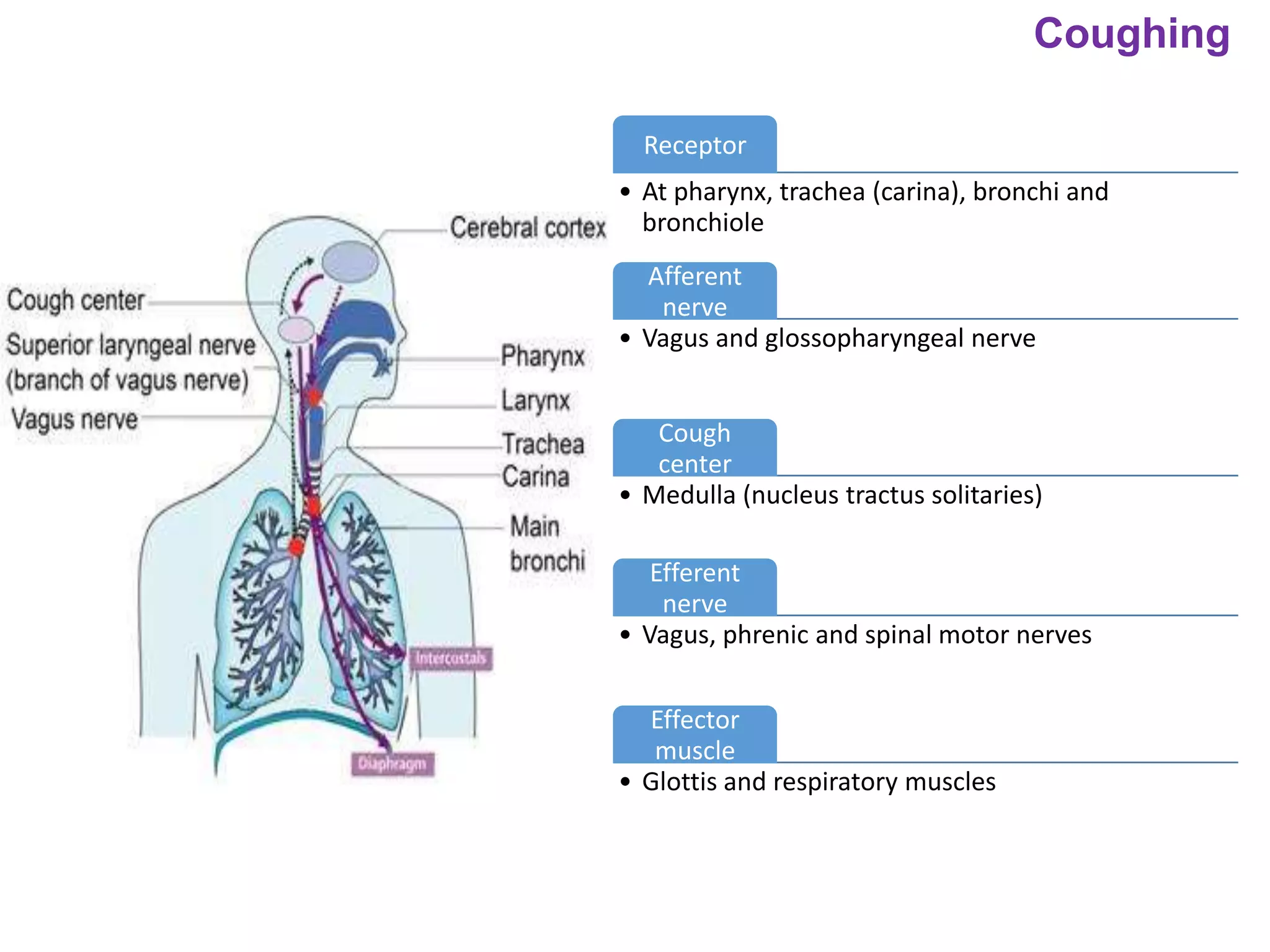
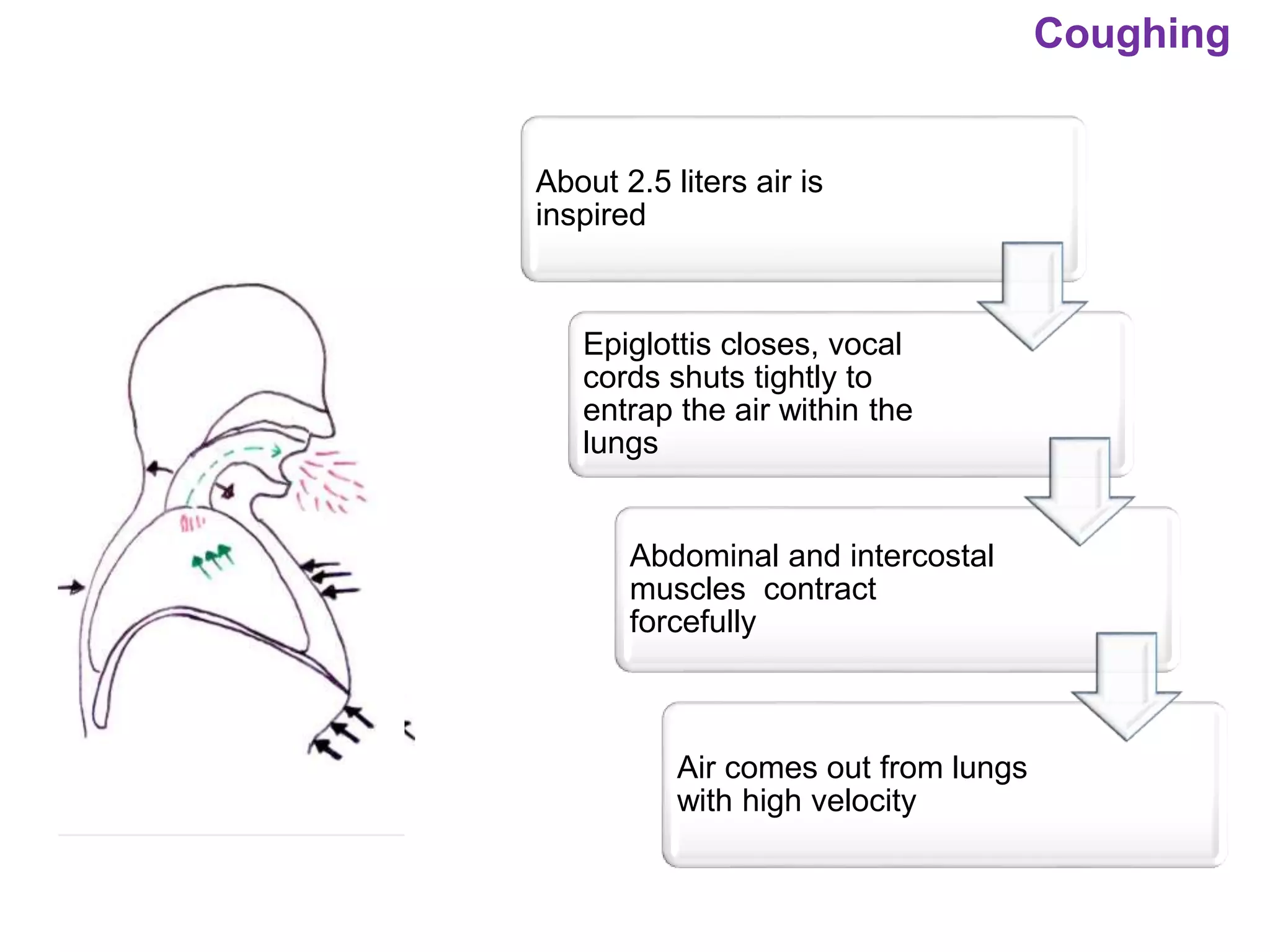
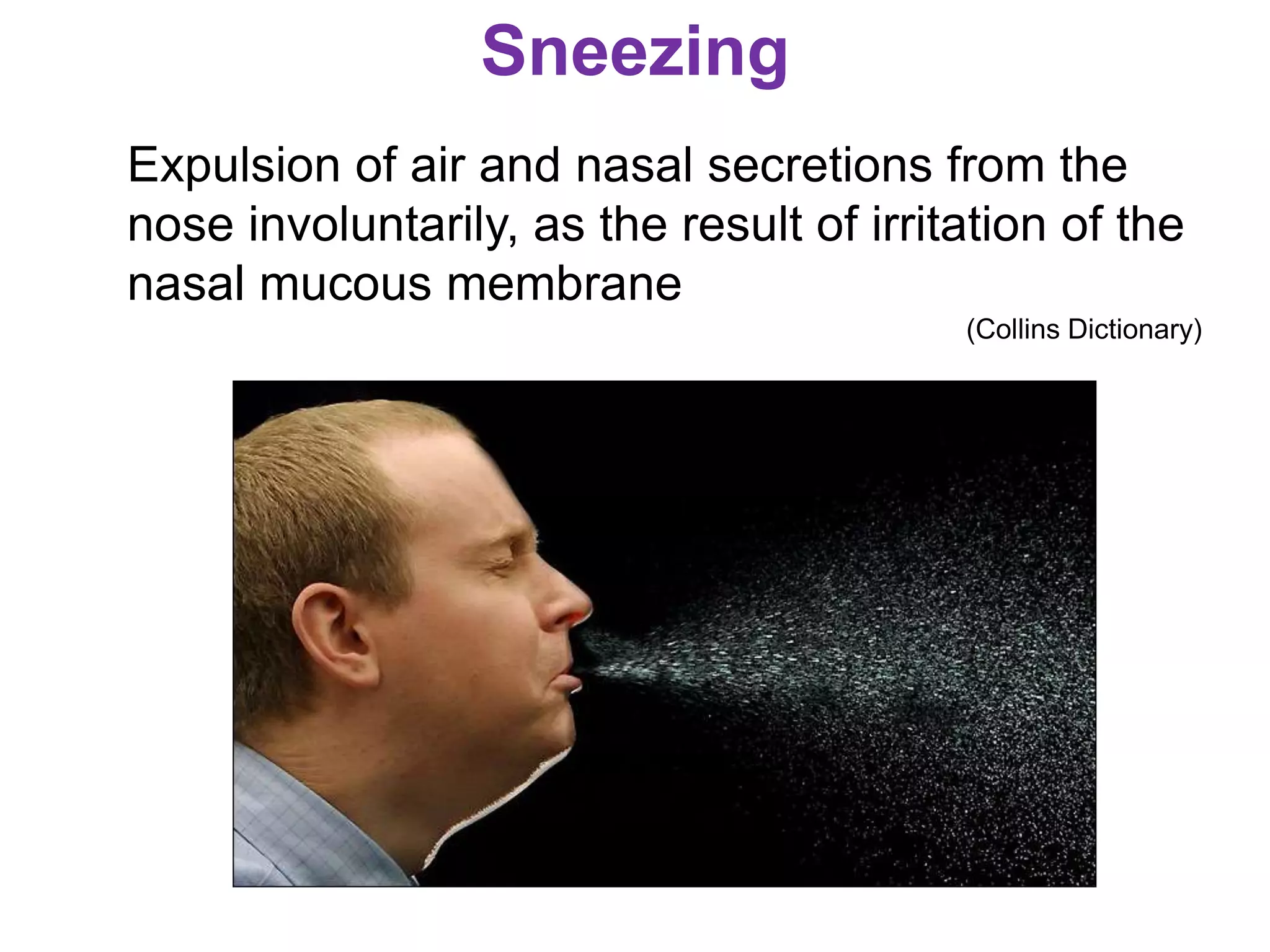
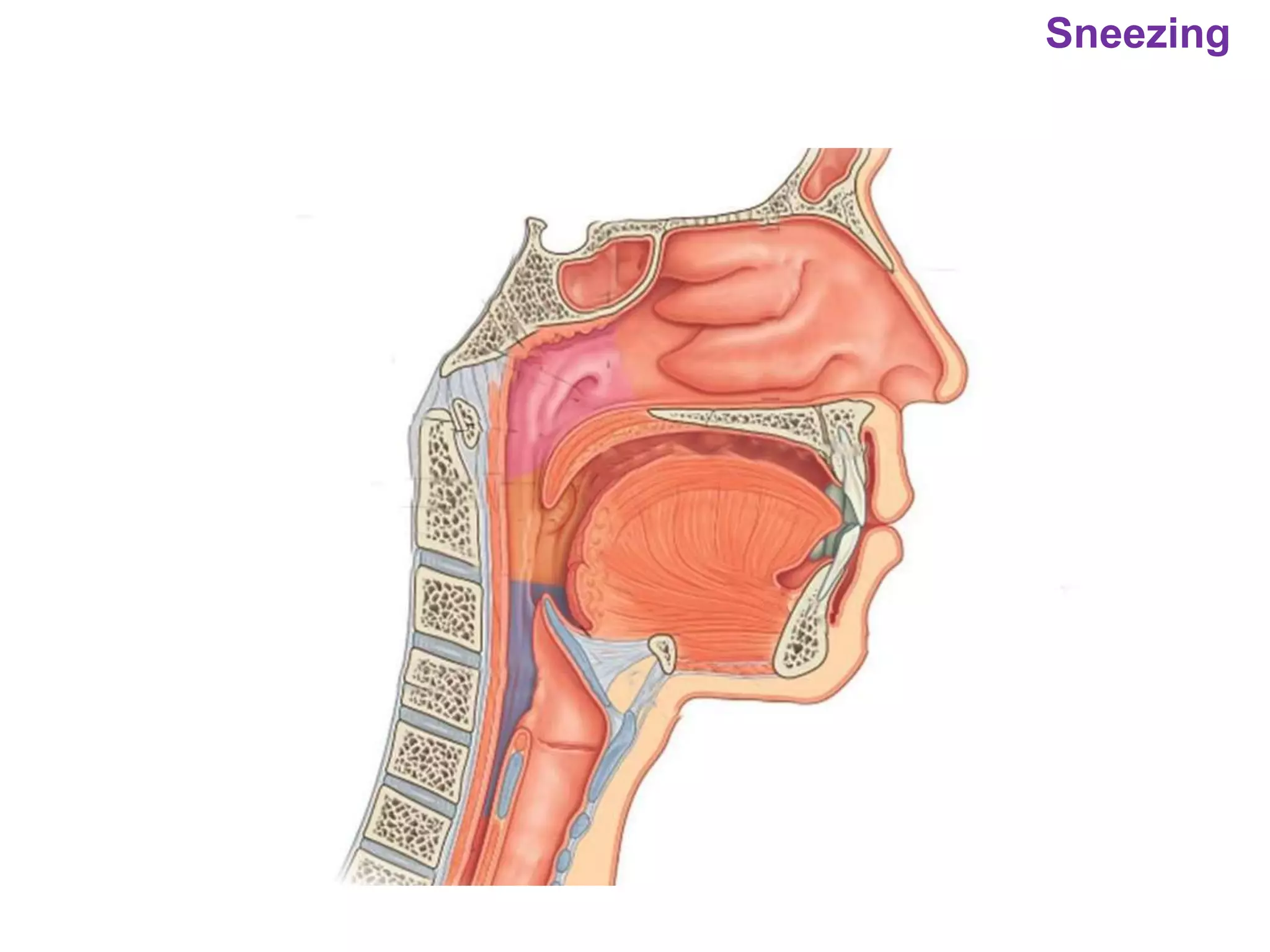
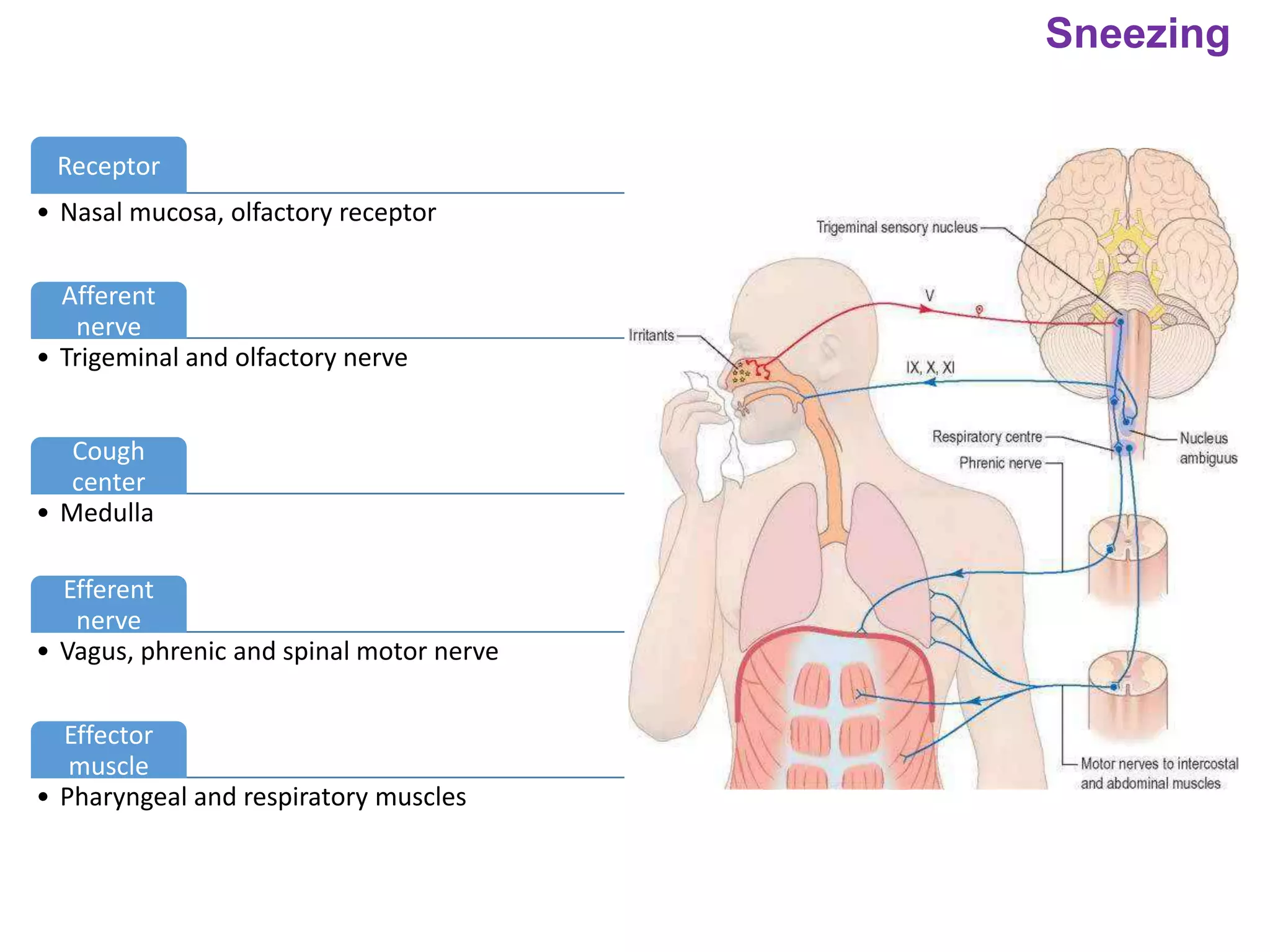
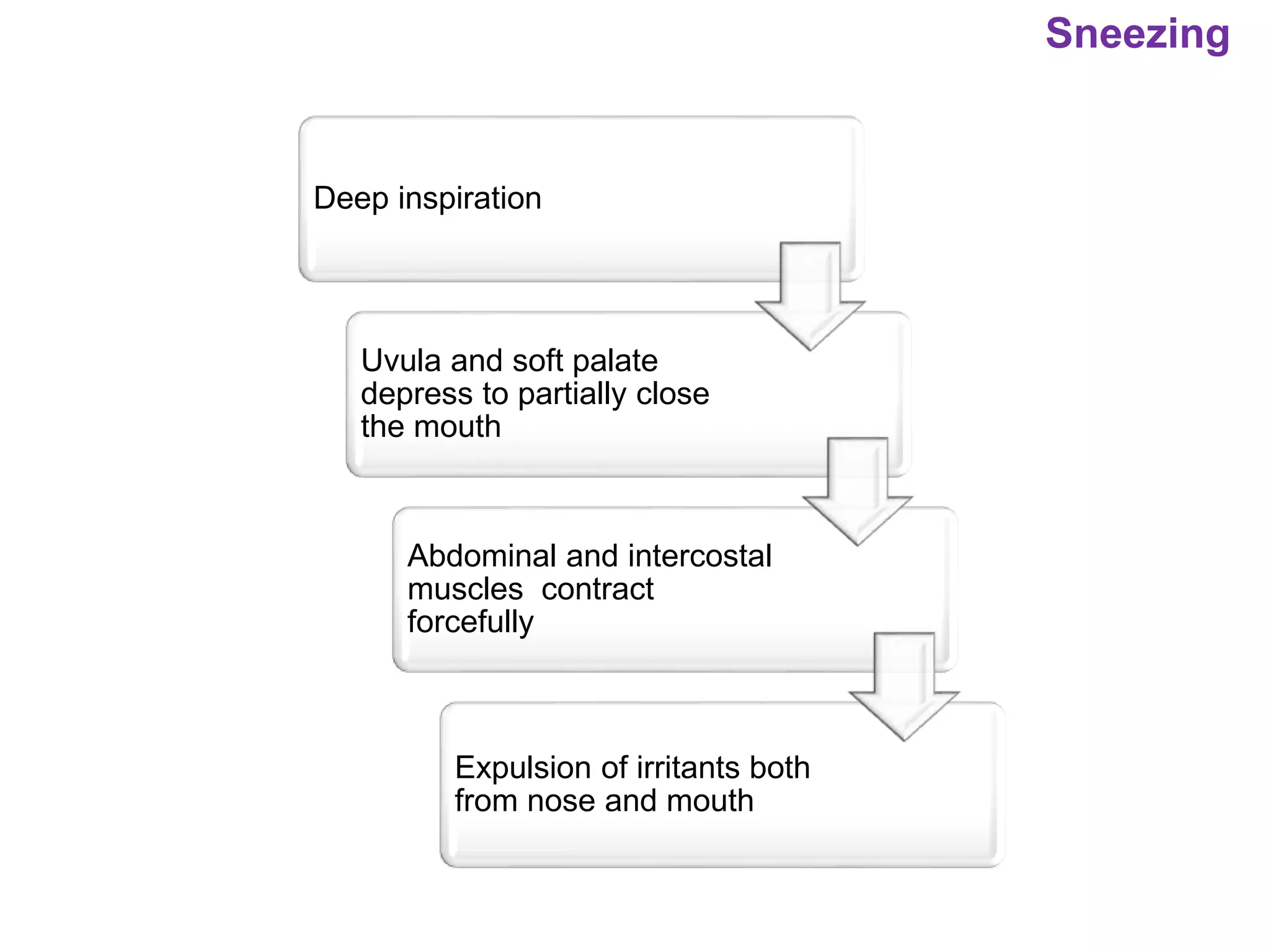
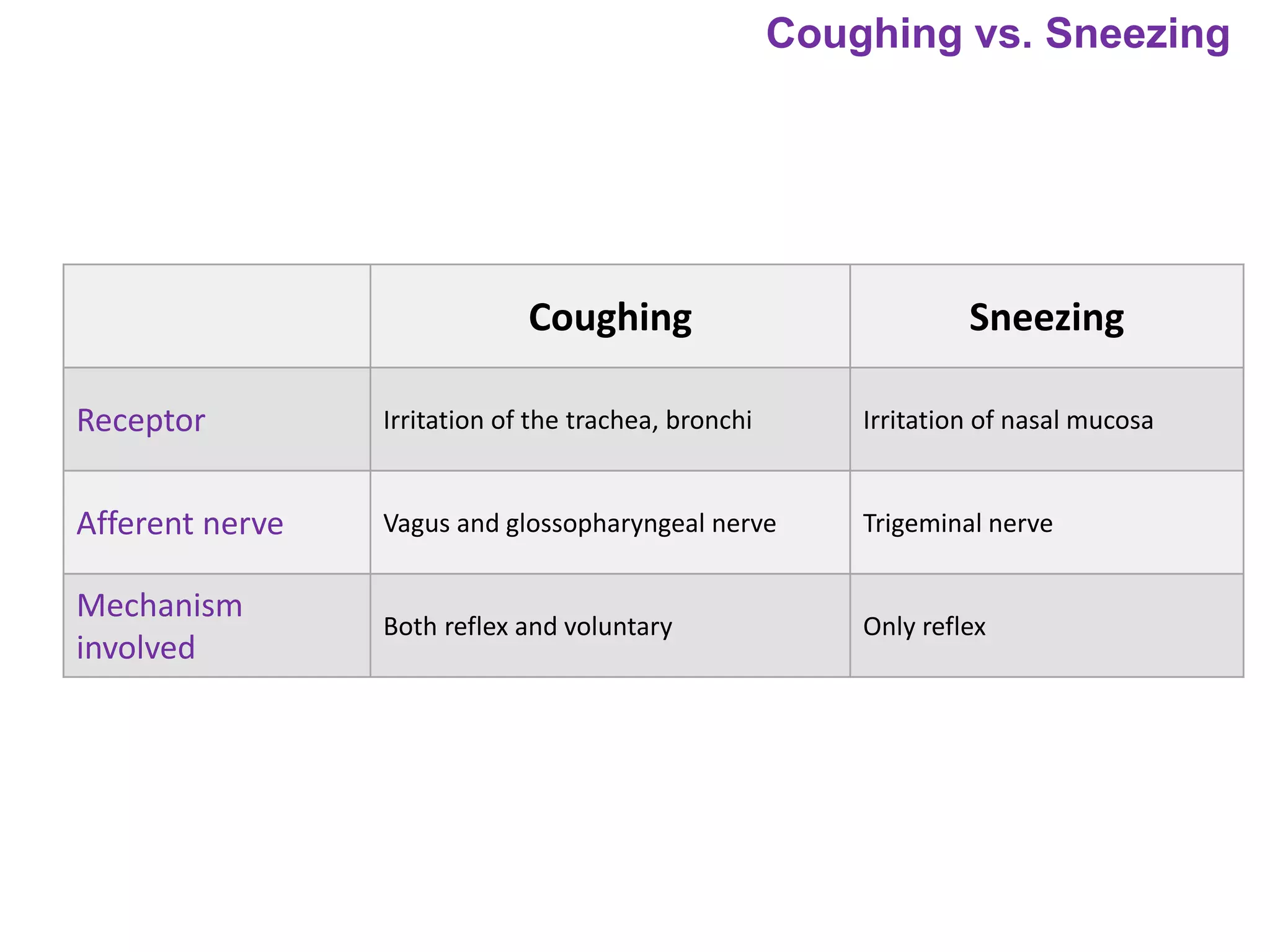
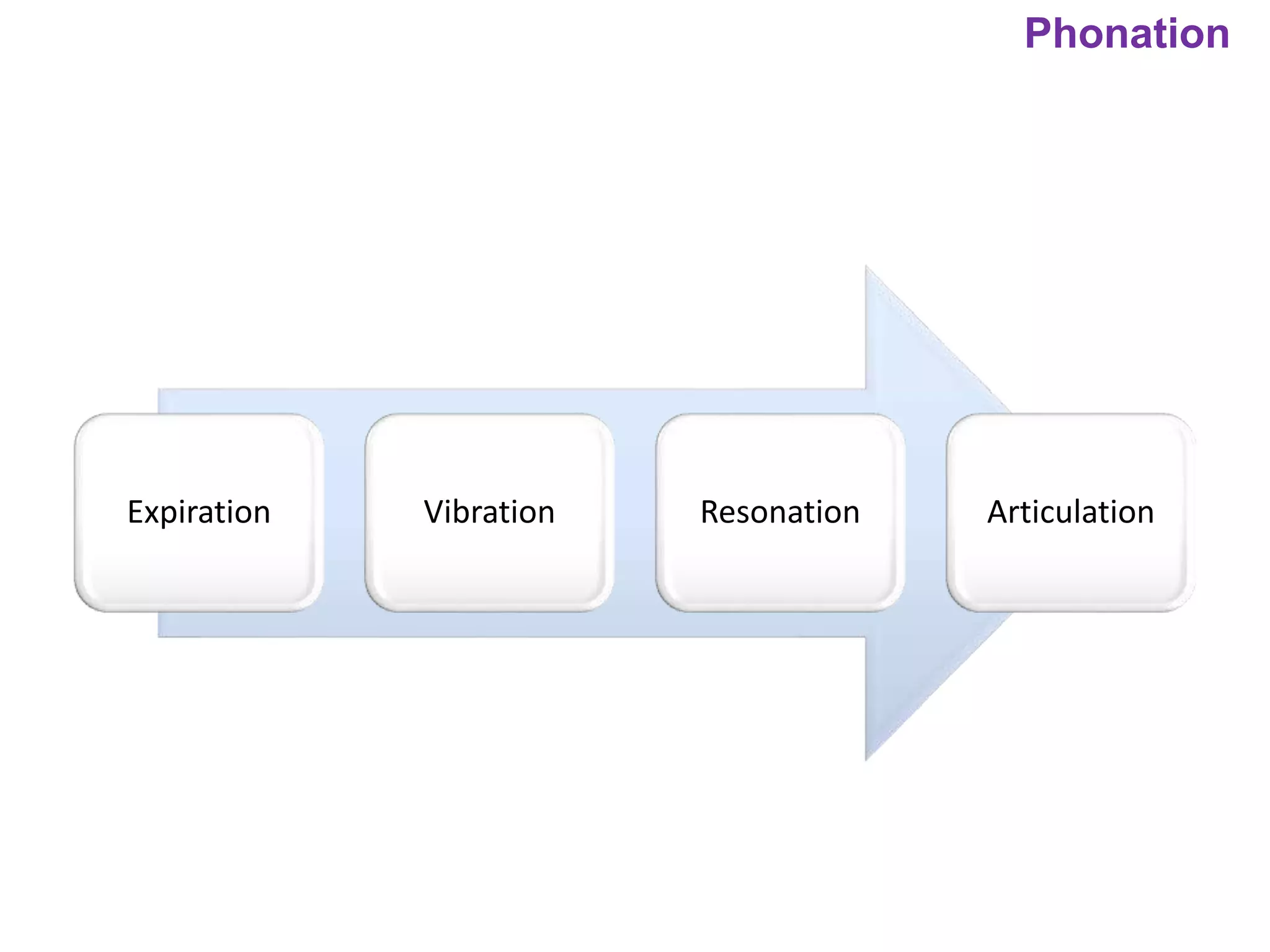
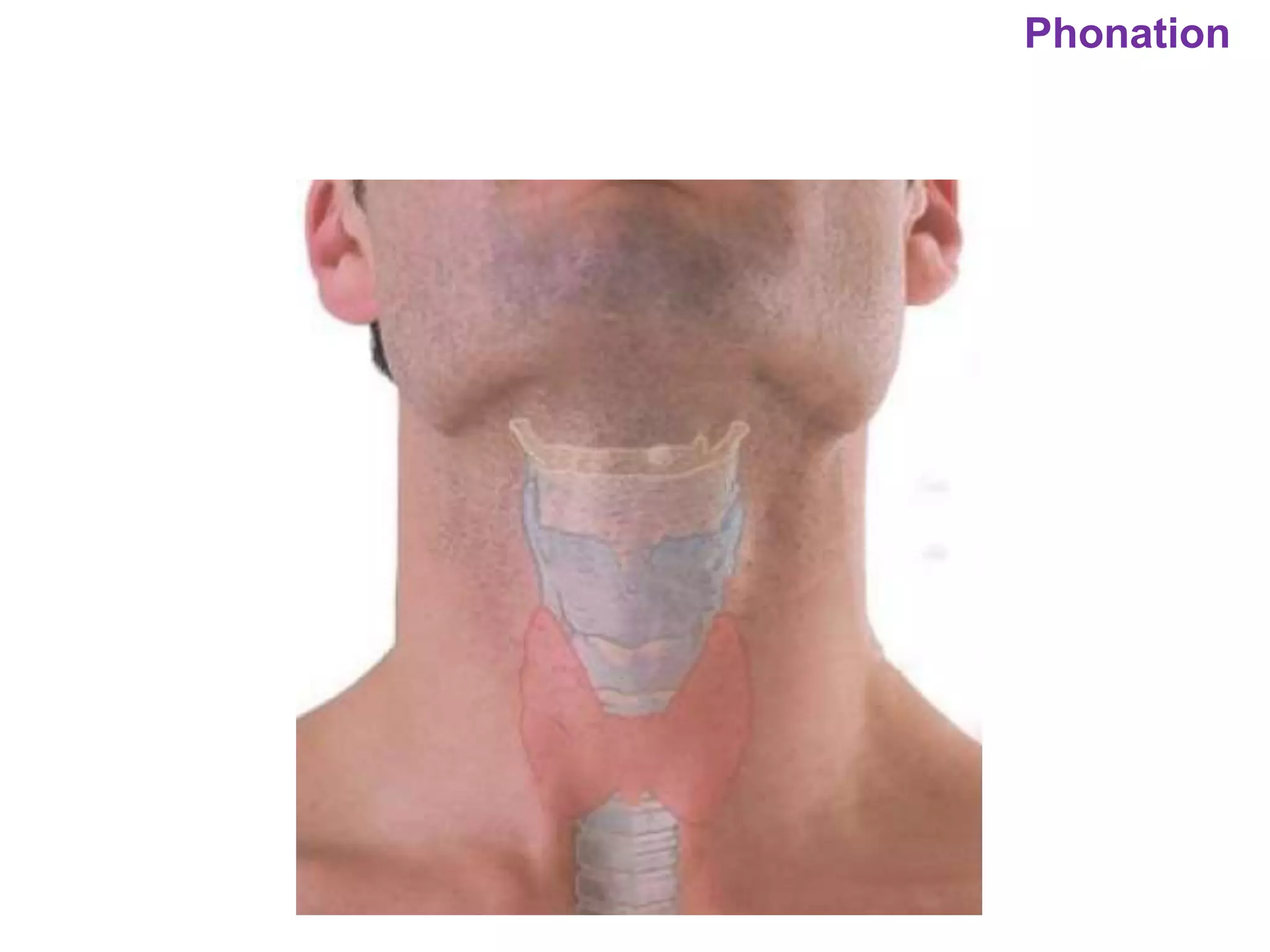
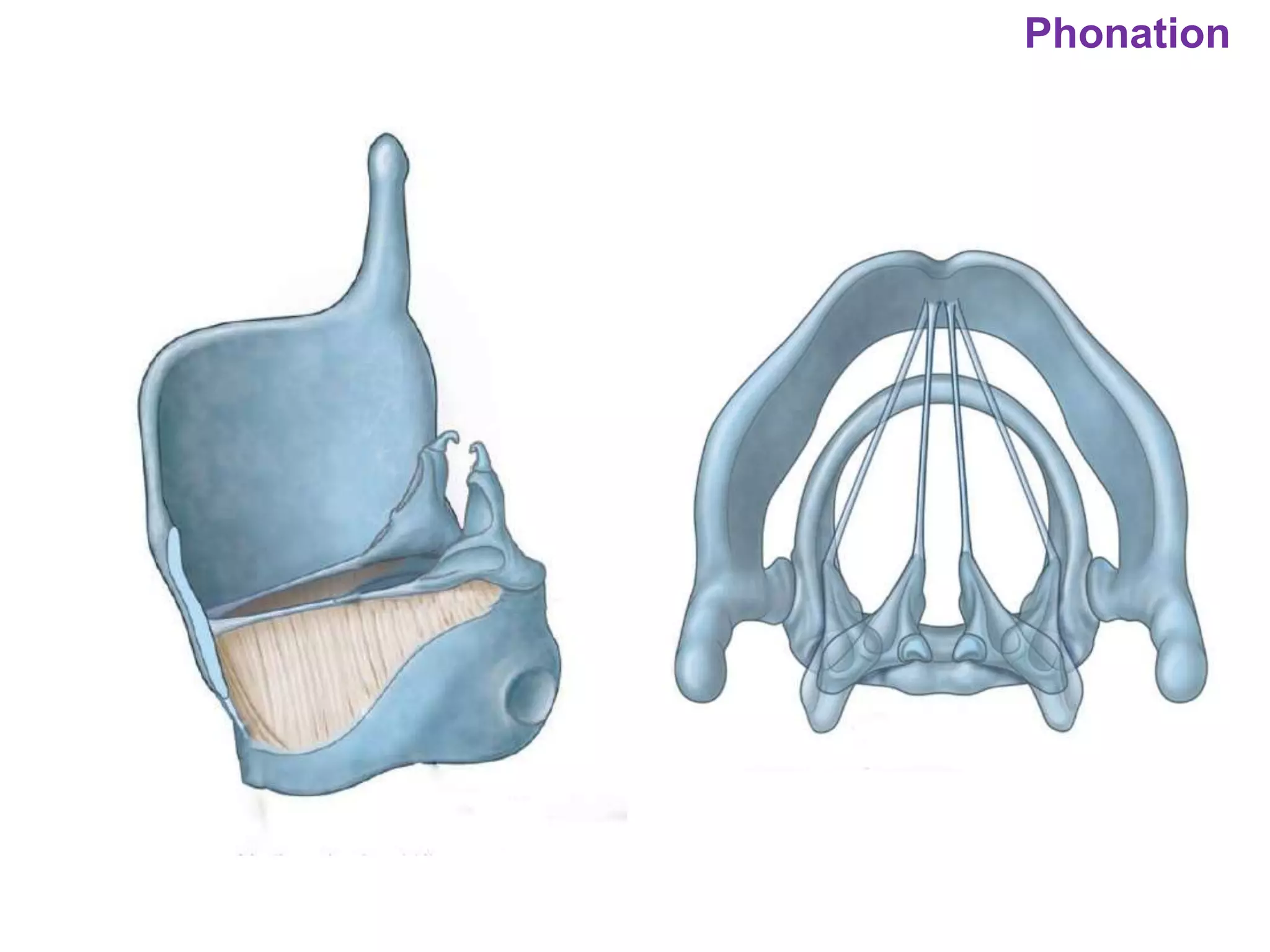
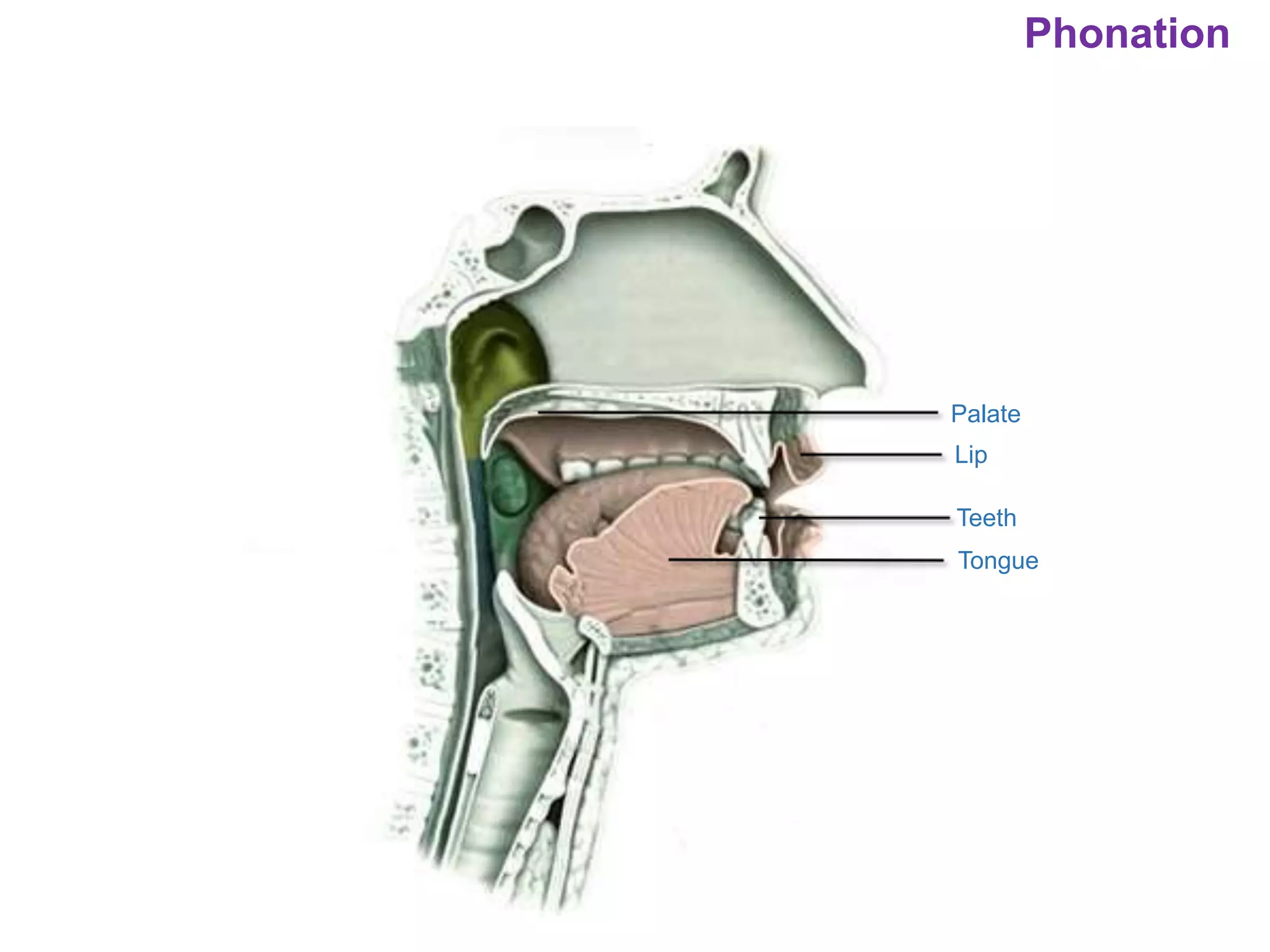
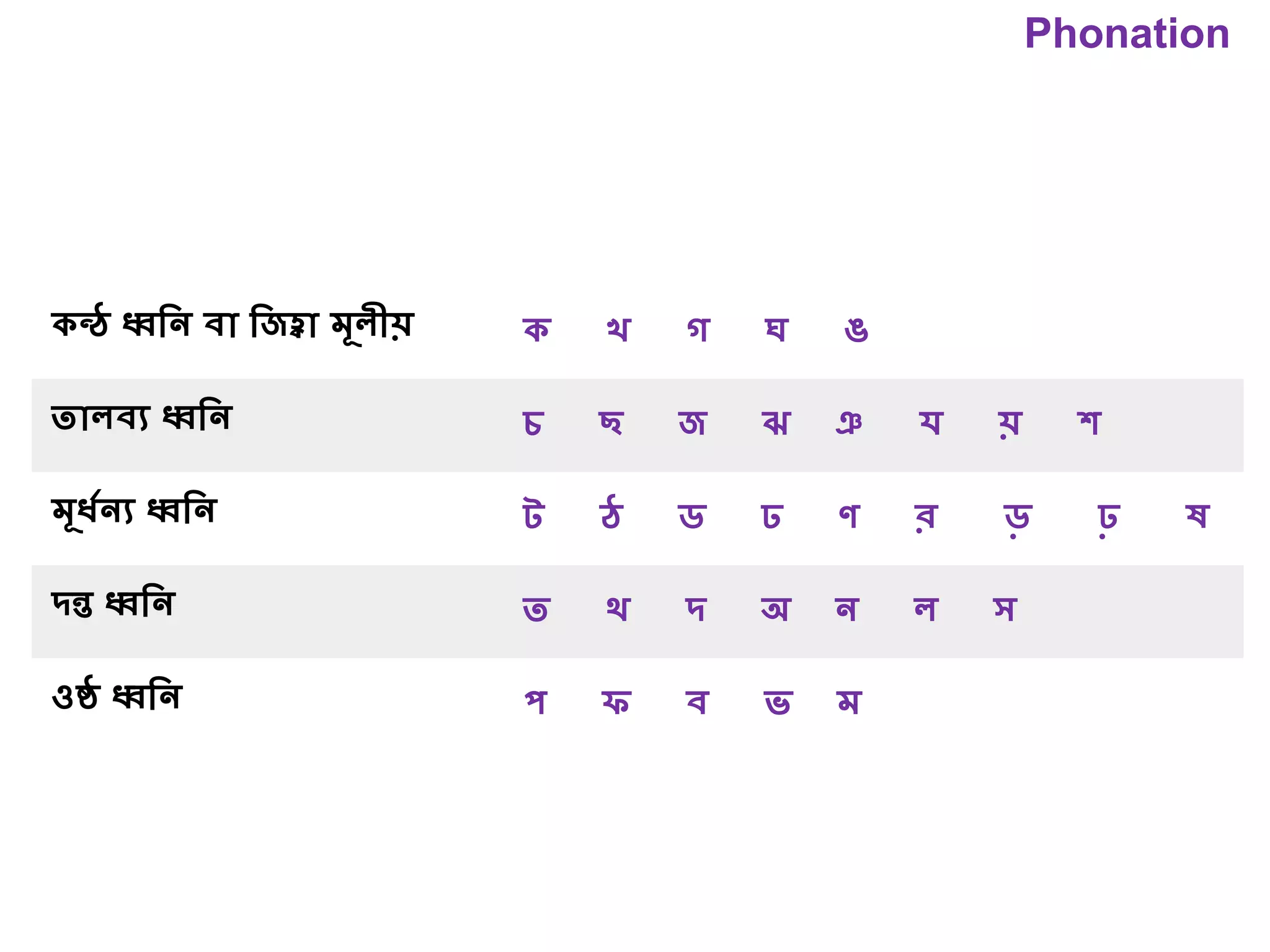
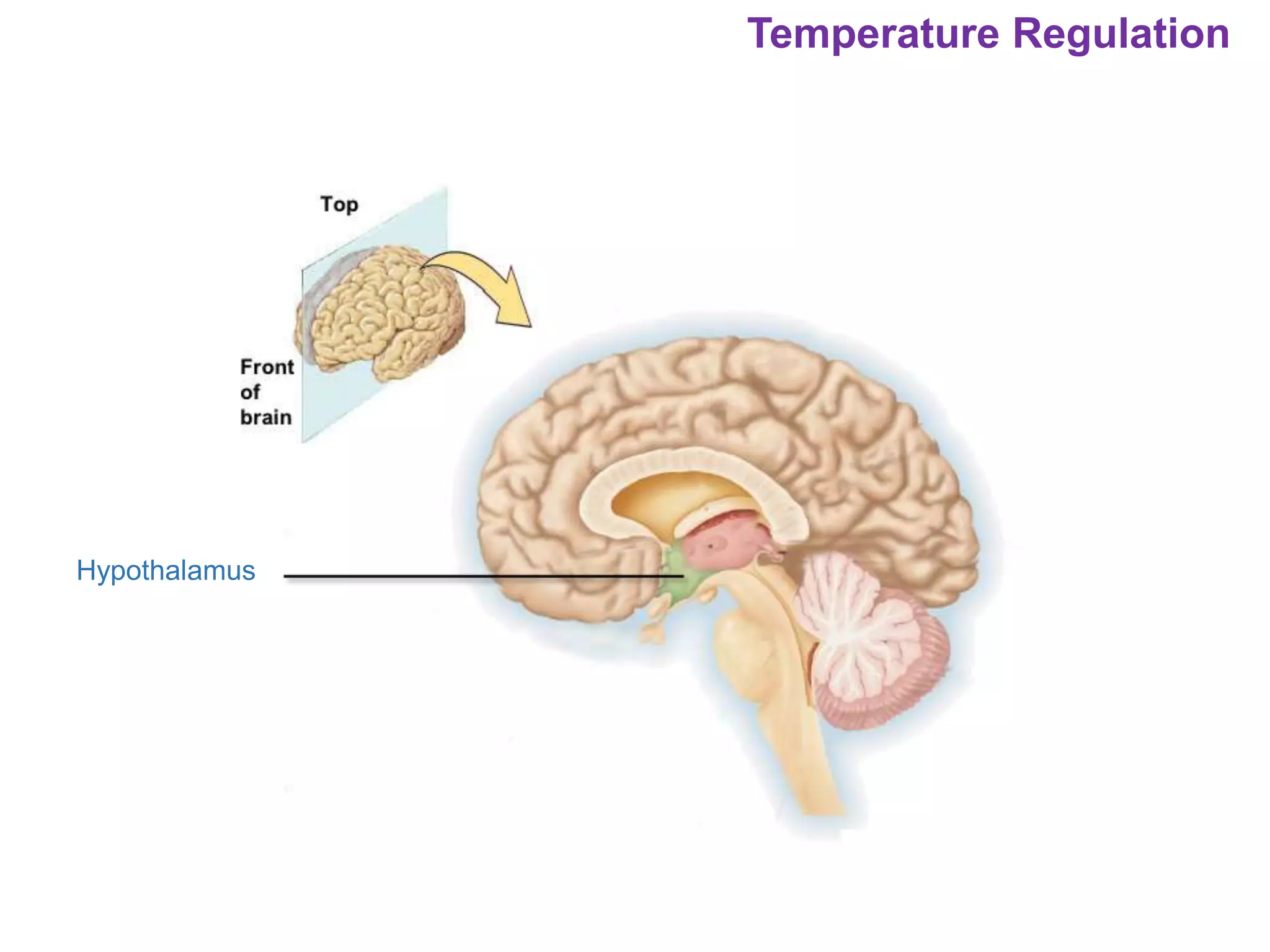
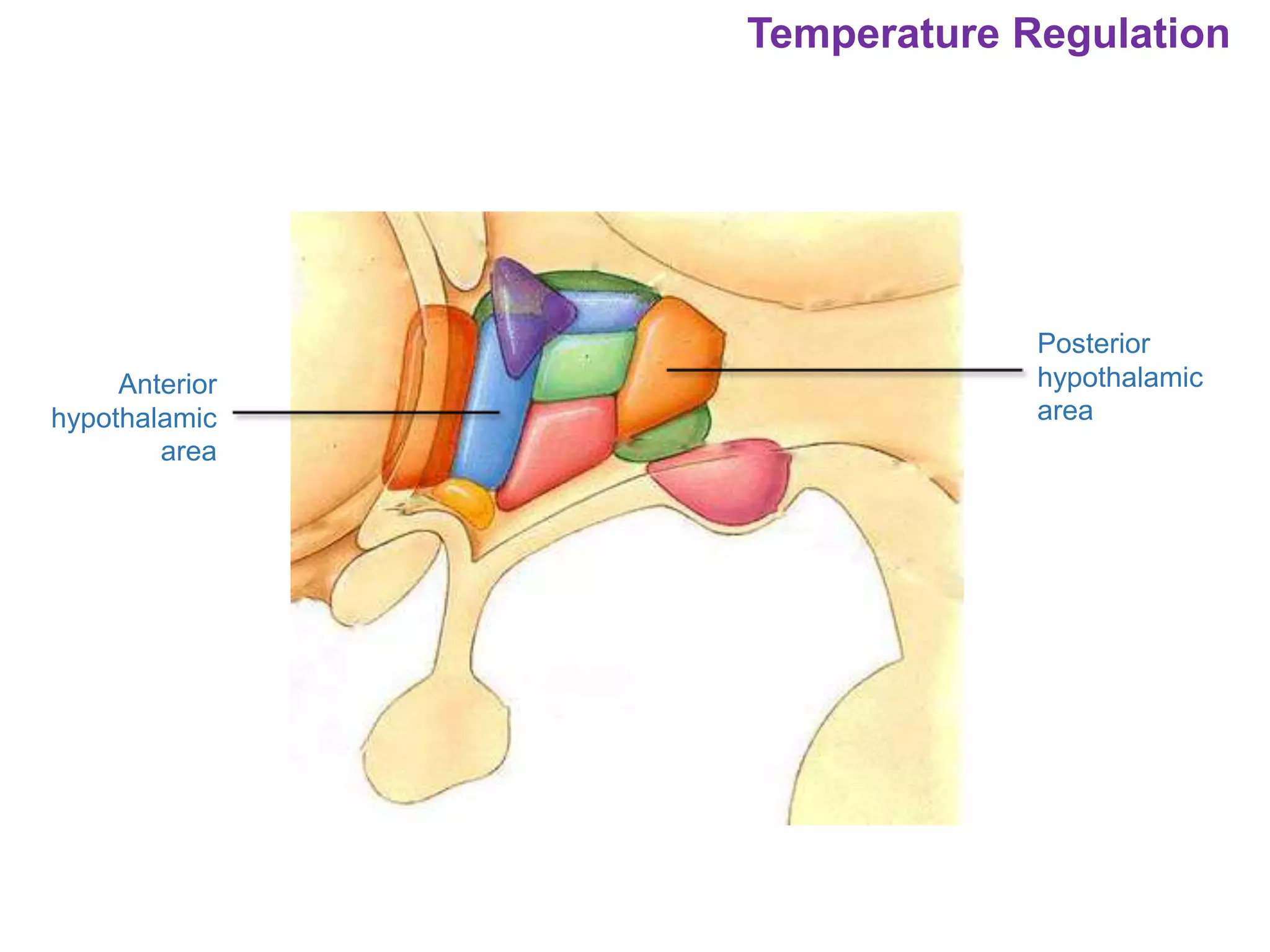
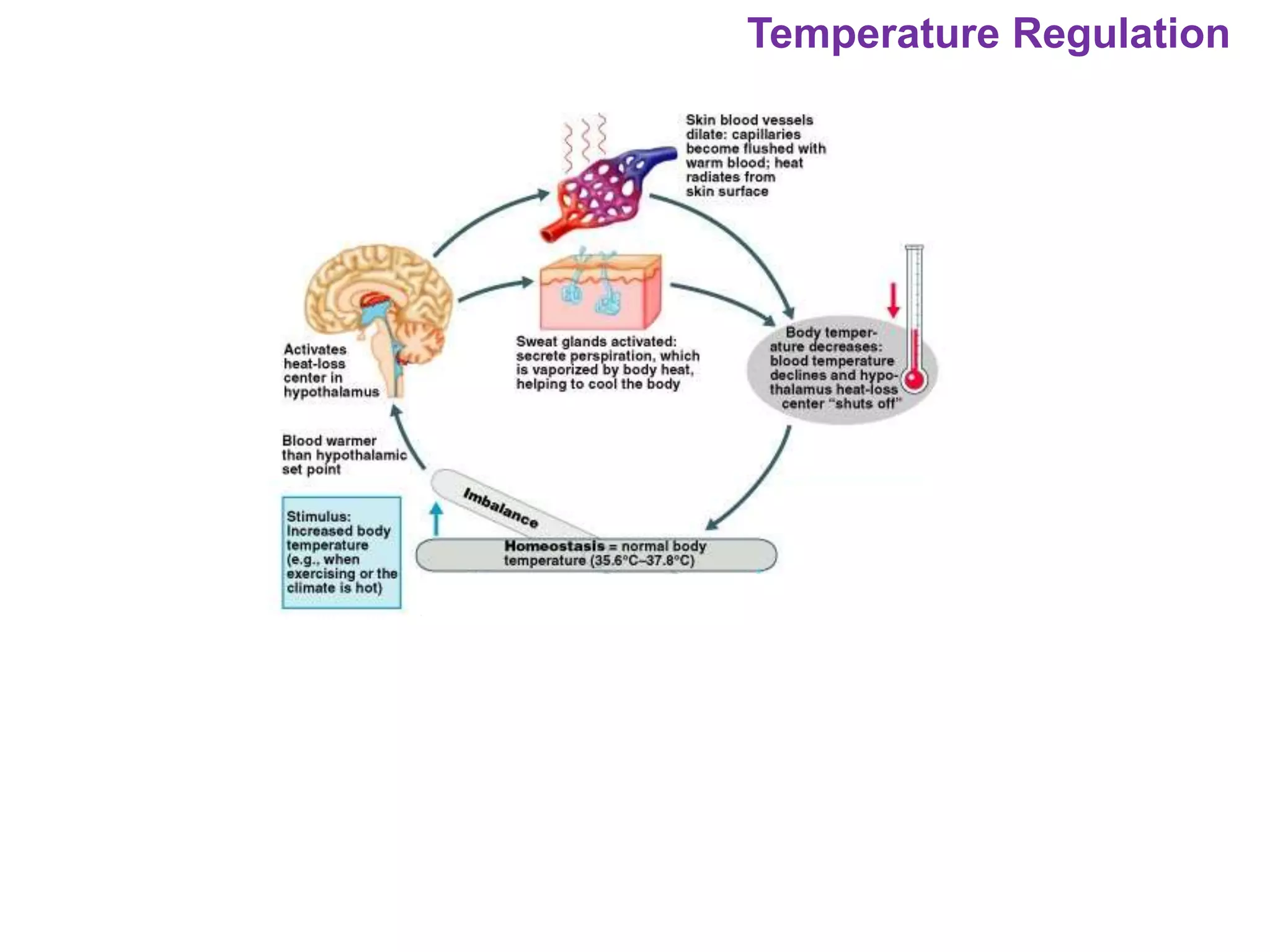
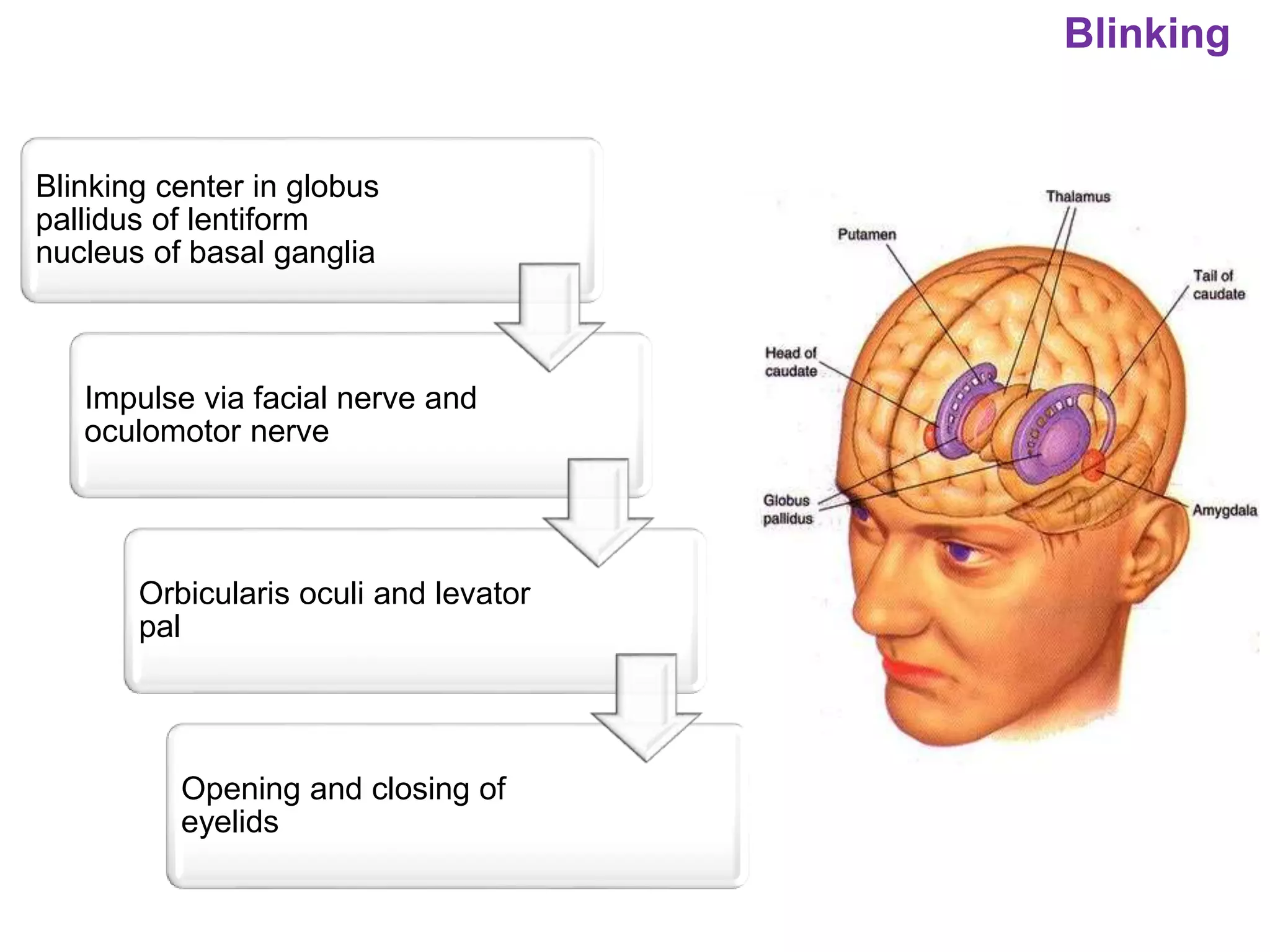
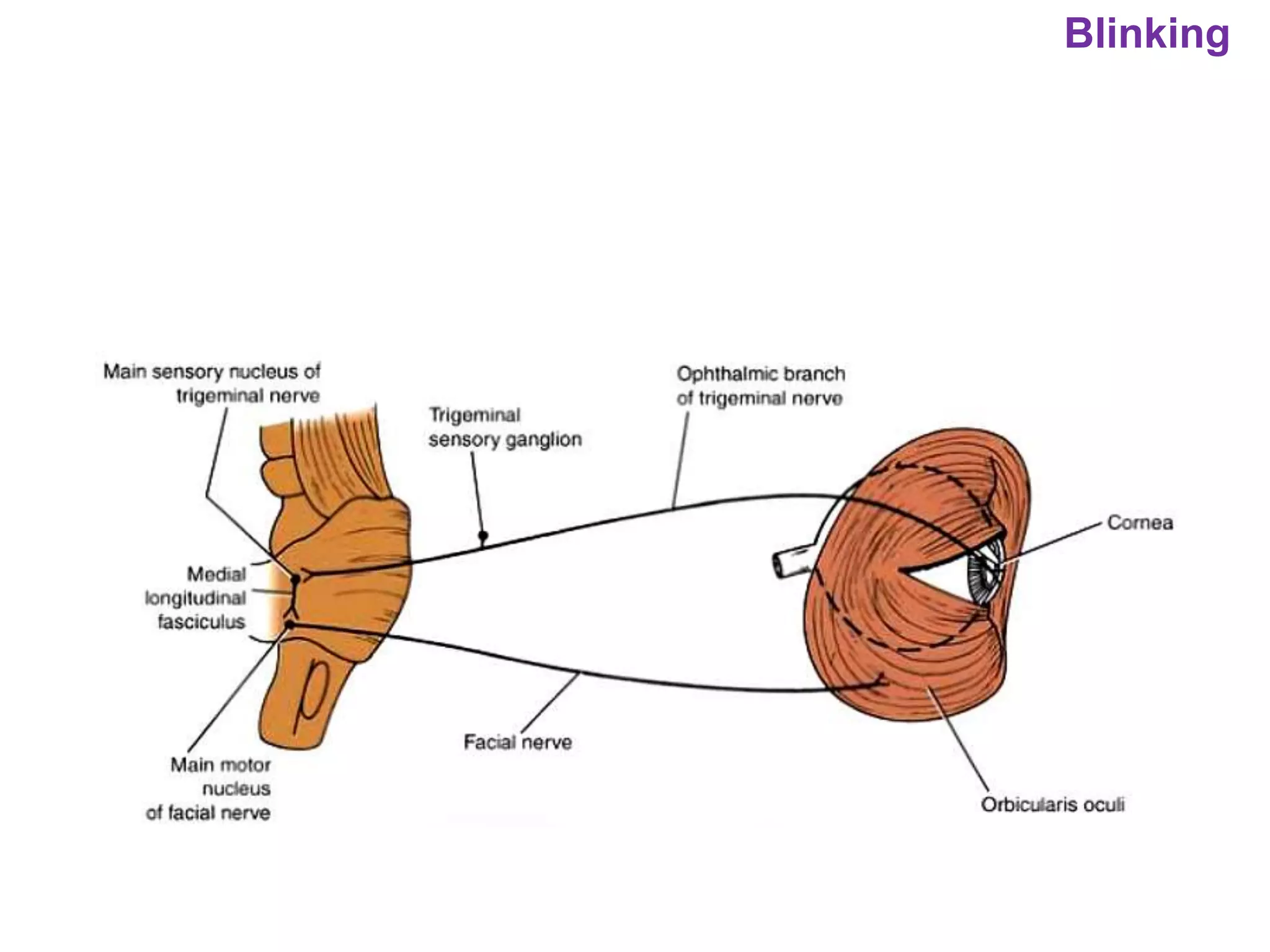
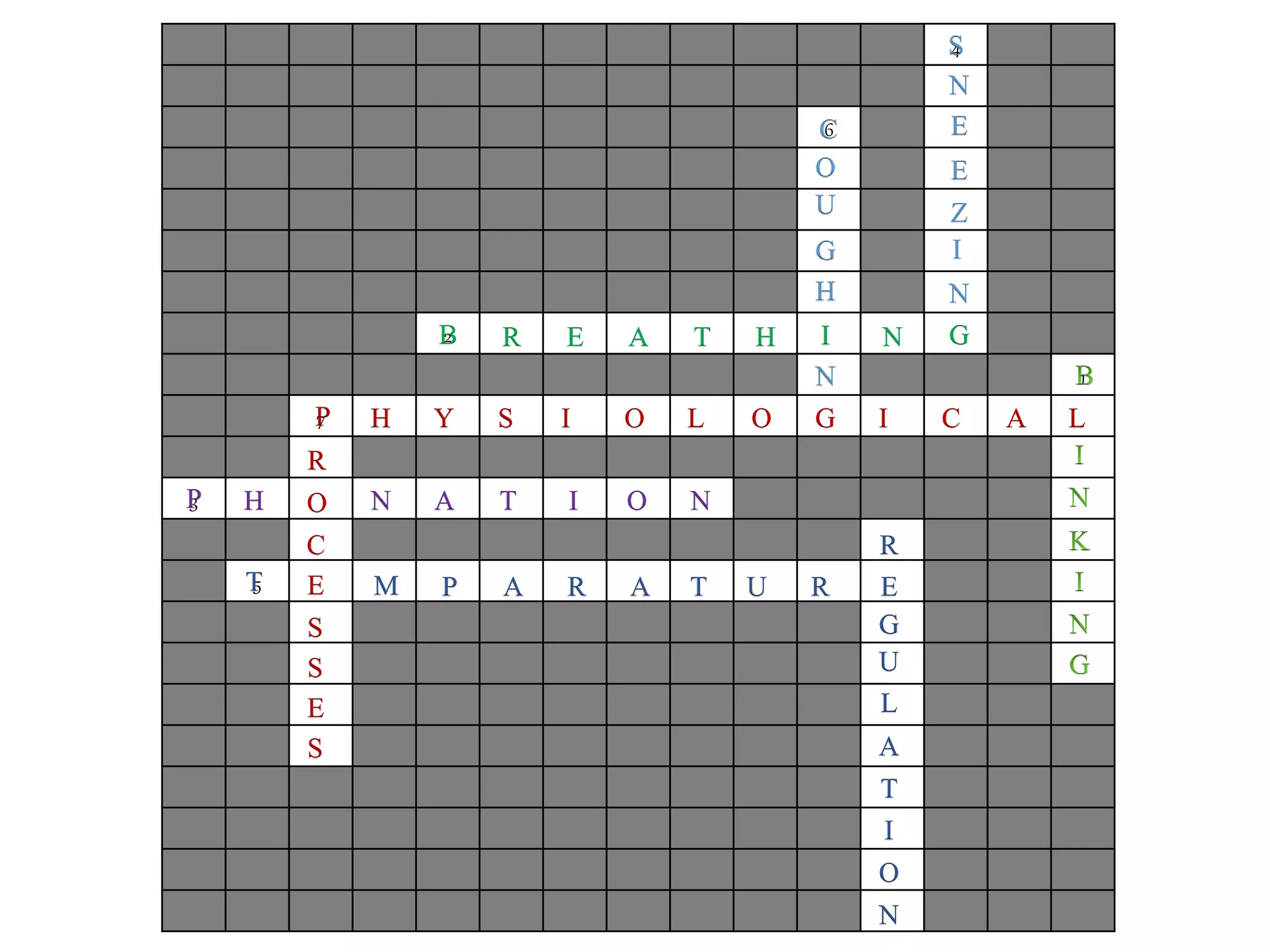
The document outlines various physiological processes, including breathing, coughing, sneezing, phonation, temperature regulation, and blinking, as explained by Dr. Zinnat Ara Yesmin and presented by Dr. Md. Mohiuddin Masum. It details mechanisms involved in each process, such as the roles of different muscles and nerves in actions like coughing and sneezing. Additionally, the document highlights the importance of temperature regulation and phonation in maintaining bodily functions.